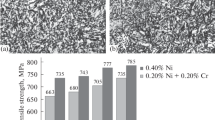
Conclusions
-
1.
The optimum combination of strength and ductility in steel is ensured by at least 90% martensite after quenching.
-
2.
The effect of the alloyed elements on the quenching depth must also be taken into account.
-
3.
Alloyed elements also affect impact strength and particularly, low temperature brittleness and brittleness induced by tempering. This effect must be taken into consideration in choosing steels for critical machine parts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Handbook of ASM, Vol. 1, USA (1961).
Kehemann, Luham, and Troiano, “TASM” (1957).
Puzak, Esepbacher, and Pellini, “Welding Res. Supp.” (1952).
Additional information
MAMI
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 30–40, May, 1963
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozlovskii, I.S. Factors determining the choice of structural steels. Met Sci Heat Treat 5, 275–281 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649337
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649337