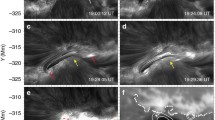
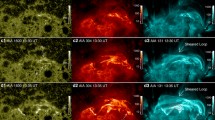
Abstract
Evidence is reviewed and extended that most, if not all, solar magnetic fields emerge as highly concentrated (⪞4000 gauss)helically twisted flux ropes, made up of hundreds or thousands of individually twisted flux fibers. The pitch angles of the twists are estimated as ⪝10° in the submerged flux ropes and roughly 1° in the flux fibers, but increase by large factors during and following emergence. The upward transmission of magnetic stresses and motions from the submerged flux-rope sections are major factors in solar physics. The helical twists account for the creation of sunspots and for their stability, fine structure, and mode of decay. They are basic features of the atmospheric structures, from the largest prominences and flare events down to arch filament systems and the smallest network components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, C. W. and Sturrock, P. A.: 1972,Astrophys. J. 174, 659.
Born, E.: 1974,Solar Phys. 38, 127.
Brester, A.: 1909,Proc. Amsterdam Acad. Sci. 11, 592.
Bruzek, A. and Durrant, C. J.: 1977,Illustrated Glossary for Solar and Terrestrial Physics, D. Reidel, Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Dunn, R. B. and Zirker, J. B.: 1973,Solar Phys. 33, 281.
Engvold, O.: 1976,Solar Phys. 49, 283.
Frazier, E. N.: 1972,Solar Phys. 26, 130.
Galloway, D. J., Proctor, M. R. E., and Weiss, N. O.: 1977,Nature 266, 686.
Gibson, E. G.: 1977,Solar Phys. 53, 123.
Giovanelli, R. G.: 1972,Solar Phys. 27, 71.
Hagyard, M. J., West, E. A., and Cummings, N. P.: 1977,Solar Phys. 53, 3.
Harvey, K. L., Harvey, J. W., and Martin, S. F.: 1975,Solar Phys. 40, 87.
Jockers, K.: 1978,Astrophys J. 220, 1133.
Jockers, K. and Engvold, O.: 1975,Solar Phys. 44, 429.
Livingston, W. C. and Orrall, R. Q.: 1974,Solar Phys. 39, 301.
Martres, M. J., Soru-Escaut, I., and Rayrole, J.: 1973,Solar Phys. 32, 365.
Meyer, F., Schmidt, H. U., and Weiss, N. O.: 1977,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 179, 741.
Meyer, F., Schmidt, H. U., Weiss, N. O., and Wilson, P. R.: 1974,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 169, 35.
Parker, E. N.: 1974,Astrophys J. 191, 245.
Piddington, J. H.: 1973, in R. G. Athay (ed.), ‘Chromospheric Fine Structure’,IAU Symp. 56, 269.
Piddington, J. H.: 1975a,Astrophys. Space Sci. 34, 347.
Piddington, J. H.: 1975b, in V. Bumba and J. K. Kleczek (eds.), ‘Basic Mechanisms of Solar Activity’,IAU Symp. 71, 389.
Piddington, J. H.: 1978,Astrophys. Space Sci. 55, 401.
Piddington, J. H.: 1979a,Astrophys. J. (in press).
Piddington, J. H.: 1979b,Australian J. Phys. 32, 671.
Priest, E. R.: 1976,Solar Phys. 47, 41.
Raadu, M. A. and Nakagawa, Y.: 1971,Solar Phys. 20, 64.
Richardson, R. S.: 1941,Astrophys. J. 93, 24.
Rompolt, B.: 1975a,Contrib. Wroclaw Astron. Observ., No. 18.
Rompolt, B.: 1975b,Solar Phys. 41, 329.
Rust, D. M.: 1976,Solar Phys. 47, 15.
Schoolman, S. A.: 1973,Solar Phys. 32, 379.
Sheeley, N. R., Bohlin, J. D., Brueckner, G. E., Purcell, J. D., Scherrer, V., and Tousey, R.: 1975,Solar Phys. 40, 103.
Störmer, C.: 1916,Astrophys. J. 43, 347.
Švestka, Z.: 1976,Solar Flares, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Tandberg-Hanssen, E.: 1974,Solar Prominences, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Vorpahl, J. A.: 1978,Solar Phys. 57, 297.
Vrabec, D.: 1970, in R. Howard (ed.), ‘Solar Magnetic Fields’,IAU Symp. 43, 329.
Vrabec, D.: 1973, in R. G. Athay (ed.), ‘Chromospheric Fine Structure’,IAU Symp. 56, 201.
Weart S. R.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 162, 987.
Weart, S. R.: 1972,Astrophys. J. 177, 271.
Wilcox, J. M.: 1968,Space Sci. Rev. 8, 258.
Worden, S. P. and Simon, G. W.: 1975, in A. Maeder (ed.), ‘Star Formation’,IAU Symp. 71, 121.
Zwaan, C.: 1978,Solar Phys. 60, 213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piddington, J.H. Twists and rotations of solar magnetic fields. Astrophys Space Sci 75, 273–287 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648642
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648642