Conclusions
-
1.
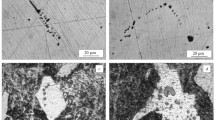
An elevated carbon concentration in the steel investigated (0.19% and higher) substantially reduces the work of crack propagation, and at 0.21% C the work of crack initiation also decreases. In this case the impact toughness decreases considerably at negative temperatures, which is evidently the main reason for the breaking of track links with 0.226% C during use.
-
2.
The optimal preliminary heat treatment for the track links is high-temperature tempering (680°C), while for heats with an elevated carbon content it is normalization with high-temperature tempering.
-
3.
The optimal values of the mechanical properties were obtained by quenching from 960–980°C.
-
4.
Double quenching from 920°C increased the impact toughness by 30% for heats with 0.24% C and by 5% for heats with 0.18% C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. P. Gulyaev, Zavod. Lab., No. 7 (1967).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 35–37, May, 1969.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bekerman, F.A. Mechanical properties of cast structural steel. Met Sci Heat Treat 11, 365–367 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648607
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648607