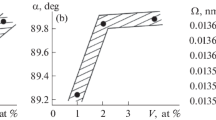
Conclusions
Increasing the concentration of the alloying element in binary alloys of vanadium with titanium, chromium, tin, and aluminum at concentrations of 0–25 wt. % leads to an increase of hardness and electrical resistivity, particularly for alloys with tin and aluminum. The strength will be highest for alloys of vanadium with tin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, Constitution of Binary Alloys, McGraw-Hill, New York (1958).
W. Köster and K. Haug, Z. Metallk., No. 6 (1957).
H. Adenstedt et al., TASM,44 (1952).
H. Martens and P. Duwez, TASM,44 (1952).
I. I. Kornilov, Physicochemical Basis of the Heat Resistance of Alloys [in Russian], Izd. Akad. Nauk SSSR (1961).
L. P. Vorob'eva et al., Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Metally, No. 1 (1969).
W. Rostoker, Metallurgy of Vanadium, Wiley, New York (1958).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 7, pp. 62–63, July, 1971.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchukova, L.V., Matveeva, N.M. & Kornilov, I.I. Some properties of binary vanadium alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 13, 594–595 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648205
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648205