Summary
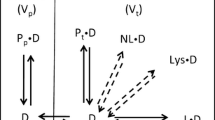
A pharmacokinetic model that incorporates linear binding of drug to plasma proteins and tissue indicates the same relationship between apparent volume of distribution and drug binding as that proposed by Gillette (1971) based on a simple distribution model. Apparent volume of distribution (V) is directly proportional to free fraction of drug in plasma (fp) and indirectly proportional to free fraction of drug in tissue (fT). In the case of a constant fT, a plot of V versus fp will be linear with an intercept equal to plasma volume (Vp). If fT changes with fp, an apparently linear plot may result but the intercept will exceed Vp. An approach to the calculation of fT, a composite binding parameter, is presented and illustrated by comparing the tissue binding of tolbutamide in patients during acute viral hepatitis and upon recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibaldi, M.: Drug distribution in renal failure. Am. J. Med.62, 471 (1977)
Gibaldi, M. and McNamara, P. J.: Tissue binding of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci.66, 1211 (1977)
Gillette, J. R.: Factors affecting drug metabolism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.179, 43 (1971)
Gugler, R., Shoeman, D. W., Huffman, D. H., Cohlima, J. B. and Azarnoff, D. L.: Pharmacokinetics of drugs in patients with the nephrotic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest.55, 1182 (1975)
Levy, G. and Yacobi, A.: Effect of plasma protein binding on elimination of warfarin. J. Pharm. Sci.63, 805 (1974)
Odar-Cederlöf, I. and Borgå, O.: Kinetics of diphenylhydantoin in uremic patients: Consequences of decreased plasma protein binding. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.7, 31 (1974)
Soberman, R., Brodie, B. B., Levy, B. B., Axelrod, J., Hollander, V. and Steele, J. M.: The use of antipyrine in the measurement of total body water in man. J. Biol. Chem.179, 31 (1949)
Wagner, J. G.: Simple model to explain effects of plasma protein binding and tissue binding on calculated volumes of distribution, apparent elimination rate constants and clearances. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.10, 425 (1976)
Wilkinson, G. R. and Shand, D. G.: A physiologic approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.18, 377 (1975)
Williams, R. L., Blaschke, T. F., Meffin, P. J., Melmon, K. L. and Rowland, M.: Influence of acute viral hepatitis on disposition and plasma binding of tolbutamide. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.21, 301 (1977)
Yacobi, A. and Levy, G.: Comparative pharmacokinetics of coumarin anticoagulants XIV: Relationship between protein binding, distribution, and elimination kinetics of warfarin in rats. J. Pharm. Sci.64, 1660 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by Grant GM-20852 from the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gibaldi, M., McNamara, P.J. Apparent volumes of distribution and drug binding to plasma proteins and tissues. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13, 373–378 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00644611
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00644611