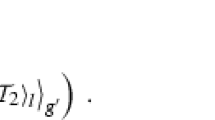Abstract
The equations for the variation of the osculating elements of a satellite moving in an axi-symmetric gravitational field are integrated to yield the complete first-order perturbations for the elements of the orbit. The expressions obtained include the effects produced by the second to eighth spherical harmonics. The orbital elements are presented in the most general form of summations by means of Hansen coefficients. Due to their general forms it is a simple matter to estimate the perturbations of any higher harmonic by simply increasing the index of summation. Finally, this paper gives the respective general expressions for the secular perturbations of the orbital elements. The formulae presented should be useful for the reductions of Earth-satellite observations and geopotential studies based on them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α:
-
semi-major axis
- C njk (ν, ω):
-
cosine functions of ν and ω
- e :
-
eccentricity of the orbit
- f :
-
acceleration vector of perturbing force
- f :
-
sin2t
- i:
-
inclination of the orbit
- J n :
-
coefficients in the potential expansion
- M :
-
mean anomaly
- n :
-
mean motion
- p :
-
semi-latus rectum of the orbit
- R, S, andW :
-
components of the perturbing acceleration
- r :
-
radius-vector of satellite
- r :
-
magnitude ofr
- S njk (ν, ω):
-
sine functions of ν and ω
- T :
-
time of perigee passage
- u :
-
argument of latitude
- U :
-
gravitational potential
- ν:
-
true anomaly
- V :
-
perturbing potential
- μ:
-
G(M++m) (gravitational constant times the sum of the masses of Earth and satellite)
- ρn,k :
-
coefficients ofR component of disturbing acceleration (funtions off)
- σn,k :
-
coefficients ofS andW components of disturbing acceleration (functions off)
- χ:
-
mean anomaly at timet=0
- X n,m0 :
-
zero-order Hansen coefficients
- Ω:
-
argument of perigee
- Ω:
-
right ascension of the ascending node
References
Gaposchkin, E. M.: 1977,Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A284, 515.
Geyling, F. and Westerman, H. R.: 1971,Introduction to Orbital Mechanics, Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass., U.S.A.
Hori, G. I. and Kozai, Y.: 1975, in G. E. O. Giacaglia (ed.),Satellite Dynamics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Kopal, Z.: 1978,Dynamics of Close Binary Systems, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Lerch, F. J., Klosko, S. M., Laubscher, R. E., and Wagner, C. A.: 1977, Goddard Space Flight Center Doc. X-921-77-246.
Taff, L. G.: 1985,Celestial Mechanics, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Zafiropoulos, B. and Kopal, Z.: 1982a,Astrophys. Space Sci. 88, 331.
Zafiropoulos, B. and Kopal, Z.: 1982b,Astrophys. Space Sci. 88, 355.
Zafiropoulos, B. and Zafiropoulos, F.: 1982,Astrophys. Space Sci. 88, 401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zafiropoulos, B. The motion of a satellite in an axi-symmetric gravitational field. Astrophys Space Sci 139, 111–128 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00643817
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00643817