Abstract
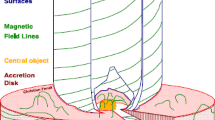
Magnetic tensions are likely to be the dominant shear force in accretion disks, larger when integrated than turbulent viscosity by an order of magnitude or more. In galactic disks, they guarantee the mass-accretion rate required by the quasar phenomenon. In fast-revolving, clumpy disks, magnetic pressures can exceed static pressures and be amplified towards ram pressures. The inner, near-rigidly rotating parts of galactic disks are suggestive candidates. The gas velocities in such magnetically controlled disks mimic higher central masses than present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken, D. K.: 1989, in M. Morris (ed.), ‘The Center of the Galaxy’,IAU Symp. 136, 457.
Allen, D. A. and Sanders, R. H.: 1986,Nature 319, 191.
Beck, R.: 1987, in R. Beck and R. Gräve (eds.),Interstellar Magnetic Fields, Proceedings of Ringberg Workshop, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 4.
Becker, W.: 1950,Sterne und Sternsysteme, Theodor Steinkopff, Dresden.
Blitz, L., Fich, M., and Stark, A. A.: 1983,Astrophys. J. Suppl. 49, 183.
Chandrasekhar, S.: 1943,Principles of Stellar Dynamics, Univ. of Chicago Press, Chicago, p. 21.
Eardley, D. M. and Lightman, A. P.: 1975,Astrophys. J. 200, 187.
Fleck, R. C., Jr.: 1981,Astrophys. J. 246, L151.
Genzel, R. and Townes, C. H.: 1987,Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 25, 377.
Harnett, J. I., Beck, R. and Buczilowski, U. R.: 1989,Astron. Astrophys.,208, 32.
Kaelble, A., de Boer, K. S., and Grewing, M.: 1985,Astron. Astrophys. 143, 408.
Kim, K.-T., Kronberg, P. P., Giovannini, G., and Venturi, T.: 1989,Nature,341, 720.
Krause, M., Beck, R., and Hummel, E.: 1989,Astron. Astrophys. 217, 17.
Kundt, W.: 1987,Astrophys. Space Sci. 129, 195.
Kundt, W.: 1989,Astrophys. Space Sci. 62, 335.
Kundt, W.: 1990,Astrophys. Space Sci. (in press).
Kundt, W. and Müller, P.: 1987,Astrophys. Space Sci. 136, 281.
Loiseau, N., Nakai, N., Sofue, Y., Wielebinski, R., Reuter, H.-P., and Klein, U.: 1990,Astron. Astrophys. 228, 331.
Lynden-Bell, D.: 1971, in D. J. K. O'Connell (ed.),Nuclei of Galaxies, Pont. Acad. Scient. Scripta Varia, Vol. 35, p. 531.
Merritt, D.: 1989,Dynamics of Dense Stellar Systems, Workshop Proceedings, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, day 1.
Morris, M.: 1989, in R. Beck, P. Kronberg, and R. Wielebinski (eds.), ‘Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields’,IAU Symp. 140.
Müller, P. and Kundt, W.: 1989,Astrophys. Space Sci. 155, 153.
Parker, E. N.: 1979,Cosmical Magnetic Fields, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford.
Peacock, J. A.: 1987, in W. Kundt (ed.),Astrophysical Jets and their Engines, NATO ASI C208, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, p. 171.
Pringle, J. P.: 1981,Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 19, 137.
Reich, W.: 1989, in R. Beck, P. Kronberg, and R. Wielebinski (eds.), ‘Galactic and Intergalatic Magnetic Fields’,IAU Symp. 140.
Rieke, G. H. and Rieke, M. J.: 1988,Astrophys. J. 330, L33.
Rohlfs, K. and Kreitschmann, J.: 1988,Astron. Astrophys. 201, 51.
Rosner, R. and De Luca, E.: 1989, in M. Morris (ed.), ‘The Center of the Galaxy’,IAU Symp. 136, 319.
Sanders, R. H. and Wrixon, G. T.: 1973,Astron. Astrophys. 26, 365.
Sarazin, C. L.: 1988,X-Ray Emission from Clusters of Galaxies, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, pp. 78, 88.
Schwarz, U. J.: 1989, in R. Beck, P. Kronberg and R. Wielebinski (eds.), ‘Galactic and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields’,IAU Symp. 140.
Schwarz, U. J., Bregman, J. D., and van Gorkom, J. H.: 1989Astron. Astrophys. 215, 33
Sellgren, K.: 1989, in M. Morris (ed.), ‘The Center of the Galaxy’,IAU Symp. 136, 477.
Shakura, N. I. and Sunyaev, R. A.: 1973,Astron. Astrophys. 24, 337.
Shibata, K., Tajima, T., and Matsumoto, R.: 1990,Astrophys. J. (submitted).
Sofue, Y. and Reich, W.: 1987, in R. Beck and R. Gräve (eds.),Interstellar Magnetic Fields, Proceedings of Ringberg Workshop, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 152.
Soltan, A.: 1982,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 200, 115.
Sparke, L.: 1982,Astrophys. J. 260, 104.
Stella, L. and Rosner, R.: 1984,Astrophys. J. 277, 317.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundt, W. Magnetic tensions can control the dynamics of accretion disks. Astrophys Space Sci 172, 285–291 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00643321
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00643321