Abstract
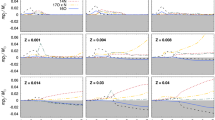
This paper deals with two main effects: First the empirical metal abundance distribution in Main Sequence disk dwarfs of the solar neighbourhood, and second, the theoretical possibility of (i) an increased helium content as the Galaxy evolves, and (ii) the presence of evolutionary effects in disk dwarfs (i.e., the age of some or all stars considered up to the subgiant phase is not necessarily longer than the age of the galactic disk). We take into account a linear increase of helium content with metal content, and we impose some constraints relative to initial, solar and present-day observed values ofY andZ, and to observed relative helium to heavy element enrichment, ΔY/ΔZ. In this way, little influence is found on the empirical metal abundance distribution in the range 0≤ΔY/ΔZ≤3, while larger values of ΔY/ΔZ would lead to a more significant influence. ‘Evolved’ and ‘unevolved’ theoretical metal abundance distributions are derived by accounting for a two-phase model of chemical evolution of galaxies and for a linear mass dependence of star lifetimes in the spectral range G2V–G8V, and are compared with the empirical distribution. All are in satisfactory agreement due to systematic shift data by different observations; several values o collapse timeT c and age of the GalaxyT are also considered. Finally, models of chemical evolution invoking homogeneous collapse without infall and inhomogeneous collapse with infall, are briefly discussed relative to the empirical metal abundance distribution in Main Sequence disk dwarfs of the solar neighbourhood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audouze, J. and Tinsley, B. M.: 1976,Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 14, 43.
Bertelli, G., Bolton, A., Chiosi, C., and Nasi, E.: 1978,Astron. Astrophys. Supp. (in press).
Biermann, P. and Biermann, L.: 1977,Astron. Astrophys. 55, 63.
Bond, H. E.: 1970,Astrophys. J., Supp. Ser. 184, 22, 117.
Busso, M., Gallino, R., and Masani, A.: 1977,Astrophys. Space Sci. 52, 479.
Caimmi, R.: 1978a,Astrophys. Space Sci. 54, 453.
Caimmi, R.: 1978b,Astrophys. Space Sci. 59, 109.
Caimmi, R.: 1978c,Astrophys. Space Sci. 59, 413.
Chiosi, C.: 1978, in E. Bazinska-Grzesik and M. Mayer (eds), ‘Chemical and Dynamical Evolution in our Galaxy’IAU Coll. 45, 61.
Cox, J. P. and Giuli, R. T.: 1968, inPrinciples of Stellar Structure, Vol. I, Gordon and Breach, p. 11.
D'Odorico, S., Peimbert, M., and Sabbadin, F.: 1976,Astron. Astrophys. 47, 341.
Fitchel, C. E. and McDonald, F. B.: 1967,Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys 7, 43.
Gustafsson, B. and Nissen, P. E.: 1972,Astron. Astrophys. 19, 261.
Hartwick, F. D. A.: 1976,Astrophys. J. 209, 418.
Hearnshaw, J. B.: 1972,Mem. Roy. Astron. Soc. 77, 55.
Kaufman, M.: 1975,Astrophys. Space Sci. 33, 265.
Larson, R. B.: 1976,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 176, 31.
Mould, J. R. and McElroy, D. B.: 1978,Astrophys. J. 220, 935.
Nissen, P. E.: 1970,Astron. Astrophys. 6, 138.
Nissen, P. E. and Gustafsson, B.: 1978, Communication presented at the Fourth European Regional Meeting in Astronomy, Uppsala, Sweden.
Pagel, B. E. J.: 1973, Internal Report IC/73/169 at International Centre for Theoretical Physics, Trieste, Italy.
Pagel, B. E. J. and Patchett, B. E.: 1975,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 172, 13.
Peimbert, M. and Costero, R.: 1969,Bol. Obs. Tonantzintla Tacubaya 5, 3.
Peimbert, M. and Torres-Peimbert, S.: 1974,Astrophys. J. 193, 327.
Peimbert, M. and Torres-Peimbert, S.: 1976,Astrophys. J. 203, 581.
Peimbert, M. and Torres-Peimbert, S.: 1977,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 169, 217.
Popper, D. M., Jørgensen, M. E., Morton, D. C., and Lackvrone, D. S.: 1970,Astrophys. J. Letters 161, L57.
Preston, G.: 1959a,Astrophys. J. 130, 507.
Preston, G.: 1959b,Contr. Lick Obs., Ser. II, No. 96.
Preston, G.: 1961,Astrophys. J. 134, 633.
Saio, H.: 1977,Astrophys. Space Sci. 50, 93.
Salpeter, E. E.: 1955,Astrophys. J. 121, 161.
Sandage, A. R. and Eggen, O. J.: 1959,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 119, 278.
Schmidt, M.: 1963,Astrophys. J. 137, 758.
Strömgren, B.: 1963,Q. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 4, 8.
Tinsley, B. M., and Larson, R. B.: 1978,Astrophys. J. 221, 554.
Torres-Peimbert, S. and Peimbert, M.: 1977,Rev. Mexicana Astronom. Astrofis. 2, 181.
Wallerstein, G. N.: 1962,Astrophys. J. Supp. 6, 407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caimmi, R. The effect of increasing helium content and disk dwarfs evolution on the chemical enrichment of the Galaxy. Astrophys Space Sci 63, 389–403 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638910
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638910