Abstract
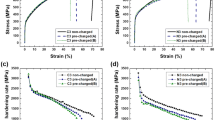
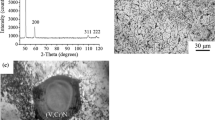
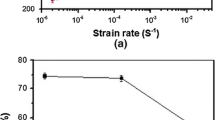
Hydrogen embrittlement of AlSl type 316, 321 and 347 stainless steels with nitrogen alloying has been studied by a tensile test through cathodic charging. The results show that addition of nitrogen improved resistance to hydrogen cracking regardless of the failure mode. Fracture surfaces of cathodically charged steels showed intergranular brittle zones on each side of the fracture surfaces. AlSl type 316 with nitrogen alloying stainless steel is more resistant to hydrogen embrittlement than AlSl type 321 with nitrogen alloying steel, whereas AlSl type 347 with nitrogen alloying steel is susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. Nitrogen alloying of stainless steel increased the mechanical properties in hydrogen environments by increasing the stability of austenite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. L. Holzworth,Corrosion 26 (1969) 107.
M. B. Whiteman andA. R. Troiano,ibid. 21 (1965) 53.
M. R. Louthan Jr, G. R. Caskey Jr,J. A. Donovan andD. E. Rawl Jr,Mater. Sci. Engng 10 (1972) 357.
M. R. Louthan Jr, in “Hydrogen in Metals”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1974) p. 53.
A. W. Thompson,ibid.“, p. 91.
A. J. West andM. R. Louthan Jr,Met. Trans. 13A (1982) 2049.
A. W. Thompson, in “Environmental Degradation of Engineering Materials”, edited by M. R. Louthan Jr, and R. P. McNitt (Printing Department, Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg, Virginia, 1977) p. 3.
A. W. Thompson andJ. A. Brooks,Metall. Trans. A6 (1975) 1931.
C. L. Briant, in “Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydrogen Effects in Metals”, Moran, 1980, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (Metallurgical Society of AIME, Warrendale, Pennsylvania 1980) p. 527.
H. Hanninen, T. Hakkarainen andP. Nenonen,ibid.“, p. 575.
P. Rozenak andD. Eliezer,Mater. Sci. Engng 61 (1983) 31.
C. Hwang andI. M. Bernstein,Acta Metall. 34 (1986) 1001.
M. L. Holzworth andH. R. Louthan Jr,Corrosion 24 (1968) 110.
R. Liu, N. Narita, C. Altstetter, H. Birnbaum andN. Pugh,Metal. Trans. 11A (1980) 1563.
W. Y. Chu, J. Yao andC. M. Hsiao,ibid. 15A (1984) 729.
D. Eliezer, G. Chakrapani, C. J. Altstetter andE. Pugh,ibid. 10A (1979) 935.
C. L. Briant,ibid. 10A (1979) 181.
A. W. Thompson,Mater. Sci. Engng 14 (1974) 253.
R. M. Vennet andG. S. Ansell,Trans. ASM 60 (1967) 242.
Y. Rosental, M. Marc-Markowitch andA. Stern,Scripta Metall. 15 (1989) 861.
H. L. G. Byrnes, M. Grujicic andW. S. Owen,Acta Metall. 35 (1987) 1853.
C. G. Rhodes andA. W. Thompson,Metal. Trans. 89A (1977) 1901.
P. Q. Swann,Corrosion 19 (1963) 102.
G. H. Eichelman andF. C. Hull,Trans. ASM 45 (1953) 77.
F. B. Pickering, in “Optimization of Processing, Properties and Service Performance through Microstructural Control”, edited by H. Abrams, G. N. Maniar, D. A. Nail and H. D. Solomon (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1979) p. 263.
T. Angel,J. Iron Steel Inst. 177 (1954) 165.
ASTM Standard E-112, (American Institute for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1977).
ASTM Standard E-8,ibid. (1976).
K. J. Irvine, T. Gladman andF. B. Pickering,J. Iron Steel Inst. 207 (1969) 1017.
K. J. Irvine, D. T. Leewellyn andF. B. Pickering,ibid. 199 (1961) 153.
A. Atrens, J. Bellima, N. Fiore andR. Coye, in “The Metal Science of Stainless Steel”, edited by E. Collings and H. Kings (American Institute of Mechanical Engineers, New York, 1979) p. 54.
P. Studebaker, C. Alstetter andW. Conley, in “Effects in Metals”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (American Institute of Mechanical Engineers, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 1981) p. 169.
B. Ladna andH. K. Birnbaum,Acta Metall. 35 (1987) 1775.
P. Rozenak, L. Zevin andD. Eliezer,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2 (1983) 63.
P. Rozenak andD. Eliezer,Acta Metall. 35 (1987) 2329.
A. W. Thompson,Metall. Trans. 10A (1979) 731.
H. Mathias, Y. Katz andS. Nadiv,Metal Sci. 12 (1978) 129.
P. Rozenak, I. M. Robertson andH. K. Birnbaum,Acta Metall., in press.
R. B. Benson, R. K. Dann andL. W. Roberts Jr,Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 242 (1968) 2199.
C. L. Briant,Scripta Metall. 12 (1978) 541.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozenak, P. Effects of nitrogen on hydrogen embrittlement in AlSl type 316, 321 and 347 austenitic stainless steels. J Mater Sci 25, 2532–2538 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638055
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638055