Summary
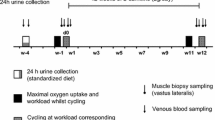
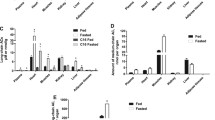
Changes in the main physiological parameters and circulating indicators of carbohydrate, protein, lipid (and ketone body) metabolism were measured in ten exercising subjects before L-carnitine (L-carn) loading, after 4 weeks of daily loading with 2 g L-carn, and 6–8 weeks after terminating L-carn administration. Measurements were made on venous blood samples collected during each experiment at fixed time intervals over an initial rest of 45 min, 60 min bicycle exercise performed near 50%\(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2}} {\text{max}}} } \) and 120 min recovery. Free and total plasma carnitine levels reached a plateau corresponding to an average rise of 25% for both fractions, 9–10 days after the beginning of the L-carn diet. These levels returned to their initial values 6–8 weeks after cessation of the supply. Generally L-carn supplementation did not significantly modify the physiological parameters and circulating metabolites. No distinct increase of the relative participation of endogenous lipids in the fuel supply of prolonged submaximal exercise was observed. In normal human subjects the increased demand for fatty acid oxidation resulting from exercise seems to be adequately supported by endogenous levels of carnitine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askew EW, Dohm GL, Weiser PC, Huston RL, Doub WH (1980) Supplemental dietary carnitine and lipid metabolism in exercising rats. Nutr Metab 24:32–42
Banister EW, Allen ME, Mekjavic IB, Singh AK, Legce B, Mutch BJC (1983) The time course of ammonia and lactate accumulation in blood during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 51:195–202
Carlin JI, Reddan WG, Sanjak M, Hodach R (1986) Carnitine metabolism during prolonged exercise and recovery in humans. J Appl Physiol 61:1275–1278
Cederblad G (1984) Fat metabolism following an intravenous bolus dose of a fat emulsion and carnitine. Clin Physiol 4:159–168
Décombaz JE, Reffet B, Bloemhard Y (1987) L-carnitine supplementation, caffeine and fuel oxidation in the exercising rat. Nutr Res 7:923–933
Eclache JP, Quard S, Carrier H, Berthillier G, Marnot B, Eichenberger D (1979) Effects d'une adjonction de carnitine au régime alimentaire sur l'exercise intense et prolongé. In: Lacour JR (ed) Place de l'alimentation dans la préparation biologique à la compétition. Comptes Rendus du Colloque de Saint Etienne, pp 163–171
Eggstein M, Kuhlmann E (1970) Triglyceride und Glyerin. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. Verlag Chemie Weinheim, pp 1765–1771
Fanelli O (1978) Carnitine and acetyl-carnitine, natural substances endowed with interesting pharmacological properties. Life Sci 23:2563–2570
Ferrari R, Cucchini F, Visioli O (1984) The metabolic effects of L-carnitine in angina pectoris. Int J Cardiol 5:213–216
Freund H, Jacqot P, Marbach J, Pellier A, Ramboarina D, Vogt JJ (1970) In vivo physiological experiments on the autoanalyzer in a computerized environment. In: Advances in automated analysis, vol 1. Mediad Incorporated, White Plains, New York, pp 195–198
Fritz IB, McEwen B (1959) Effects of carnitine on fatty acid oxidation by muscle. Science 129:334–335
Harrisson MH (1985) Effects of thermal stress and exercise on blood volume in humans. Physiol Rev 65:149–209
Holloszy JO, Booth FW (1976) Biochemical adaptations to endurance exercise in man. Annu Rev Physiol 38:273–291
Kuramasi K, Ishiharaa, Uehara H (1972) Determination of ammonia in blood plasma by an ion exchange method. Clin Chim Acta 42:141–146
Lebrun P, Guezennec Y, Bonnet P, Muh JP, Aymond M, Morand P (1984) Influence d'une prise de D,L-carnitine par voie orale sur les paramètres physiologiques et biochimiques au cours de deux types d'épreuves d'effort. Intéret chez l'athlète d'endurance. Med Nutr 20:235–240
Leibowitz B (1984) Carnitine. The vitamin BT phenomenon. A Dell Book, New York, pp 173
Maccari F, Pessotto P, Ramacci MT, Angelucci L (1985) The effect of exogenous L-carnitine on fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in the rat. Life Sci 36:1967–1975
McGarry JD, Foster DW (1976) An improved and simplified radioisotopic assay for the determination of free and esterified carnitine. J Lip Res 17:277–281
Marconi C, Sassi G, Carpinelli A, Cerretelli P (1985) Effects of L-carnitine loading on the aerobic and anaerobic performance of endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:131–135
Mutch BJC, Banister EW (1983) Ammonia metabolism in exercise and fatigue: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:41–50
O'Connor JE, Costell M, Grisolia S (1984) Protective effect of L-carnitine on hyperammonemia. FEBS Lett 166:331–334
Orzali A, Maetzke G, Donzelli F, Rubaltelli FF (1984) Effect of carnitine on lipid metabolism in the neonate. II Carnitine addition to lipid infusion during prolonged total parenteral nutrition. Pediatrics 104:436–440
Rebouche CJ (1983) Effect of dietary carnitine isomers and γ-butyrobetaine on L-carnitine biosynthesis and metabolism in the rat. J Nutr 113:1906–1913
Secombe D, Burget D, Frohlich J, Hahn P, Cleator J, Gourlay RH (1984) Oral L-carnitine administration after jejunoileal by-pass surgery. Int J Obes 8:427–433
Tabacco AT, Meiattini F, Moda E, Tarli P (1979) Simplified enzymic calorimetric serum urea nitrogen determination. Clin Chem 25:336–337
Trinder P (1969) Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann Clin Biochem 6:24–27
Williamson DH, Mellanby J, Krebs HA (1962) Enzymic determination of D(−)-β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J 80:90–96
Williamson DH (1974) L-alanine. Determination with alanine dehydrogenase. In Bergmeyer HU (ed). Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1679–1685
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyono-Enguelle, S., Freund, H., Ott, C. et al. Prolonged submaximal exercise and L-carnitine in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 58, 53–61 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636603
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636603