Abstract
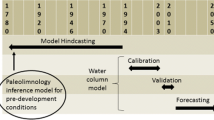
The empirical direct distribution model for lake acidification is calibrated for use in an integrated assessment model which predicts the regional impact of an acid deposition control strategy. The calibration is based on the mechanistic Model of Acidification of Groundwater in Catchments (MAGIC). The models are applied jointly to a set of 33 statistically-selected lakes in the Adirondack region of New York. Calibration of the direct distribution model is based on a step-function application of acid deposition to MAGIC. Comparative evaluations of the resulting model predictions are made using historic deposition estimates and two alternative future deposition scenarios. The predictions of the direct distribution model match well the shapes and patterns of change of the regional distributions of ANC and pH predicted by MAGIC, the short- and medium-term dynamics of these changes, and the effect of including organic acids. However, small, long-term decreases in the fraction of incoming acid deposition neutralized by lakes and their watersheds predicted by MAGIC are not reproduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcamo, J., Amann, M., Hettelingh, J.-P., Holmberg, M., Hordijk, L., Kämäri, J., Kauppi, L., Kauppi, P., Kornai, G., and Makela, M.: 1987, ‘Acidification in Europe: A Simulation Model for Evaluating Control Strategies’,Ambio 16(5). 232–245.
Bouzaher, A., Lakshminarayan, P. G., Cabe, R., Carriquiry, A., Gassman, P. W. and Shogren, J. F.: 1993, ‘Metamodels and Nonpoint Pollution Policy in Agriculture’,Water Resources Research 29(6), 1579–1587.
Brakke, D. F. and Henriksen, A.: 1989, ‘Uncertainties in Using Empirical, Steady-state Models to Estimate Critical Loads of Strong Acids to Lakes’,Regional Acidification Models: Geographic Extent and Time Development, J. Kämäri, D. F. Brakke, A. Jenkins, S. A. Norton, R. E. Wright, (Eds.), Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 45–54.
Church, M. R., Thornton, K. W., Shaffer, P. W., Stevens, D. L., Rochelle, B. P., Holdren, R. G., Johnson, M. G.: Lee, J. J., Turner, R. S., Cassell, D. L., Lammers, D. A., Campbell, W. G., Liff, C. I., Brandt, C. C., Liegel, L. H., Bishop, G. D., Mortenson, D. C., and Pierson, S. M. S. M.: 1989, ‘Future Effects of Long-term Sulfur Deposition on Surface Water Chemistry in the Northeast and Southeastern Blue Ridge Province (Results of the Direct/Delayed Response Project)’, EPA 4600/3-89/061, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Cosby, B. J., Hornberger, G. M., Galloway, J. N., and Wright, R. F.: 1985a, ‘Time Scales of Catchment Acidification: A Quantitative Model for Estimating Freshwater Acidification’,Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1144–1149.
Cosby, B. J., Hornberger, G. M., and Galloway, J. N.: 1985b, ‘Modeling the Effects of Acid Deposition: Assessment of a Lumped Parameter Model for Soil Water and Streamwater Chemistry’,Water Resour. Res. 21, 51–63.
Cosby, B. J., Hornberger, G. M., and Galloway, J. N.: 1985c, ‘Modeling the Effects of Acid Deposition: Estimation of Long-term Water Quality Responses in a Small Forested Catchment’,Water Resour. Res. 21(11), 1591–1601.
Cosby, B. J.: 1987, ‘Modeling Reversibility of Acidification with Mathematical Models’,Reversibility of Acidification, H. Barth (Ed.) London, Elsevier Applied Sciences, pp. 114–125.
Crawford, S. L., DeGroot, M. H., Kadane, J. B. and Small, M. J.: 1992, ‘Modeling Lake-Chemistry Distributions: Approximate Bayesian Methods for Estimating a Finite Mixture Model’,Technometrics 34(4), 441–453.
Cumming, B. F., Smol, J. P., Kingston, J. C., Charles, D. F., Birks, H. J. B., Camburn, K. E., Dixit, S. S., Uutala, A. J. and Selle, A. R.: 1992, ‘How Much Acidification Has Occurred in Adirondack Region Lakes (New York, USA) Since Preindustrial times?’,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49, 128–141.
Davis, P. A., Sheppard, M. I. and Andres, T. H.: 1993, ‘A Simple Model to Predict the Long-term Fate of Contaminants in Unsaturated Soils’,Waste Management 13, 25–40.
Driscoll, C. T., Lehtinen, M. and Sullivan, T. J.: 1994, ‘Modeling the Acid-base Chemistry of Organic Solutes in Adirondack N. Y. Lakes’,Water Resour. Res. 30, 297–306.
El-Shaarawi, A. H. and Naderi, A.: 1990, ‘A Probability Model for Acid Rain Data’,Water Res. 24, 1335–1340.
Henriksen, A.: 1979, ‘A Simple Approach for Identifying and Measuring Acidification of Freshwater’,Nature 278, 542–545.
Henriksen, A.: 1984, ‘Changes in Base Cation Concentration Due to Freshwater Acidification’,Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 22, 692–698.
Henriksen, A., Lien, L., Traaen, T. S., Sevaldrud, I. S. and Brakke, D. F.: 1988, ‘Lake Acidification in Norway — Present and predicted Chemical Status’,Ambio 17, 259–266.
Hornberger, G. M., Cosby, B. J. and Galloway, J. N.: 1986, ‘Modeling the Effects of Acid Deposition: Uncertainty and Spatial Variability in Estimation of Long-term Sulfate Dynamics in a Region’,Water Resour. Res. 22(8), 1293–1302.
Kämäri, J. (Ed.): 1990,Impact Models to Assess Regional Acidification, Dordrecht: Publishers. Kluwer Academic.
Kleijnen, J. P. C.: 1987,Statistical Tools for Similation Practitioners, New York: Marcel Dekker.
Kretser, W., Gallagher, J. and Nicolette, J.: 1989,Adirondack Lakes Study, 1984–1987, Adirondack Lakes Survey Corporation, Ray Brook, NY.
Labieniec, P. A., Small, M. J. and Cosby, B. J.: 1989, ‘Regional Distributions of Lake Chemistry Predicted by Mechanistic and Empirical Lake Acidification Models’,Regional Acidification models: Geographic Extent and Time Development, J. Kämäri, D. F. Brakke, A. Jenkins, S. A. Norton and R. F. Wright (eds.), Berlin Springer-Verlag, pp. 185–202.
Munson, R. K. and Gherini, S. A.: 1993, ‘Influence of organic acids on the pH and acid-neutralizing capacity of Adirondack lakes’,Water Resour. Res. 29(4), 891–899.
NAPAP: 1991,Acidic Deposition: State of Science and Technology, Volumes I–IV, National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program, Washington, DC.
Oliver, B. G., Thurman, E. M. and Malcolm, R. L.: 1983, ‘The Contribution of Humic Substances to the Acidity of Colored Natural Waters’,Geochim, Cosmochin, Acta 47, 2031–2035.
Posch, M. and Kämäri, J.: 1990, ‘Modeling Regional Acidification of Finnish Lakes’,Impact Models to Assess Regional Acidification, J. Kämäri, (ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 145–166.
Robinson, D. C. E. and Marmorek, D. R.: 1991, ‘Direct Distribution Models of Acidification’,Methods for Projecting Future Changes in Surface Water Acid-Base Chemistry, Thornton, K. W. Marmorek, D. T., Ryan, P. F. (Eds.) NAPAP State of Science and Technology Report 14, National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program, Washington, DC, pp. 79–82.
Rubin, E. S., Small, M. J. Bloyd, C. N., Marnicio, R. J. and Henrion, M.: 1990, ‘Atmospheric Deposition Assessment Model: Applications to Regional Aquatic Acidification in Eastern North America’,Impact Models to Assess Regional Acidification, J. Kämäri (ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic, Publishers, pp. 253–284.
Rubin, E. S., Small, M. J. Bloyd, C. N. and Henrion, M.: 1992, ‘Integrated Assessment of Aciddeposition Effects on Lake Acidification’,J. Environ. Engineering, ASCE,118, 120–134.
Schecher, W. D. and Driscoll, C. T.: 1988, ‘Principles and Applications of Surface Water Acidification Models’,Hazard Assessment of Chemicals, J. Saxena, (ed.) Vol. 6, New York: Hemisphere Publishing, pp. 187–224.
Schindler, D. W., Kaslan, S. E. M. and Hesslein, R. H.: 1989, ‘Biological Impoverishment in Lakes of the Midwestern and Northeastern United States From Acid Rain’,Environ. Sci. Technol. 25(5), 573–580.
Small, M. J. and Sutton, M. C.,: 1986a, ‘A Regional pH-Alkalinity Relationship’,Water Research 20, 335–343.
Small, M. J. and Sutton, M. C.: 1986b, ‘A Direct Distribution Model for Regional Aquatic Acidification’,Water Resour. Res. 22(13), 1749–1758.
Small, M. J., Labieniec, P. A. and Sutton, M. C.: 1987, ‘Modeling Distribution of Aquatic Chemistry in Regions Impacted by Acid Deposition’,Systems Analysis in Water Quality Management, M. B. Beck, (Ed.) Oxford: Pergamon Press, pp. 161–172.
Small, M. J., Sutton, M. C. and Milke, M. W.: 1988, ‘Parametric Distributions of Regional Lake Chemistry: Fitted and derived’,Environ. Sci. Techno. 22(2), 196–204.
Small, M. J., Labieniec, P. A. and Sutton, M. C.: 1990, ‘Identification of a Direct Distribution Model from a Regionalized Mechanistic Model of Aquatic Acidification’,Impact Models to Assess Regional Acidification, J. Kämäri, (ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 167–181.
Small, M. J.: 1991, ‘Parametric Distributions’,Historical Changes in Surface Water Acid-Base Chemistry in Response to Acidic Deposition, NAPAP State of Science and Technology Report No. 11, T. J. Sullivan, Washington DC: National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program, pp. 77–81, 102–107.
Sullivan, T. J.: 1990,Historical Changes in Surface Water Acid-Base Chemistry in Response to Acid Deposition, NAPAP State of Science and Technology Report Number 11, Washington, DC: National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program.
Sullivan, T. J., Charles, D. F., Smol, J. P., Cumming, B. F., Selle, A. R., Thomas, D. R., Bernert, J. A. and Dixit, S. S.: 1990, ‘Quantification of Changes in Lakewater Chemistry in Response to Acid Deposition’Nature 345, 54–58.
Sullivan, T. J. Cosby, B. J., Bernert, J. A., Charles, D. F., Jenne, E. A., Selle, A. R., and Eilers, J. M.: 1991,Comparison of MAGIC and Diatom Paleolimnological Model Hindcasts of Lakewater Acidification in the Adirondack Region of New York, Pacific Northwest Laboratory for U.S. DOE, PNL-7487, UC-603, Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Battelle Memorial Institute, Richland, Washington.
Sullivan, T. J., Cosby, B. J., Driscoll, C. T., Charles, D. F., and Hemond, H. F.: 1994, ‘Influence of Organic Acids on Model Projections of Lake Acidification’,Environmental Science and Technology (in review).
Thornton, K. W., Marmorek, D. R. and Ryan, P. F.: 1991,Methods for Projecting Future Changes in Surface Water Acid-Base Chemistry, Washington, DC: NAPAP State of Science and Technology Report 14, National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program.
Wright, R. F. and Henriksen, A.: 1983, ‘Restoration of Norwegian Lakes by Reduction in Sulphur Deposition’,Nature 305, 422–424.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Small, M.J., Cosby, B.J., Marnicio, R.J. et al. Joint application of an empirical and mechanistic model for regional lake acidification. Environ Monit Assess 35, 113–136 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00633710
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00633710