Abstract
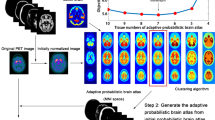
A computerized brain atlas, adjustable to the patients anatomy, has been developed. It is primarily intended for use in positron emission tomography, but may also be employed in other fields utilizing neuro imaging, such as stereotactic surgery, transmission computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The atlas is based on anatomical information obtained from a digitized cryosectioned brain. It can be adjusted to fit a wide range of images from individual brains with normal anatomy. The corresponding transformation is chosen so that the modified atlas agrees with a set of CT or NMR images of the patient. The computerized atlas can be used to improve the quantification and evaluation of PET data by:
-
- Aiding and improving the selection of regions of interests.
-
- Facilitating comparisons of functional image data from different individuals or groups of individuals.
-
- Facilitating the comparison of different examinations of the same patient, thus reducing the need of reproducible fixation systems.
-
- Providing external a priori anatomical information to be used in the image reconstruction.
-
- Improving the attenuation and scatter corrections.
-
- Aiding in selecting a suitable patient orientation during the PET study.
By applying the inverse atlas transformation to PET data set it is possible to relate the PET information to the anatomy of the reference atlas. Thus reformatted PET data from different patients can be averaged, and averages from different categories of patients can be compared. This procedure will facilitate the identification of statistically significant differences in the PET information from different groups of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohm C, Greitz T, Kingsley D, Berggren BM, Olsson L (1983) Adjustable computerized stereotaxic brain atlas for transmission and emission tomography. Am J Neuroradiol 4:731
Bohm C, Greitz T, Kingsley D, Berggren BM, Olsson L (1985) A computerized individually variable stereotaxic brain atlas. In: Greitz, Ingvar, Widen (eds) The metabolism of the human brain studied with positron emission tomography. Raven Press, New York, p 85
Bohm C, Greitz T, Blomquist G, Farde L, Forssgren PO, Kingsley D, Sjögren I, Wiesel F, Wik G (1986) Applications of a computerized adjustable brain atlas in positron emission tomography. Acta Radiol [Suppl] 369:449–452
Evans AC, Beil C, Marrett S, Thompson CJ, Hakim A (1988) Anatomical-functional correlation using an adjustable MRI-based region of interst atlas with positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:513–530
Fox PT, Perlmutter JS, Raichle ME (1985) A stereotactic method of anatomical localization for positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:141–153
Fox PT, Mintun MA, Reiman EM, Raichle ME (1988) Enhanced detection of focal brain responses using intersubject averaging and change-distribution analysis of subtracted PET images. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:642–653
Giorgi C, Garibotto G, Garozzo S, Micca G, Piretta G (1982) Three-dimensional processing of a stereotactic brain atlas. Appl Neurophysiol 45:419
Giorgi C, Broggi G, Garibotto G, Passerini A, Cerchiari U, Abele MG, Koslow M (1983) Three-dimensional neuroanatomic images in CT guided stereotaxic neurosurgery. Am J Neuroradiol 4:719
Mazziotta JC, Phelps ME, Plummer D, Kuhl DE (1981) Quantitation in positron emission computed tomography: 6. physicalanatomical effects. J Comput Assist Tomogr 5:734–743
Mazziotta JC (1984) Physiologic Neuroanatomy: New brain imaging methods present a challenge to an old dicipline. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:481
Tasker RR, Rowe IH, Hawrylyshyn P, Organ LW (1976) Computer mapping of brain-stem sensory centers in man. J Neurosurg 44:458
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohm, C., Greitz, T. & Eriksson, L. A computerized adjustable brain atlas. Eur J Nucl Med 15, 687–689 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00631757
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00631757