Abstract
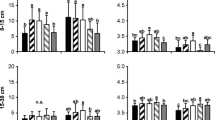
When comparing the species composition of herb layers in loess beech forests of the Westphalian Bight (Northrhine-Westphalia, F.R. Germany) in the years 1976 and 1983, findings show that acidophilic plants tended to be favored during this period. Apart from many other factors, depositions have also been considered as causes for this. Where they should actually play a role, comparable locations having a higher acid deposition rate would have to show a stronger tendency towards acid-indicators than those having a lower one.
It is the stemflow area of the beech tree (Fagus sylvatica L.) which attracts more precipitation than the rest of the forest area, on account of its infundibular treetop. Furthermore, stemflow water from Fagus sylvatica exhibits a higher degree of acidity than rain dripping from the treetop. Thus, the stemflow area as an area with higher acidic incidence may be compared with the normal forest area displaying minor acidic incidence. Findings from all the surveys so far conducted in Middle Europe show that soil pH recorded in the stemflow area is distinctly lower, and that there are less base- and weak acid-indicators but correspondingly more (strong) acid-indicators, than in “normal” forest soil. It must be noted that the phenomena observed need not be due to acidic precipitation. They could as well be attributable to a special feature pertaining to the stemflow area of the beech as specifically natural phenomena.
In the event of natural causes being detected, these would have to be observable in the overall growth area of the beech. In Southern Europe, however, we did not find any indication whatsoever for acidification of the stemflow area. This phenomenon appears to be restricted to Central European regions affected by higher pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burrichter, E. and Wittig, R.: 1977,Mitt. Flor.-soz. Arb. gem. NF 19/20, 377
Cuatrecasas, J.: 1932,Veöffentl. Geobot. Inst. Rübel,9, 443
Eidmann, F.E.: 1959,Union géodesique et géographique internationale 48, 5
Ellenberg, H.: 1950,Landwirtschaftl.Pflanzensoziologie 1, 1
Ellenberg, H.: 1979,Scripta Geobotanica 9 (2nd edition) 1 and 39
Fluckinger, W., Braun, W. and Flückinger-Keller, H.: 1984,Schweiz. Zeitschrift Forstwesen 135, 389
Gersper, P. and Holowaychuk, N.: 1971,Ecology 52, 691
Glatzel, G., Sonderegger, E. and Kazda, M.: 1983,Allg.Forstzeitung 94, 111
Glavac, H., Jochheim, H., Koenies, H., Rheinstädter, R. and Scöhafer, H.: 1985,Allg. Forst. Zeitschr. 40, 1397
Glavac, V., Krause, A. and Wolff-Straub, R.: 1970,Schriftenreihe Vegetationskunde 5, 187
Jochheim, H.: 1985:Ber. Forschun gszentrum Waldökosysteme/Waldsterben,10, 1
Koenies, H.: 1982,Ber. Forschungszentrum Waldokosysteme/Waldsterben,9, 1
Mayer, R. and Ulrich, B.: 1973, in Ellenberg, H. (ed),Ökosystemforschung, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp. 165
Neite, H. and Wittig, R.: 1985,Acta Oecologica/Oecologia Plantarum 6, 375
Runge, M.: 1983,Verhandl. Ges. Ökol. 11, 339
Sachs, L.: 1974,Angewandte Statistik, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 545 pp.
Trepl, L.: 1982,Tuexenia, lditt.Flor.soz.Arb.gem.NS 2, 195
Tuxen, R.: 1972, in Tüxen, R. (ed.),Grundfragen und Methoden in der Pflanzensoziologie, De Junk Publishers, Den Haag, pp. 168
Tüxen, R.: 1977, in Tuxen, R. (ed.),Vegetation und Klima, J. Cramer, Vaduz, pp. 127
Wittig, R. and Neite, H.: 1983,Allg.Forst.Zeitschr. 38, 1232
Wittig, R. and Neite, H.: 1985,Vegetatio 64, 113
Wittig, R., Ballach, H.J. and Brandt, C.J.: 1985 a,Angewandte Botanik 56, 219
Wittig, R., Werner W. and Neite, H.: 1985 b,VDI Bericht 560, 21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wittig, R. Acidification phenomena in beech (Fagus sylvatica) forests of Europe. Water Air Soil Pollut 31, 317–323 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00630847
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00630847