Abstract
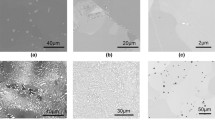
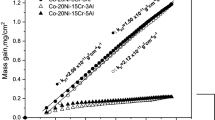
The isothermal oxidation of Co-Cr-Al alloys, containing 10–30 % Cr and 1 or 4.5% Al in 1 atm flowing oxygen at 1000 and 1200°C has been studied by thermogravimetric methods, optical metallography, electron probe microanalysis, and scanning electron microscopy. The addition of 1 % Al to Co-10% Cr and Co-15% Cr has little effect on the over-all oxidation rate, although there is increased internal oxidation and the outer-inner scale thickness ratio is decreased. The oxidation rate is controlled largely by Co2+ ion diffusion out through the entire scale, with oxygen gas transport across voids, spinel blocking effects and doping in the inner layer probably playing subsidiary roles. With Co-15 %-Cr-1%Al, limited healing by Cr2O3 increases progressively with time at the alloy-oxide interface. An addition of 1 % Al to Co-30 %Cr assists the formation of an initially protective Cr2O3-rich surface layer by internally oxidizing, thereby allowing more of the chromium to diffuse to the surface and form an external scale. This Cr2O3 layer tends to lift and crack open, enabling CoO-rich scales to form on the exposed alloy. Co-15%Cr-4.5% Al produces a protective α-Al2O3 layer on certain surface regions, sometimes with an overlying Cr2O3 layer and internal α-Al2O3 particles in the underlying alloy. In other regions, rapidly growing CoO-rich nodules develop from the outset, or after early lifting and fracture of the α-Al2O3 scale. Generally, the presence of 28% Cr and 4.5% Al is sufficient to ensure an external scale of α-Al2O3, the chromium acting as an oxygen “getter.” If such scale fractures, healing is very rapid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Caplan and M. Cohen,J. Electrochem. Soc. 108, 438 (1961).
A. Preece and G. Lucas,J. Inst. Metals 81, 219 (1952).
A. Davin, D. Coutsouradis, and L. Habraken,Ind. Chim. Belge 32, 446 (1967).
A. Davin, D. Coutsouradis, and L. Habraken,Cobalt 35, 69 (1967).
G. C. Wood and D. P. Whittle,Corrosion Sci. 4, 263 (1964).
F. H. Stott, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester, July (1970).
G. C. Wood,Oxidation of Metals 2, 11 (1970).
F. H. Stott, G. C. Wood, and M. G. Hobby,Oxidation of Metals 3, 103 (1971).
G. C. Wood, F. H. Stott, and B. Chattopadhyay, Extended Abstracts, Fall Meeting of the Electrochemical Society, Atlantic City, October, 1970, p. 282.
G. R. Wallwork and A. Z. Hed, Ref. 9, p. 287.
Metals and Materials,4, 389 (1970).
F. H. Stott and G. C. Wood, submitted toCorrosion Sci.
G. C. Wood and F. H. Stott, submitted toBrit. Corrosion J.
G. C. Wood and T. Hodgkiess,J. Electrochem. Soc. 113, 319 (1966).
M. G. Hobby and G. C. Wood,Metallurgia 75, 143 (1967).
I. G. Wright, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester, 1969.
G. C. Wood, I. G. Wright, T. Hodgkiess, and D. P. Whittle,Werkstoffe Korrosion 21, 900 (1970).
P. K. Kofstad and A. Z. Hed,J. Electrochem. Soc. 116, 224, 229, 1543 (1969).
D. P. Whittle, D. J. Evans, D. B. Scully, and G. C. Wood,Acta Met. 15, 1421 (1967).
G. C. Wood and B. Chattopadhyay,Corrosion Sci. 10, 471 (1970).
B. Chattopadhyay and G. C. Wood,Oxidation of Metals 2, 373 (1970).
G. C. Wood and F. H. Stott, unpublished work.
C. Wagner,Corrosion Sci. 5, 751 (1965).
D. L. Douglass and J. S. Armijo,Oxidation of Metals 2, 207 (1970).
V. R. Howes,Corrosion Sci. 8, 221 (1968);10, 99 (1970).
E. A. Gulbransen and K. F. Andrew,J. Electrochem. Soc. 106, 294 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, G.C., Stott, F.H. The influence of aluminum additions on the oxidation of Co-Cr alloys at 1000 and 1200°C. Oxid Met 3, 365–398 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614630
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614630