Summary
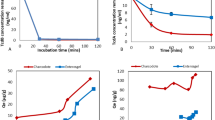
The claim that activated charcoal should be ineffective or even contraindicated in intoxication due to tolbutamide is based only on limited in vitro studies. To test the claim, the effect of activated charcoal 50 g on the absorption of tolbutamide and, as a reference, of sodium valproate, was studied in 6 healthy volunteers. Each volunteer swallowed tolbutamide 500 mg and sodium valproate 300 mg with 50 ml water 1 h after a light breakfast, and within 5 min they took in randomized order either a suspension of activated charcoal or water. The absorption of tolbutamide, calculated as the peak concentration and the area under the serum drug concentration-time curve during 0–48 h, was reduced by 90% by charcoal (p<0.001). The absorption of valproate in these conditions was reduced on average by 65% (p<0.01). In each subject charcoal had a greater effect on the absorption of tolbutamide than of valproate. According to these findings and preliminary in vitro studies on other sulphonylureas high doses of activated charcoal can be recommended for the preventing the absorption of sulphonylureas in acute intoxications. The poor aqueous solubility of these substances at the gastric pH probably delays their gastrointestinal absorption, so that they may be adsorbed on to charcoal even given several hours later.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah AH, Tye A (1967) A comparison of efficacy of emetic drugs and stomach lavage. Am J Dis Child 113: 571–575
Andersen AH (1947) Experimental studies on the pharmacology of activated charcoal. II. The effect of pH on the adsorption by charcoal from aqueous solutions. Acta Pharmacol 3: 199–218
Boyd JR (1982) Drug facts and comparisons. JB Lippincott, Philadelphia-Toronto, p 1839
Cooney DO (1980) Activated charcoal, antidotal and other medical uses. Marcel Dekker, New York Basel, p 85
Decker WJ, Combs HF, Corby DG (1968) Adsorption of drugs and poisons by activated charcoal. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 13: 454–460
Decker WJ, Shpall RA, Corby DG, Combs HF, Payne CE (1969) Inhibition of aspirin absorption by activated charcoal and apomorphine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 4: 710–713
Editorial (1979): Medicoal (effervescent activated charcoal) in the treatment of acute poisoning. Drug Therap Bull 17: 7–8
Hayden JW, Comstock EG (1975) Use of activated charcoal in acute poisoning. Clin Toxicol 8: 515–533
Holt LE Jr, Holz PH (1963) The black bottle. J Pediatr 63: 306–314
Matthew H, Mackintosh TF, Tompsett SL, Cameron JC (1966) Gastric aspiration and lavage in acute poisoning. Br Med J 1: 1333–1337
Neuvonen PJ, Elfving SM, Elonen E (1978) Reduction of absorption of digoxin, phenytoin and aspirin by activated charcoal in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13: 213–218
Neuvonen PJ, Elonen E (1980) Effect of activated charcoal on absorption and elimination of phenobarbitone, carbamazepine and phenylbutazone in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17: 51–57
Neuvonen PJ, Tokola O, Vartiainen M (1982) Comparison of activated charcoal and ipecac syrup in prevention of drug absorption. Clin Pharmacol Ther 31: 255–256
Raghow G, Meyer MC (1981) High-performance liquid chromatographic assay of tolbutamide and carboxytolbutamide in human plasma. J Pharm Sci 70: 1166–1168
Vale JA, Meredith TJ (1981) Poisoning — diagnosis and treatment. Update Books, London Dordrecht Boston, p 187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuvonen, P.J., Kannisto, H. & Hirvisalo, E.L. Effect of activated charcoal on absorption of tolbutamide and valproate in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24, 243–246 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613825
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613825