Abstract
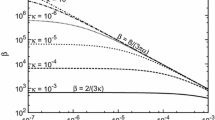
The permeability tensor of a fractured reservoir, which will typically be anisotropic because of the presence of stress, is an important parameter to be taken into account when formulating a production strategy for the reservoir. Extensive computational effort is involved in calculating the permeabilities of model fracture systems by solving the fluid flow equations through finite realisations of the systems, and this renders a search for alternative techniques worthwhile. An attractive approach is to perform a rough mapping of the fracture system onto a lattice so that effective medium theory can be applied. For isotropic systems that are well-connected, this technique works well, but it gives increasingly poor results as the degree of anisotropy increases. In this contribution, a refinement of the lattice mapping is presented that incorporates an important aspect of the randomness present in the original system. This greatly increases the applicability of the technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baecher, G. B., Lanney, N. A., and Einstein, H. H., 1977, Statistical descriptions of rock properties and sampling,Proc. 18th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics, vol. 5C1, pp. 1–8.
Bernasconi, J., 1974, Conduction in anisotropic disordered systems: effective medium theory,Phys. Rev. B9, 4575–4579.
Englman, R., Gur, Y., and Jaeger, Z., 1983, Fluid flow through a crack network in rocks,J. Appl. Mech. 50, 707–711.
Harris, C. K., 1990, Application of generalised effective-medium theory to transport in porous media,Transport in Porous Media 5, 517–542.
Hestir, K. and Long, J. C. S., 1990, Analytical expressions for the permeability of random two-dimensional Poisson fracture networks based on regular lattice percolation and equivalent media theories,J. Geophys. Res. 95, 21565–21581.
Long, J. C. S., Remer, J. S., Wilson, C. R., and Witherspoon, P. A., 1982, Porous media equivalents for networks of discontinuous fractures,Water Resour. Res. 18, 645–658.
Long, J. C. S. and Witherspoon, P. A., 1985, The relationship of the degree of interconnection to permeability in fracture networks,J. Geophys. Res. 90, 3087–3098.
Robinson, P. C., 1984, Connectivity of fracture systems — a percolation theory approach, DPhil Thesis, Univ. of Oxford, U.K.
Sayers, C. M., 1990, Stress-induced fluid flow anisotropy in fractured rock,Transport in Porous Media 5, 287–297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, C.K. Effective-medium treatment of flow through anisotropic fracture system — Improved permeability estimates using a new lattice mapping. Transp Porous Med 9, 287–295 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611972
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611972