Summary
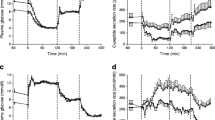
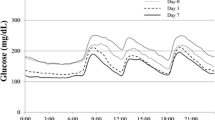
Ten Type 2 diabetics were examined during long-term treatment, at two dosage levels, with chlorpropamide once daily and glipizide t.i.d. Drug concentrations were measured by gas chromatography and high-pressure liquid chromatography, respectively, plasma insulin (IRI) by radio-immunoassay, and blood glucose enzymatically. Both drugs gave continuous sulfonylurea exposure, even at the lower dosage, and the mean plasma concentrations were almost doubled after the increase in dose. Neither the IRI nor the glucose response to meals showed any therapeutic improvement following the increase in chlorpropamide dosage. The lower dosage of glipizide produced better glucose utilization than chlorpropamide. On the other hand, the increased dose of glipizide led to impairment instead of further improvement. As this was associated with enhanced rather than reduced IRI levels, the impairment might have been due to increased peripheral insulin resistance. Thus, glipizide offers a therapeutic advantage over chlorpropamide, but its effectiveness may be restricted not only by limitations set by the disease, but also by counter-regulatory mechanisms that develop during continuous exposure to sulfonylureas at high levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melander A, Sartor G, Wåhlin E, Scherstén B, Bitzén P-O (1978) Serum tolbutamide and chlorpropamide concentrations in patients with diabetes mellitus. Br Med J 1:142–144
Sartor G, Melander A, Scherstén B, Wåhlin-Boll E (1980) Serum glibenclamide in diabetic patients, and influence of food on the kinetics and effects of glibenclamide. Diabetologia 18:17–22
Bergman U, Christenson I, Jansson B, Wiholm BE, Östman J (1980) Wide variation in serum chlorpropamide concentration in out-patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18:165–169
Sartor G, Melander A, Scherstén B, Wåhlin-Boll E (1980) Comparative single-dose kinetics and effects of four sulfonylureas in healthy volunteers. Acta Med Scand 208:301–307
Lebovitz HE, Feinglos MN, Bucholtz HK, Lebovitz FL (1977) Potentiation of insulin action: A probable mechanism for the anti-diabetic action of sulfonylurea drugs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 45:601–604
Beck-Nielsen H, Pedersen O, Lindskov HO (1979) Increased cellular sensitivity and cellular insulin binding in obese diabetics following treatment with glibenclamide. Acta Endocrinol 90:451–462
Almér L-O, Johansson E, Melander A, Wåhlin-Boll E (1982) Influence of sulfonylurea on the secretion, disposal and effect of insulin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22:26–31
Coburn HJ, Carrol JJ (1973) Improved manual and automated colorimetric determination of serum glucose, with use of hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Clin Chem 19:127–130
Wide L, Axén R, Porath J (1967) Radioimmunosorbent assay for proteins. Immunochemistry 4:381–386
Prescott LF, Redman DR (1972) Gas liquid chromatographic estimation of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide in plasma. J Pharm Pharmacol 24:713–716
Wåhlin-Boll E, Melander A (1979) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of glipizide and some other sulfonylurea drugs in serum. J Chromatogr 164:541–546
Tanese T, Lazarus NR, Devrim S, Recant L (1979) Synthesis and release of proinsulin and insulin by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest 49:1349–1404
Dunbar JC, Foa PP (1974) An inhibitory effect of tolbutamide and glibenclamide (glyburide) on the pancreatic islets of normal animals. Diabetologia 10:27–35
Olefsky JM (1976) Decreased insulin binding to adipocytes and circulating monocytes from obese subjects. J Clin Invest 57:1165–1172
Smith U (1980) Regulation of the number of insulin receptors in human fat cells. Acta Endocrinol Suppl 239:19–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wåhlin-Boll, E., Sartor, G., Melander, A. et al. Impaired effect of sulfonylurea following increased dosage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22, 21–25 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606420
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606420