Abstract
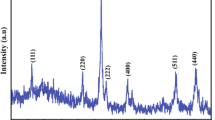
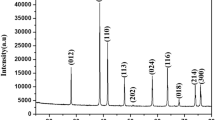
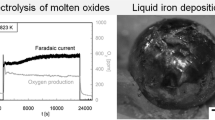
The oxidation characteristics of iron containing about 0.27% of carbon at room temperature in laboratory atmosphere are described. In general, the oxide film thickness increases logarithmically with time. Except for films of thickness greater than about 10Å, several breaks have been found in the oxidation curve. These breaks can be explained as due to the compressional stress developed in the film, and this stress is modified by the thickness and structure of the vapor-deposited films. Application of a positive potential to the film increases the oxidation rate, whereas a negative potential decreases the rate. All these observed results are explained based on the Fehlner-Mott theory and suggest that the growth of ferric oxide is due to the diffusion of oxygen ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. B. Pfeil,J. Iron Steel Inst. 119, 501 (1929).
U. R. Evans,The Corrosion and Oxidation of Metals (Edwin Arnold, London, 1960) Chap. 2.
D. Eurof Davies and U. R. Evans,J. Chem. Soc. 4373 (1956).
M. Cohen,J. Electrochem. Soc. 121, 191C (1974).
Brian Cox,Oxid. Met. 3, 529 (1971).
T. Mills and U. R. Evans,J. Chem. Soc. 2182 (1956).
H. H. Uhlig,Acta Metall. 4, 541 (1956).
E. C. Williams and P. C. S. Hayfield,Vacancies and Other Point Defects in Metals and Alloys (Institute of Metals, London, 1958), p. 131.
H. H. Uhlig, J. Pickett, and J. MacNairn,Acta Metall. 7, 111 (1959).
Tor Hurlen,J. Inst. Met. 89, 128 (1960–1961).
A. B. Winterbottom,Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 76, 326 (1939).
Kenneth R. Lawless,Rep. Prog. Phys. 37, 271 (1974).
F. P. Fehlner and N. F. Mott,Oxid. Met. 2, 59 (1970).
N. Cabrera and N. F. Mott,Rep. Prog. Phys. 12, 163 (1948–49).
B. E. Warren,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 21, 259 (1938);J. Appl. Phys. 13, 603 (1942).
D. D. Eley and P. R. Wilkinson,Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A:254, 327 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhavani, K., Vaidyan, V.K. Oxidation of iron and influence of an electric field at room temperature. Oxid Met 15, 137–145 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603758
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603758