Abstract
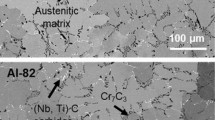
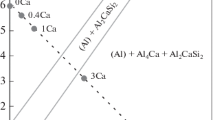
The scaling behavior of an iron alloy containing 5 wt. % aluminum has been assessed (involving kinetic, metallographic, x-ray diffraction, and electron probe microanalysis studies) in sulfur vapor at 10 ton in the range 500–700°C. For comparison purposes similar experiments were also performed with pure iron. The reaction kinetics observed with the alloy were linear after an initial short period of exposure during which the kinetics were parabolic. Parabolic kinetics, however, were exhibited over the entire period of sulfidation by the pure iron, and the overall rate of sulfidation of the iron was an order of magnitude greater than that of the alloy at all temperatures. Duplex scales were formed both on the alloy and the iron after prolonged periods of exposure. However, whereas the nature and composition of the outer layer of scale formed from both materials was similar, the inner layer of scale on the alloy was significantly different from that grown on the pure iron, both morphologically and in composition containing Al2S3 in addition to FeS. The probable mechanism of sulfidation of the alloy is discussed in relation to current theories regarding the behavior of pure iron.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
O. Kubaschewski and B. E. Hopkins,The Oxidation of Metals and Alloys (Butterworths, London, 1962), p. 234.
W. C. Hagel,Corrosion 21, 316 (1965).
K. N. Strafford, The sulphidation of metals and alloys,Metallurgical Rev. (1969), to be published.
F. Smith, I.C.I. Ltd., Widnes, private communication.
T. Murakami and K. Nagasaki,Nippon Kinzoku Gakkai-Si 4, 221 (1940).
R. B. Setterlund and G. R. Prescott,Corrosion 17, 277t (1961).
F. K. Naumann,Chemische Fabrik 11, 31 (1938).
K. N. Strafford and R. Manifold.Corrosion Sci. (1969), to be published.
J. A. von Fraunhofer and G. A. Pickup,Corrosion Sci. 7, 379 (1967).
K. Hauffe and A. Rahmel,Z. Physik. Chem. 199, 152 (1952).
P. V. Geld and A. K. Krasovskaya,Zh. Fiz. Khim. 34, 1585 and 1721 (1960).
H. Arm, P. Delahay, C. Hudgins, F. Hügli, L. D. Hulett, Jr., and M. Qureshi,J. Electrochem. Soc. 107, 264 (1960).
W. D. Kingery, ed.,Kinetics of High Temperature Processes (Wiley, New York, 1959), p. 97.
A. Bruckman,Corrosion Sci. 7, 51 (1967).
A. Bruckman and J. Romanski,Corrosion Sci. 5, 185 (1965).
J. Romanski,Corrosion Sci. 8, 67, 89 (1968).
S. Mrowec,Corrosion Sci. 7, 563 (1967).
G. C. Wood, I. G. Wright, and J. M. Ferguson,Corrosion Sci. 5, 645 (1965).
C. Wagner,J. Electrochem. Soc. 103, 627 (1956).
S. Mrowec, K. Wallischowa, and T. Werber,Roczniki Chem. 34, 337 (1960).
I. A. Menzies and K. N. Strafford,J. Mater. Sci. 2, 358 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strafford, K.N., Manifold, R. The scaling behavior of an iron-5% aluminum alloy in sulfur vapor. Oxid Met 1, 221–240 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603517
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603517