Abstract
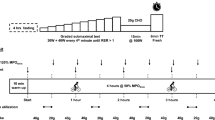
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects on physical performance of three levels of energy intake during a 5-day period of prolonged physical exercise and relative sleep deprivation. A group of 27 male soldiers were randomly assigned to three groups receiving either 1800 kcal · 24 h−1 (7560 kJ, LC), 3200 kcal · 24h−1 (13440 kJ, MC) or 4200 kcal-24h−1 (17640 kJ, HC). They took part in a 5-day combat course (CC) of heavy and continuous physical activities, with less than 4 h sleep per day. Performance capacity was tested just before and at the end of CC. Maximal oxygen uptake (\(\dot V\)O2max) was determined during an exhausting incremental exercise test on a cycle ergometer. Anaerobic performance was measured from the time during which exercise could be maintained at supra maximal loads on a cycle ergometer. After CC, the subjects receiving LC exhibited a 14% decrease in power output at exhaustion in the incremental exercise test [from 325 (SEM 8) to 278 (SEM 9) W,P < 0.001] and a significant decrease in\(\dot V\)O2max of 8% [from 3.74 (SEM 0.06) to 3.45 (SEM 0.05) l · min−1,P<0.05]. The remaining two experimental groups demonstrated the same mechanical and metabolic performances on days 1 and 5. Anaerobic performance was not influenced by energy intake and the field course. Blood samples were obtained at rest on days 1 and 5. At the end of CC, the data demonstrated a significant decrease in blood glucose concentrated ion (P<0.01) for LC diet only. Plasma free fatty acid, blood glycerol and β-OH butyrate were significantly increased in all groups, from day 1, but the values observed for LC were higher than those for the MC and HC diets. The concentrations of the anabolic hormones, insulin and testosterone, decreased in the three groups, the lowest values being observed in the LG group (P < 0.05). In conclusion, we found that only a severe energy deficit decreased physical performance during submaximal exercise. A moderate deficit between energy intake and expenditure did not affect performance. Supramaximal exercise did not appear to be influenced by energy intake and CC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aakvag A, Bentdal O, Quigstad K, Walstad P, Rondengen H, Fonnum H (1978) Testosterone and testosterone binding globulin (TeBG) in young men during prolonged stress. Int J Androl 1:22–31
Bahr R, Opstad PK, Medbo JI, Sejersted OM (1991) Strenuous prolonged exercise elevates testing metabolic rate and causes reduced mechanical efficiency. Acta Physiol Scand 141:555–63
Bergmeyer H (1963) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag chimic. Academic Press, New York, p 360
Bergstrom J, Hermansen L, Hultman E, Saltin B (1967) Diet, muscle glycogen and physical performance. Acta Physiol Scand 71:140–150
Bigard AX, Satabin P, Lavier P, Canon F, Taillandier D, Guezennec CY (1993) Effect of protein supplementation during prolonged exercise at moderate altitude on performance and plasma amino acid pattern. Eur J Appl Physiol 66:5–10
Brue F, Montmayeur A, Melin B, Bagot L (1981) Determination of the differential aerobic and anaerobic fitness in various sports using a new mechanical cycle ergometer. Can J Appl Sport Sci 11:17–24
Chaouloff F, Elghozi JL, Guezennec CY, Laude D (1985) Effects of conditioned running on plasma, liver and brain tryptophan on brain 5 hydroxytryptamine metabolism of the rat. Br J Pharmacol 86:33–41
Delany JP, Shoeller DA, Hoyt RW, Askew EW, Sharp MA (1989) Field use of D2180 to measure energy expenditure of soldiers at different energy intakes. J Appl Physiol 67:1922–1929
Dohm GL, Becker RT, Israel RG, Tapscott EB (1986) Metabolic responses to exercise after fasting. J Appl Physiol 61:1363–1368
Dohm GL, Tapscott EB, Kasperek GJ (1987) Protein degradation during endurance exercise and recovery. Med Sci Sports Exerc 19:166–171
Gleeson M, Greenhaff PL, Maughan RJ (1988) Influence of a 24 h fast on high intensity cycle exercise performance in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:653–659
Greenhaff CL, McCormick K, Maughan MJ (1987) The metabolic response to prolonged walking in fed and fasted men. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:115–119
Guezennec CY, Ferre P, Serrurier B, Merino D, Pesquies PC (1982) Effects of prolonged physical exercise and fasting upon plasma testosterone level in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 49:159–168
Guezennec CY, Ferre P, Serrurier B, Merino D, Aymonod M, Pesquies PC (1984a) Metabolic effects of testosterone during prolonged physical exercise and fasting. Eur J Appl Physiol 52:300–304
Guezennec CY, Serrurier B, Aymonod M, Merino D, Pesquies PC (1984b) Metabolic and hormonal response to short term fasting after endurance training in the rat. Horm Metab Res 16:572–575
Hultman E (1967) Physiological role of muscle glycogen in man with special reference to exercise. Circ Res 20-21 [Suppl 1]:1–99 to 1–112
Hultman E, Nilson LH (1971) Liver glycogen in man. Effect of different diets and muscular exercise. Adv Exp Med Biol 11:143–147
Knapik JJ, Jones BH, Meredith C, Evans WJ (1987) Influence of a 3.5 day fast on physical performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:428–432
Loy SF, Conlee RK, Winder WW, Nelson AG, Arnell DA, Fisher AG (1986) Effects of a 24 hour fast on cycling endurance time at two different intensities. J Appl Physiol 61:654–659
Marniemi J, Vuori I, Kinnunen V, Rahlika P, Vainikka M, Peltonon P (1984) Metabolic changes induced by combined prolonged exercise and low calorie intake in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:121–127
Maughan RJ, Greenhaff PL, Gleeson M, Fenn CE, Leiper JB (1987) The effect of dietary carbohydrate intake on the metabolic response to prolonged walking on consecutive days. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:583–591
Opstad PK, Aakvaag A (1981) The effect of a high calorie diet on hormonal changes in young men during prolonged physical strain and sleep deprivation. Eur J Appl Physiol 46:31–39
Parry-Billing M, Budgett R, Kontedakis Y, Blomstrand E, Brooks S, Williams C, Calder C, Pilling S, Baigrie R, Newsholme EA (1992) Plasma amino acid concentrations in the overtraining syndrome: possible effects on the immune system. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:1353–1358
Rognum TO, Vaage O, Hostmark A, Opstad PK (1981) Metabolic responses to bicycle exercise after several days of physical work and energy deficiency. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 412:565–571
Satabin P, Portero P, Defer G, Bricout J, Guezennec CY (1987) Metabolic and hormonal responses to lipid and carbohydrate diets during exercise in man. Med Sci Spors Exerc 19:218–223
Symons JP, Jacobs I (1989) High intensity exercise performance is not impaired by low intramuscular glycogen. Med Sci Sports Exerc 21:550–557
Walberg JL, Leidy MK, Sturgill DJ, Hinkle DE, Ritchey SJ, Sebolt DR (1988) Macronutrient content of a hypoenergy diet affects nitrogen retention and muscle function in weight lifters. Int J Sports Med 9:261–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guezennec, C.Y., Satabin, P., Legrand, H. et al. Physical performance and metabolic changes induced by combined prolonged exercise and different energy intakes in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 68, 525–530 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00599524
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00599524