Abstract
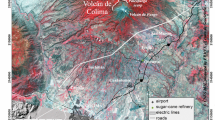
Volcanic hazards from Pico de Orizaba volcano are presented here tor the first time. Some 1.3 million people live within the hazard zone, which in the most severe case would encompass the Mexican Gulf coast, east of the volcano. Three major cities located in the eastern part of the hazard zone account for 800 000 of this population and about 200 000 people live within a 20 km radius of the volcano. Probability calculations are presented as an attempt to quantify the hazards in the surroundings of the volcano. Such quantification can be of use in planning for future land use within the hazard zones.
A zone of about 10 km radius centred on the top crater is a high hazard zone for gravity-driven flows and fallout ejecta. For large volume eruptions, the radius could be extended to 120 km to the east and 60 km to the west. The asymmetrical distribution is related to the topography of the volcano. Hazards from Pyroclastic-fall deposits are principally to the west of the volcano, since easterly winds are dominant in the area lava-flow hazards are greatest within a 10 km radius from the summit crater. Pyroclastic flow hazards are high up to 20 km from the volcano summit.
In the case of reactivation of the volcano, melting of a glacier covering the summit of Pico de Orizaba having a volume equivalent to some 45 × 109 litres of water, would produce lahars which would descend the flanks of the volcano.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blong, R. J.: 1984,Volcanic Hazards, a Source Book on the Effects of Eruptions, Academic Press, Sydney.
Borgia, A. and Linneman, S. R.: 1990, On the mechanisms of lava flow emplacement and volcano growth: Arenal, Costa Rica, in J. H. Fink (ed.),Lava Flows and Domes: Emplacement Mechanism and Hazard Implications, IAVCEI, Proceedings in Volcanology 2, Springer, Berlin.
Crandell, D. R. and Hoblitt, R. P.: 1986, Lateral blasts at Mount St. Helens and hazard zonation,Bull. Volcanol. 48, 27–37.
Fisher and Schmincke, H-.U., 1984,Pyroclastic Rocks, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Gringorten, I. I.: 1963, A rule for extreme probability paper,J. Geophys. Res. 68, 813–814.
Höskuldsson, A.: 1992, Le complexe volcanique Pico De Orizaba-Sierra Negra-Cerro Las Cumbres (Sud-Est Mexicain): Structure, dynamismes eruptifs et évaluations des aléas. Thèse de Doctorat d'Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont Ferrand.
Höskuldsson, A. and Robin, C.: 1993, Late Pleistocene to Holocene eruptive history of Pico de Orizaba, Eastern Mexico,Bull. Volcanol. 53(8), 571–587.
INEGI: 1991,Resultatos Preliminares: XI Censo General de Poblacion y Vivienda, 1990, Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Información, Mexico.
Paterson, W. S. B.: 1981,The Physics of Glaciers, Pergamon Press, New York.
Pierson, T. C. and Scott, K. M.: 1985, Downstream dilution of lahar-transition from debris flow to hyperconcentrated streamflow,Water Resour. Res. 21, 1511–1524.
Scott, W. E.: 1989, Volcanic and related hazards, in R. I. Tilling (ed.),Volcanic Hazards, American Geophysical Union, Washington, pp. 9–24.
Sheridan, M. F.: 1979, Emplacement of pyroclastic flows. A review, in C. E. Chopin and W. E. Elston (eds.),Ash Flow Tuffs, Am. Geol. Soc. Spec. paper 180, pp. 125–136.
Siebert, L.: 1984, Large volcanic debris avalanches: Characteristics of source areas, deposits and associated eruptions,J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 22, 163–197.
Siebert, L., Glicken, H., and Ui, T.: 1987, Volcanic hazards from Bezymianny and Bandai type eruptions,Bull. Volcanol. 49, 453–459.
Simkin, T., Siebert, L., McClelland, L., Bridge, D., Newhall, C., and Latter, J. H.: 1981,Volcanoes of the World. A Regional Directory Gazetteer and Chronology of Volcanism During the Last 10,000 years. Smithsonian Institution, Stroudsbourg, Pennsylvania, Hutchinson & Ross.
Sparks, R. S. J.: 1976, Grain size variations in ignimbrites and implications for the transport of pyroclastic flows,Sedimentology 23, 147–188.
Sparks, R. S. J., Wilson, L., and Hulme, G.: 1978, Theoretical modelling of the generation, movement and emplacement of pyroclastic flows by column collapse,J. Geophys. Res. 83, 1727–1739.
Swanson, D. A. and Christiansen, R. I.: 1973, Tragic base surge in 1790 at Kilauea volcano,Geology 1, 83–86.
Tilling, R. I.: 1989, Volcanic hazards and their mitigation: Progress and Problems,Rev. Geophys. 27, 237–269.
UNAM, 1974,Precipitacion y probabilidad de la lluvia en la republica Mexicana y su Evaluacion, Instituto Geografica UNAM, Mexico.
Ui, T. and Glicken, H.: 1986, Internal structure variations in a debris avalanche deposits from ancestral Mount Shasta, California, U.S.A.,Bull. Volcanol. 48, 189–194.
Ui, T., Ymamoto, H., and Suzuki-Kamata, K.: 1986, Characterization of debris avalanche deposits in Japan,J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 29, 231–243.
Wadge, G.: 1978, Effusion rates and shape of lava flow-fields on Mount Etna,Geology 6, 503–506.
Wilson, E. M.: 1984,Engineering Hydrology, MacMillan, London.
Wilson, L.: 1980, Relationships between pressure, volatile content and ejecta velocity in three types of volcanic explosion,J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 8, 297–313.
Wilson, L., Pinkenon, H., and Macdonald, R.: 1987, Phycical processes in volcanic eruptions,Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 15, 73–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Höskuldsson, Á., Cantagrel, J.M. Volcanic hazards in the surroundings of Pico de Orizaba, eastern Mexico. Nat Hazards 10, 197–219 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00596142
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00596142