Abstract
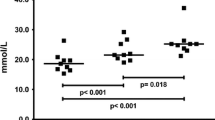
The effects of 30 min running with stepwise increasing intensity (exhaustive, energy demand approx. 50 → 100% ofVO2max), 60 s supramaximal running (anaerobic, ≥125% ofVO2max) and 40–60 min low-intensity running (acrobic, 40–60% ofVO2max) on serum concentration of muscle-derived proteins were studied in 5 male and 5 female elite orienteerers. S-Carbonic anhydrase III (S-CA III) was used as a marker of protein leakage from type I (slow oxidative) muscle fibres and S-myoglobin (S-Mb) as a non-selective (type I+II) muscular marker. The fractional increase in S-CA III (ΔS-Ca III) was 0.37±0.09 (mean±SEM,p<0.001), 0.10±0.05 (N. S.) and 0.46±0.09 (p<0.001) 1 h after exhaustive, anaerobic and aerobic exercise, respectively. The corresponding values for ΔS-Mb were 1.45±0.36 (p<0.001), 0.39±0.13 (p<0.01) and 0.67±0.18 (p<0.001). The value for the ΔS-CA III/ΔS-Mb ratio was 0.68±0.03 after the acrobic exercise, but only 0.25–0.26 (p vs. aerobic exercise <0.001) after the two high-intensity forms of exercise. Since type I fibres of skeletal muscle are known to be responsible for power production during low-intensity exercise, whereas fibres of both type I and type II are active at higher intensities, the ΔS-CA III/ΔS-Mb ratio may depend on the recruitment profile of type I vs. type I+II fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph L, Lorenz A (1982) Enzyme diagnosis in diseases of the heart, liver and pancreas. Karger, Basel New York
Armstrong RB (1986) Muscle damage and endurance events. Sports Med 3:370–381
Carter N, Jeffery S, Shiels A, Edwards Y, Tipler T, Hopkinson DA (1979) Characterization of human carbonic anhydrase III from skeletal muscle. Biochem Genet 17:837–854
Carter ND, Heath R, Jeffry S, Jackson MJ, Newham DJ, Edwards RHT (1983) Carbonic anhydrase III in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Chim. Acta 133:208–210
Durnin J, Rahaman M (1967) The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurement of skinhold thickness. Br J Nutr 21:681–689
Galun E, Epstein Y (1984) Serum creatine kinase activity following a 120 km march. Clin Chim Acta 1431:281–283
Gimenez M, Florentz M (1984) Serum enzyme variations in men during an exhaustive “square-wave” endurance exercise test. Eur J Appl Physiol 52:219–224
Harms SJ, Hickson RC (1983) Skeletal muscle mitochondria and myoglobin, endurance, and intensity of training. J Appl Physiol 54:798–802
Hikida RS, Straton RS, Hagerman FH, Sherman WM, Costill DL (1983) Muscle fiber necrosis associated with human marathon runners. J Neurol Sci 59:185–203
Jeffery S, Carter ND, Edwards Y (1980) Distribution of CA III in fetal and adult human tissue. Biochem Genet 18:843–849
Jeffry S, Carter ND, Smith A (1987) Thyreidectomy significance after carbonic anhydrase III concentration and fiber distribution in rat muscle. J Histochem Cytochem 35:663–668
Magazanik A, Shapiro Y, Meyfes I (1974) Enzyme blood levels and water balance during a marathon race. J Appl Physiol 36:214–217
Noakes TD (1987) Effect of exercise on serum enzyme activities in humans. Sports Med 4:245–267
Osterman PO, Askmark H, Wistrand PJ (1985) Serum carbonic anhydrase III in neuromuscular disorders and in healthy persons after a long-distance run. J Neurol Sci 70:347–357
Salminen A, Vihko V (1983) Suspectibility of mouse skeletal muscles to exercise injuries. Muscle Nerve 6:596–601
Saltin B, Gollnick PD (1983) Skeletal muscle adaptability: significance for metabolism and performance. In: Beachey CD (ed) Handbook of physiology, section 10, skeletal muscle. American Physiol Society, Bethesda, MD
Shephard RJ (1982) Physiology and biochemistry of exercise energy transducers. Preager Publishers, New York, pp 95–134
Shiels A, Jeffry S, Wilson C, Carter N (1984) Radio-immunoassay of carbonic anhydrase III in rat tissues. Biochem J 218:281–284
Shima K, Tashiro K, Hibi N, Tsukosia Y, Hirai Y (1983) Carbonic anhydrase III. Immunohistochemical localization in human skeletal muscle. Acta Neuropathol 59:237–239
Väänänen HK, Kumpulainen T, Korhonen LK (1982) Carbonic anhydrase in the type I skeletal muscle fibers of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 30:1109–1113
Väänänen HK, Paloniemi M, Vuori J (1985) Purification and localization of human carbonic anhydrase III. Typing of skeletal muscle fibers in paraffin embedded section. Histochemistry 83:231–235
Väänänen HK, Leppilampi M, Vuori J, Takala TES (1986) Liberation of muscle carbonic anhydrase into serum during extensive physical exercise. J Appl Physiol 61(2):561–564
Väänänen HK, Takala T, Morris DC (1986) Immunoelectron microscopic localization of carbonic anhydrase III in rat skeletal muscle. Histochemistry 86:175–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takala, T.E.S., Rahkila, P., Hakala, E. et al. Serum carbonic anhydrase III, an enzyme of type I muscle fibres, and the intensity of physical exercise. Pflugers Arch. 413, 447–450 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00594171
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00594171