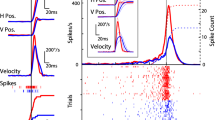
Summary
The stimulus correlated discharge periodicities of single neurons described in the literature for all parts of the acoustic channel below the geniculatum mediale were confirmed for the colliculus inferior. Furthermore a quite different kind of discharge periodicity in the geniculatum mediale is reported. With these results structure models are given for the neuronal temporal measurement of coincidence. Finally a possibility of discrimination between intra-modality-specific and intra-modality-nonspecific processing mechanism is shown.
Zusammenfassung
Die in der Literatur für alle Teile der Hörbahn unterhalb des Geniculatum mediale beschriebenen reizkorrelierten Entladungsperiodizitäten einzelner Neurone wurden für den Colliculus inferior bestätigt. Darüber hinaus wird über eine ganz andersartige Entladungsperiodizität im Geniculatum mediale berichtet. Davon ausgehend werden Strukturmodelle für die neuronale zeitliche Koinzidenzmessung angegeben. Schließlich wird auf eine Unterscheidungsmöglichkeit von intramodalitätsspezifischen und intramodalitätsunspezifischen neuronalen Verarbeitungsmechanismen hingewiesen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Békésy, G. v.: Synchronism of neural discharges and their demultiplication in pitch perception on the skin and in hearing. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.31, 338 (1959).
— Hearing theories and complex sounds. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.35, 588–601 (1963).
David, E., P. Finkenzeller, S. Kallert, u.W. D. Keidel: Die Bedeutung der temporalen Hemmung im Bereich der akustischen Informationsverarbeitung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.298, 322–335 (1968a).
————: Die Bed Mikroelektroden ableitbare Reaktion einzelner Elemente des colliculus inferior und des corpus geniculatum mediale auf akustische Reize verschiedener Form und verschiedener Intensität. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.299, 83–93 (1968b).
Derbyshire, A. J., andH. Davis: The action potentials of the auditory nerves. Amer. J. Physiol.113, 476–504 (1935).
Galambos, R., andH. Davis: Inhibition of activity in single auditory nerve fibers by acoustic stimulation. J. Neurophysiol.7, 287–303 (1944).
—, andH. Davis: The response of single nerve fibers to acoustic stimulation. J. Neurophysiol.6, 39–58 (1943).
—,J. Schwarzkopff, andA. Rupert: Microelectrode study of superior olivary nuclei. Amer. J. Physiol.197, 527–536 (1959).
Gerard, J. M., W. H. Marshall, andL. J. Saul: Electrical activity of the cat's brain. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.)36, 675–735 (1936).
Goldberg, J. M., andW. D. Neff: Frequency discrimination after bilateral ablation of cortical auditory areas. J. Neurophysiol.24, 119–128 (1961).
——: Frequency discrimination after bilateral section of the brachium of the inferior colliculus. J. comp. Neurol.116, 265–290 (1961/62).
Hilali, S., andI. C. Whitfield: Response of the trapezoid body to acoustic stimulation with pure tones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)122, 158–171 (1953).
Hind, J. E., D. J. Anderson, J. F. Brugge, andJ. E. Rose: Coding of information pertaining to paired low-frequency tones in single auditory nerve fibers of the squirrel monkey. J. Neurophysiol.30, 794–816 (1967).
Katsuki, Y., T. Sumi, H. Uchiyama, andT. Watanabe: Electric responses of auditory neurons in cat to sound stimulation. J. Neurophysiol.21, 569–588 (1958).
Keidel, W. D.: Vibrationsrezeption. Der Erschütterungssinn des Menschen. Erlanger Forschungen, Reihe B, Naturwissenschaften, Bd. 2, Universitätsbund, Erlangen 1956.
—: Informationsphysiologische Aspekte des Hörens. Studium Generale22, 49–82 (1969).
Kemp, H. E., G. E. Coppée, andE. H. Robinson: Electric responses of the brain stem to unilateral auditory stimulation. Amer. J. Physiol.120, 304–315 (1937).
Kiang, N. Y. S., R. R. Pfeiffer, W. B. Warr, andA. S. Backus: Stimulus coding in the cochlear nucleus. Ann. Otol74, 463–484 (1965).
Magoun, H. W.: The waking brain. Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas 1960.
Moushegian, G., A. L. Rupert, andT. L. Langford: Stimulus coding by medial superior olivary neurons. J. Neurophysiol.30, 1239–1261 (1967).
Neff, W. D.: Role of the auditory cortex in sound discrimination. In: Neural Mechanism of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems. Ed.G. L. Rasmussen, W. F. Windle. Capt. 15, pp. 211–216 (1960).
Pfeiffer, R. R.: Classification of response patterns of spike discharges for units in the cochlear nucleus: tone-burst stimulation. Exp. Brain Res.1, 220–235 (1966).
Rose, J. E., J. F. Brugge, D. J. Anderson, andJ. E. Hind: Phase-locked response to low-frequency tones in single auditory nerve fibers of the squirrel monkey. J. Neurophysiol.30, 769–793 (1967).
—N. B. Gross, C. D. Geisler, andJ. E. Hind: Some neural mechanisms in the inferior colliculus of the cat which may be relevant to localization of a sound source. J. Neurophysiol.29, 288–314 (1966).
Rupert, A., G. Moushegian, andR. Galambos: Unit responses to sound from auditory nerve of the cat. J. Neurophysiol.26, 449–465 (1963).
Saul, L. J., andH. Davis: Electrical phenomena of the auditory mechanism. Trans. Amer. otol. Soc.22, 137–145 (1932).
Tasaki, I.: Nerve impulses in individual auditory nerve fibers of guinea pig. J. Neurophysiol.17, 97–122 (1954).
Wever, E. G.: Theory of hearing. New York: Wiley 1949.
—, andG. W. Bray: The nature of the acoustic response: The relation between sound frequency and frequency of impulses in the auditory nerve. J. exp. Psychol.13, 373–387 (1930).
Whitfield, I. C.: Electrophysiology of the central auditory pathway. Brit. med. Bull.12, 105 (1956).
Worden, F. G., andJ. T. Marsh: Frequency-following (microphonic like) neural responses evoked by sound. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.25, 42–52 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, E., Finkenzeller, P., Kallert, S. et al. Reizfrequenzkorrelierte “untersetzte” neuronale Entladungsperiodizität im Colliculus inferior und im corpus geniculatum mediale. Pflugers Arch. 309, 11–20 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592278
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592278