Summary
The inhibition of the actomyosin ATPase-activity and of the production of tension in glycerol extracted muscle fibres (dorsolongitudinal flight muscle ofLethocerus maximus, DLM) by Ca-removal with EGTA depends on the troponintropomyosin-factor system.
This factor can be removed from glycerinated fibrillar-but not from afibrillar-muscle by short extraction with 0.05 MKCl 0.02 M Tris buffer pH 7.5–8.0. Combination of EGTA-insensitive (synthetic) skeletal muscle actomyosin with the extracted factor restores the EGTA-sensitivity.
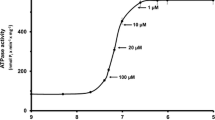
After alkaline extraction of the factor the fibres are able to develop the full contractile tension with MgATP even in the presence of EGTA. Under these conditions the ATPase is equally active as with Ca-ions before extraction. The contractile tension and the ATPase-activity can then be reversibly inhibited by 0.5 M thiourea. This means, that the contractile cycle can be isolated from its control by Ca-ions and the troponin-factor without impairing the development of tension.
After alkaline extraction the fibres have lost their ability to oscillate. They are no longer activated by stretch or deactivated by release. Hence they are able to contract to 30% L0 in the presence of MgATP.
Zusammenfassung
Die Hemmung der ATPase und der Kontraktion durch Entzug von Calciumionen hängt auch bei extrahierten Insektenmuskeln (dorsolongitudinale Flugmuskeln vonLethocerus maximus, DLM) von der Anwesenheit des Troponin-Tropomyosin-Faktors ab.
Der Faktor kann nur aus den fibrillären,—nicht aber aus den afibrillären—, glycerinextrahierten Insektenmuskelfasern durch Tris-KCl-Lösung, Ionenstärke:I } 0,04, schon bei pH 7,5–8,0 extrahiert werden. Mit dem alkalisch extrahierten Faktor gelang es, synthetisches Skeletmuskel-Actomyosin wiedern beeinflußbar durch Calciumionen bzw. EGTA zu machen.
Nach Extraktion des Faktors ist in den fibrillären Muskelfasern die ATPase aktiviert und die Spannungsentwicklung ist mindestens ebenso hoch wie vor alkalischer Extraktion bei maximaler Aktivierung mit Calciumionen.
Die ATP-Kontraktion in extrahierten Fasern kann durch den Interaktions-inhibitor Thioharnstoff (0,5 M) reversibel gehemmt werden. Damit ist erstmalig der Kontraktionsvorgang in glycerinextrahierten Muskelfasern ohne Beeinträchtigung der Spannungsentwicklung von seiner Steuerung durch Calciumionen und den Troponin-Faktor funktionell isoliert worden.
Die alkalisch extrahierten Fasern verlieren ihre Dehnungsaktivierbarkeit und die Fähigkeit zur Oscillation. Auch die Deaktivierung bei Verkürzung und die Kontraktionsbegrenzung bei 80% der Ruhelänge fehlt. Deswegen verkürzen sich die alkalisch extrahierten Fasern bis 30% Ruhelänge.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ashhurst, D. E.: Z-line of the flight muscle of belostomatid water bugs. J. molec. Biol.27, 385–390 (1967).
Brocke, H. H., v.: The activating effects of calcium ions on the contractile systems of insect fibrillar flight muscle. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.290, 70–79 (1966).
Davies, R. E.: A molecular theory of muscle contraction: Calcium-dependent contractions with hydrogen bound formation plus ATP-dependent extensions of part of the myosin-actin cross-bridges. Nature (Lond.)199, 1068–1074 (1963).
Ebashi, S., andM. Endo: Calcium ions and muscle contraction. Progr. biophys. and molec. Biol.18, 123–183 (1968).
—, andF. Ebashi: A new protein component participating in the superprecipitation of myosin B. J. Biochem. (Tokyo)55, 604–613 (1964).
Hartshorne, D. J., S. V. Perry, andM. C. Schaub: A proteinfactor inhibiting the magnesium activated adenosinetriphosphatase activity of desensitized actomyosin. Biochem. J.104, 909–913 (1967).
Hasselbach, W.: Relaxing factor and the relaxation of muscle. Progr. Biophys.14, 169–217 (1964).
Jewell, B. R., andJ. C. Rüegg: Oscillatory contraction of insect fibrillar muscle after glycerol extraction. Proc. roy. Soc. B164, 428–459 (1966).
Maruyama, K., J. W. S. Pringle, andR. T. Tregear: The Ca-sensitivity of ATPase-activity of myofibrills and actomyosin from insect flight and leg muscle. Proc. roy. Soc. B169, 229–240 (1968).
Meinrenken, W.: Besonderheiten der Erschlaffung des isolierten contractilen Apparates von fibrillären (oscillierenden) Insekten-Flugmuskeln. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.294, 45 (1967).
Pringle, J. W. S.: The contractile mechanism of insect fibrillar muscle. Progr. in biophys. molec. Biol.17, 1–60 (1967).
Reedy, M. C., K. C. Holmes, andR.T. Tregear: Induced changes in orientation of the cross-bridges of glycerinated insect flight muscle. Nature (Lond.)207, 1276–1280 (1965).
Rockstein, M., andP. W. Herron: Colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate in microgram quantities. Analyt. Chem.23, 1500–1501 (1951).
Rüegg, J. C.: Oscillatory mechanism in fibrillar insect flight muscle. Experientia (Basel)24, 529–536 (1968).
Schädler, M.: Proportionale Aktivierung von ATPase-Aktivität und Kontraktionsspannung durch Calciumionen in isolierten contractilen Strukturen verschiedener Muskelarten. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.296, 70–90 (1967).
Schaub, M. C., D. H. Hartshorne, andS. V. Perry: The ATPase-activity of desensitized actomyosin. Biochem. J.104, 263–269 (1967).
Weber, A., andS. Winicur: The role of calcium in the superprecipitation of actomyosin. J. biol. Chem.236, 3198–3202 (1961).
Zebe, E., W. Meinrenken u.J. C. Rüegg: Superkontraktion glyzerinextrahierter asynchroner Insektenmuskeln in Gegenwart von ITP. Z. Zellforsch.87, 603–621 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (RU 154/1).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meinrenken, W. Calciumionen-unabhängige Kontraktion und ATPase bei glycerinierten Muskelfasern nach alkalischer Extraktion von Troponin. Pflugers Arch. 311, 243–255 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00590528
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00590528