Summary
The effect, on the endocochlear resting potential (ERP) of anoxemia, cyanide, pH changes and changes of the electrolyte composition of the perilymph was studied.
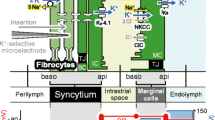
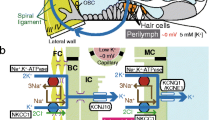
The ERP appears to be composed of two components: a negative potentialE-mainly determined by the K+ gradient between endolymph and perilymph or plasma and a positive potentialE + due to an ouabain- and anoxia-sensitive electrogenic K+ pump represented by the Na+-K+-ATPase system of the stria vascularis.
Maintenance of the ionic concentrations of the endolymph appears to require in addition active transport of Na+ and Cl− out of the endolymph.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonting, S. L., Becker, B.: Studies on sodium-potassium activated adenosine-triphosphatase XIV. Inhibition of enzyme activity and aqueous humor flow in the rabbit eye after intravitreal injection of ouabain. Invest. Ophthal.3, 523 (1964).
—, Canady, M. R.: Studies on Na−K activated ATPase XII. Na−K-activated ATPase and sodium transport in toad bladder. Amer. J. Physiol.207, 1005 (1964).
—, Caravaggio, L. L., Canady, M. R., Hawkins, N. M.: Studies on sodium-potassium activated adenosinetriphosphatase XI. The salt gland of the herring gull. Arch. Biochem.106, 49 (1964).
Bosher, S. K., Warren, R. L.: Observations on the electrochemistry of the cochlear endolymph of the rat: a quantitative study of its electrical potential and ionic composition as determined by means of flame spectrophotometry. Proc. roy. Soc. B.171, 227 (1968).
Butler, R. A.: Some experimental observations on the resting potentials in the guinea pig cochlea. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.37, 429 (1965).
Cole, D. F.: Electrochemical changes associated with the formation of aqueous humor. Brit. J. Ophthal.45, 202 (1961).
Duvall, A. J.: Ultrastructure of the lateral cochlear wall following intermixing of fluids. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis)77, 317 (1968).
Eggemann, S., Bruchmüller, W.: Die Kohlensäureanhydratase im Innenohr des Meerschweinchens und ihre Hemmung. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.,- Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk.190, 450 (1968).
Erulkar, S. D., Maren, T. H.: Carbonic anhydrase and the inner ear. Nature (Lond.)189, 459 (1961).
Haskell J. A., Clemons, R. D., Harvey, W. R.: Active transport by the cecropia midgut. I. Inhibitors, stimulants and potassium transport. J. cell. comp. Physiol.65, 45 (1965).
Herrera, F. C.: Bioelectric properties and ionic content in toad bladder. J. gen. Physiol.51, 261 (1968).
Hodgkin, A. L., Katz, B.: The effect of ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J. Physiol. (Lond.)108, 37 (1949).
Honrubia, V., Johnstone, B. M., Butler, R. A.: Maintenance of cochlear potentials during asphyxia. Acta oto-larnyg. (Stockh.)60, 105 (1965).
Johnson, R. L., Spoendlin, H. H.: Structural evidence of secretion in the stria vascularis. Ann. Otol., (St. Louis)75, 127 (1966).
Johnstone, B. M.: The relation between endolymph and the endocochlear potential during anoxia. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.)60, 113 (1965).
—: Genesis of the cochlear endolymphatic potential. Curr. Topics in Bioenerg.2, 335 (1967).
Koefoed-Johnsen, V.: Effect, of g-strophantin (ouabain) on the active transport of sodium through isolated frog skin. Acta physiol. scand.42, Suppl.145, 87 (1957).
Konishi, T., Butler, R. A., Fernández, C.: Effect of anoxia on cochlear potentials. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.33, 349 (1961).
—, Kelsey, E.,: Effect of sodium deficiency on cochlear potentials. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.43, 462 (1968).
——: Effect of tetrodotoxin and procain on cochlear potentials. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.43, 471 (1968).
——, Singleton, G. T.: Effects of chemical alteration in the endolymph on the cochlear potentials. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.)62, 393 (1966).
Kuijpers, W.: Cation transport and cochlear function Thesis, Nijmegen 1969.
— Bonting, S. L..: Localization and properties of ATPase in the inner ear of the guinea pig. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)173, 477 (1969).
——: The cochlear potentials. I. The effect of ouabain on the cochlear potentials of the guinea pig. Pflügers Arch.320, 348 (1970).
Loewenstein, W. R., Terzuolo, A. A., Washizu, Y.: Separation of transducer and impulse-generating processes in sensory receptors. Science142, 1180 (1963).
Marmor, M. F., Gorman, A. L. F.: Membrane potential as the sum of ionic and metabolic components. Science167, 65 (1970).
Misrahy, G. A., Hildreth K. M., Clark, L. C., Shinabarger, E. W.: Measurement of the pH of the endolymph in the cochlea of guinea pigs. Amer. J. Physiol.194, 393 (1958).
Morizono, T., Johnstone, B. M., Kaldor., J.: Cochlear blood volume in the guinea pig measured with Cr51 labelled red blood cells. Otol. Fukuoka.14, 82 (1968).
Ozaki, M., Sato, M.: Changes in the membrane potential and the membrane conductance associated with a sustained depolarization of the non-myelinated nerve terminal in Pacinian corpuscles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)180, 186 (1965).
Patlak, C. S.: Potential difference of the ventricular fluid in vivo and in vitro in dogfish. Fed. Proc.23, 211 (1964).
Rauch, S.: Biochemie des Hörorgans. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1964.
Rice, E. A., Shinabarger, E. W.: Studies on the endolymphatic DC potential of the guinea pig's cochlea. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.33, 922 (1961).
Schoffeniels, E.: Cellular aspects of membrane permeability. Oxford: Pergamon 1967.
Slegers, J. F. G., Moons, W. M.: Effect, of acetazolamide on the chloride shift and the sodium pump in secretory cells. Nature (Lond.)220, 181 (1968).
Tasaki, I., Davis, H., Eldredge, D. H.: Exploration of cochlear potentials in guinea pig with a microelectrode. J. acoust. Soc. Amer.26, 765 (1954).
Thesleff, S., Schmidt-Nielsen, K.: An electrophysiological study of the salt gland of the herring gull. Amer. J. Physiol.202, 597 (1962).
Ussing, H. H., Biber, T. V., Bricker, N. S.: Exposure of the isolated frog skin to high potassium concentration at the internal surface. II. Changes in epithelial cell volume, resistance and response to antidiuretic hormone. J. gen. Physiol.48, 425 (1965).
Vates, T., Bonting, S. L., Oppelt, W. W.: Na−K-activated adenosine triphosphatase and formation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cat. Amer. J. Physiol.206, 1165 (1964).
Wood, J. L., Farrand, P. S., Harvey, W. R.: Active transport of potassium by the cecropia, midgut. VI. Microelectrode potential profile. J. exp. Biol.50, 169 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuijpers, W., Bonting, S.L. The cochlear potentials. Pflugers Arch. 320, 359–372 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588214
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588214