Summary
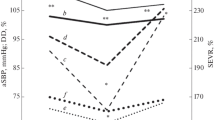
In rats born and staying their whole life at a simulated altitude of 3500 m a severe cardiac hypertrophy develops which is most pronounced in the right ventricle. On histological sections muscle fiber and capillary densities were counted and the surfaces occupied by muscle fibers and capillaries in the slides were estimated. Mean muscle fiber diameter and half mean distance between capillaries (diffusion distance) were obtained in the heart ventricles and were compared with those of control animals. In both ventricles an increase of the mean muscle fiber diameter occurred (true hypertrophy), being more pronounced in the right ventricle. We cannot tell whether also hyperplasia of muscle fibers occurred or not. The diffusion distance in the left ventricle of rats exposed to hypoxia was about the same as in control animals but was shorter in the right ventricle. This indicates that the total number of capillaries is higher in both ventricles of rats born in the low pressure chamber (hyperplasia of the capillaries). The shortening of the diffusion distance in the right ventricle of rats born and living their whole life at simulated high altitude was on the average smaller than that of rats exposed to simulated high altitude later in life. The physiological importance of this observation is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias-Stella, J.: Chronic mountain sickness: pathology and definition. In: CIBA Foundation Symposium High Altitude Physiology: Cardiac and respiratory aspects, R. Porter and J. Knight, Eds., pp. 31–40. Edinburgh-London: Churchill Livingstone 1971
Becker, E. L.: Myocardium in puppies born at a simulated altitude of 20,000 feet. Amer. J. Physiol.183, 203–205 (1955)
Becker, E. L., Cooper, R. G., Hataway, G. D.: Capillary vascularization in puppies born at a simulated altitude of 20,000 feet. J. appl. Physiol.8, 166–168 (1955)
Henning, A.: Das Problem der Kernmessung. Eine Zusammenfassung und Erweiterung der mikroskopischen Meßtechnik. Mikroskopie12, 174–202 (1957)
Hort, W.: Quantitative Untersuchungen über die Capillarisierung des Herzmuskels im Erwachsenen- und Greisenalter bei Hypertrophie und Hyperplasie. Virchows Arch. path. Ant.327, 560–576 (1955)
Krogh, A.: The anatomy and physiology of capillaries. New Haven Yale University: Press 1922
Peñaloza, D., Sime, F., Ruiz, L.: Cor pulmonale in chronic mountain sickness: present concept of Monge's disease. In: CIBA Symposium High Altitude Physiology: Cardiac and respiratory aspects, R. Porter and J. Knight, Eds., pp. 41–52. Edinburgh-London: Churchill Livingstone 1971
Rakušan, K.: Oxygen in the heart muscle. Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas 1971
Snedecor, G. W., Cochran, W. G.: Statistical Methods. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press 1967
Timiras, P. S.: Comparison of growth and development of the rat at high altitude and at sea level. In: The physiological effects of high altitude, W. H. Weihe, Ed., pp. 21–30. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1964
Timiras, P. S., Krum, A. A., Pace, N.: Body and organ weights of rats during acclimatization to an altitude of 12470 feet. Amer. J. Physiol.191, 589–604 (1957)
Timiras, P. S., Woolley, D. E.: Functional and morphological development of brain and other organs of rats at high altitude. Fed. Proc.25, 1312–1320 (1966)
Turek, Z., Frans, A., Kreuzer, F.: Hypoxic pulmonary steady-state diffusing capacity for CO and alveolar-arterial O2 pressure differences in growing rats after adaptation to a simulated altitude of 3500 m. Pflügers Arch.335, 1–9 (1972a)
Turek, Z., Grandtner, M., Kreuzer, F.: Cardiac hypertrophy, capillary and muscle fiber density, muscle fiber diameter, capillary radius and diffusion distance in myocardium of growing rats adapted to a simulated altitude of 3 500 m. Pflügers Arch.335, 19–28 (1972b)
Turek, Z., Ringnalda, B. E. M., Grandtner, M., Kreuzer, F.: Myoglobin distribution in the heart of growing rats exposed to a simulated altitude of 3 500 m in their youth or born in the low pressure chamber. Pflügers Arch.340, 1–10 (1973a)
Turek, Z., Grandtner, M., Ringnalda, B. E. M., Kreuzer, F.: Hypoxic pulmonary steady-state diffusing capacity for CO and cardiac output in rats born at a simulated altitude of 3 500 m. Pflügers Arch.340, 11–18 (1973b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grandtner, M., Turek, Z. & Kreuzer, F. Cardiac hypertrophy in the first generation of rats native to simulated high altitude. Pflugers Arch. 350, 241–248 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587803
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587803