Summary
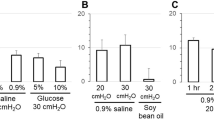
The urinary excretion of water, sodium and potassium by salineloaded rats treated with antibradykinin serum was studied. Control animals received normal rabbit serum. Blockade of the kallikrein system by bradykinin-binding antibodies resulted in a decreased natriuretic and diuretic response to expansion of the extracellular space. The fractional excretion of sodium and water was lower in antibradykinin-treated rats. Antibradykinin serum did not affect the clearances of PAH or inulin, nor did it influence potassium excretion. The reduced ability of antibradykinin-treated rats to excrete a saline load suggests that a normally functioning kallikrein system may be a prerequisite for the occurrence of saline diuresis after extracellular fluid volume expansion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adetuyibi, A., Mills, I. H.: Relation between urinary kallikrein and renal function, hypertension and excretion of sodium and water in man. Lancet1972 II, 203–207
Barraclough, M. A., Mills, I. H.: Effect of bradykinin on renal function. Clin. Sci.28, 69–74 (1956)
Beilenson, S., Schachter, M., Smaje, L. H.: Secretion of kallikrein and its role in vasodilatation in the submaxillary gland. J. Physiol. (Lond.)199, 303–317 (1968)
Boissonas, R. A., Guttmann, St., Jaquenoud, P. A.: Synthèse de la L-arg-L-pro-L-pro-L-gly-L-phe-L-ser-L-pro-L-phe-L-arg, un nonapeptide présentant les propriétés de la bradykinine. Helv. chim. Acta43, 1349–1358 (1960)
Bonjour, J. Ph., Peters, G.: Non-occurrence of a natriuretic factor in circulating blood of rats after expansion of the extracellular or the intravascular space. Pflügers Arch.318, 21–34 (1970)
Bratton, A. C., Marshall, E. K., Jr.: A new coupling component for sulfanilamide determination. J. biol. Chem.128, 537–550 (1939)
Diezi, J., Michoud, P.: SNGFR and renal cortical plasma flow during compensatory pensatory adaptation in rats. Abstracts: Société Suisse de Néphrologie. Kidney Int.5, 309 (1974)
Edwards, O. M., Adetuyibi, A., Mills, I. H.: Kallikrein excretion during the “escape” from the sodium retaining effect of fludrocortisone. J. Endocr.59, XXXIV (1973)
Elliot, D. F., Lewis, G. P., Horton, E. W.: The structure of bradykinin-a plasma kinin from ox blood. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.3, 87–91 (1960)
Geller, R. G., Margolius, H. S., Pisano, J. J., Keiser, H. R.: Effect of mineralocorticoids, altered sodium intake and adrenalectomy on urinary kallikrein in rats. Circulat. Res.31, 857–861 (1972)
Gill, J. R., Melmon, K. L., Gillespie, L., Jr., Bartter, F. C.: Bradykinin and renal function in normal man: effects of adrenergic blockade. Amer. J. Physiol.209, 844–848 (1965)
Goodfriend, T. L., Levine, L., Fassman, G.: Antibodies to bradykinin and angiotensin: a use for carbodiimides in immunology. Science144, 1344–1346 (1964)
Harrison, H. E.: A modification of the diphenylamine method for determination of inulin. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)49, 111–114 (1942)
Hilton, S. M., Lewis, G. P.: The mechanism of the functional hyperemia in the submandibular salivary gland. J. Physiol. (Lond.)129, 253–271 (1955)
Kellermeyer, R. W., Graham, R. G., Jr.: Kinins-possible physiologic and pathologic roles in man. New Engl. J. Med.279, 754–759, 802–807, 859–866 (1968)
Margolius, H. S., Geller, R., de Jong, W., Pisano, J. J., Sjoerdsma, A.: Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in rats with hypertension. Circulat. Res.30, 358–362 (1972)
Margolius, H. S., Geller, R., Pisano, J. J., Sjoerdsma, A.: Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in human hypertension. Lancet1971II, 1063–1065
Marin Grez, M., Carretero, O. A.: Urinary kallikrein excretion in rats under low and high sodium intake. Physiologist14, 189 (1971)
Marin Grez, M., Carretero, O. A.: The relationship between urinary kallikrein and natriuresis, in: Kininogenases (Kallikreins). G. L. Haberland and J. W. Rohen, Eds., pp. 113–122. Stuttgart: F. K. Schattauer 1973
Marin Grez, M., Cottone, P., Carretero, O. A.: Evidence for an involvement of kinins in regulation of sodium excretion. Amer. J. Physiol.223, 794–796 (1972)
Marin Grez, M., Marin Grez, M. S., Peters, G.: Inhibition of oxytocic and hypotensive activities of bradykinin by bradykinin binding antibodies. Europ. J. Pharmacol. (in press) (1974).
Nasjletti, A., Azzam, M. E.: Variations of plasma kininogen content due to high sodium intake in rats. Experientia (Basel)26, 280–281 (1970)
Nicolaides, E. D., de Wald, H. A., MacCarthy, D. E.: Synthesis of biologically active decapeptide having the structure proposed for kallidin. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.6, 210–212 (1961)
Peters, G.: Der Einfluß von Nebennierenrindenhormonen auf die renale Wasser- und Elektrolytausscheidung bei adrenalektomierten und normalen Ratten nach Gabe von Wasser oder isotonischer NaCl-Lösung und im Durst. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.235, 155–184 (1959)
Roch-Ramel, F., Gardaz, P. C., Carmignac, D., Gasser, J., Peters, G.: The relationship between diversion of glomerular filtration from superficial to deep nephrons induced by angiotensin II and its diuretic effect. In: Recent advances in renal physiology. J. Wirz and F. Spinelli, Eds., pp. 284–290. Basle: S. Karger 1972
Schachter, M.: Kallikrein and kinins. Physiol. Rev.49, 509–547 (1969)
Stein, J. H., Congbalay, R. C., Karsh, D. L., Osgood, R. W., Ferris, T. F.: The effect of bradykinin on proximal tubular reabsorption in the dog: evidence for functional nephron heterogeneity. J. clin. Invest.51, 1709–1721 (1972)
Stein, J. A., Ferris, T. F., Huprich, J. E., Smith, T. C., Osgood, R. W.: Effects of renal vasodilatation on distribution of cortical blood flow in the kidney of the dog. J. clin. Invest.50, 1429–1438 (1971)
Webster, M. E., Gilmore, J. P.: Influence of kallidin-10 on renal function. Amer. J. Physiol.206, 714–718 (1964)
Willis, C. R., Ludens, J. H., Hook, J. B., Williamson, H. E.: Mechanism of natriuretic action of bradykinin. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 1–5 (1969)
Wright, F. S., Brenner, M., Bennett, C. M., Kleimowitz, R. I., Berliner, R. W., Schrier, R. N., Verroust, P. J., de Wardener, H. E., Holzgreve, H.: Failure to demonstrate a hormonal inhibitor of proximal sodium reabsorption. J. clin. Invest.48, 1107–1113 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Fonds National Suisse de la Recherche Scientifique, Grant No. 3.7420.72.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grez, M.M. The influence of antibodies against bradykinin on isotonic saline diuresis in the rat. Pflugers Arch. 350, 231–239 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587802
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587802