Summary
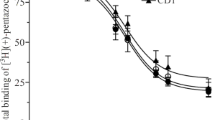
Using tritiated opiates with a high specific radioactivity, a high affinity binding to brain homogenates has been observedin vitro. Strong evidence was given that this type of binding is due to the interaction of labelled opiates with their specific receptors in the brain, since the ability of a wide variety of opiates to inhibit this binding corresponds very well with the potency of the drugs to produce their pharmacological effectsin vivo. We have found that the simultaneous injection of labelled opiates into animals together with high doses of nonradioactive opiates decreases the brain concentration of the labelled drug. This displacement from brain satisfies criteria similar to those used for the identification of the opiate receptorin vitro. Furthermore, opiates produce their pharmacological effects in the same dose range in which they are able to displace a radiolabelled opiate from the brain. This strongly suggests that the receptor occupation by opiates can be identified by concentration changes in the brain of living animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cerletti, C., Manara L., Mennini, T.: Brain levels of the potent analgesic etorphine in rats and their functional significance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 52, 440 P (1974)
Höllt, V., Dum, J., Bläsig, J., Schubert, P., Herz, A.: Comparison ofin vivo andin vitro parameters of opiate receptor binding in naive and tolerant/dependent rodents. Life Sci. 16, 1823–1828 (1975)
Höllt, V., Haarmann, I., Herz, A.: Identification of opiate receptor bindingin vivo. Arzneim.-Forsch. (Drug Res.) 26, 1102–1104 (1976)
Höllt, V., Herz, A.:In vivo receptor occupation by opiates and its correlation with antinociception in the mouse. In: Opiates and Endogenous Opioid Peptides, Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam (1976)
Kuhar, M. J., Pert, C. B., Snyder, S. H.: Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature 245, 447–450 (1973)
Pert, C. B., Snyder, S. H.: Opiate receptor: Demonstration in nervous tissue. Science 179, 1011–1014 (1973)
Pert, C. B., Kuhar, M. J., Snyder, S. H.: Autoradiographic localization of the opiate receptor in rat brain. Life Sci. 16, 1849–1854 (1975)
Schubert, P., Höllt, V., Herz, A.: Autoradiographic evaluation of the intracerebral distribution of3H-etorphine in the mouse brain. Life Sci. 16, 1855–1856 (1975)
Simon, E. J., Hiller, J. M., Edelman, I.: Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic3H-etorphine in rat brain homogenate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 1947–1949 (1973)
Snyder, S. H., Matthysse, S.: Opiate Receptor Mechanisms. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass. (1975)
Terenius, L.: Characteristics of the receptor for narcotic analgesics in synaptic membrane fractions from the rat brain. Acta pharmac. Toxicol. 33, 377–384 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Höllt, V. Opiate receptor identification in vitro and in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297 (Suppl 1), S49–S50 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587775
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587775