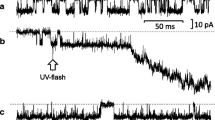
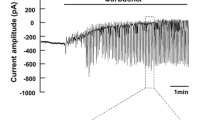
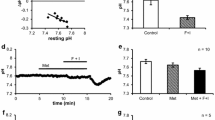
Summary
In order to elucidate whether or not active secretion of potassium and bicarbonate by the rat submaxillary duct epithelium operates independently of sodium reabsorption, Na+ transport was blocked by amiloride, which is known to inhibit Na+ entry from lumen into cell.
With 10−4 M amiloride in HCO −3 -Ringer at the luminal side, the transepithelial electrical potential difference approached zero, the Na+ conductance of the luminal cell membrane was drastically reduced, and the K+ conductance was significantly reduced. Net K+ secretion was reduced by 80%, whereas net HCO −3 secretion was significantly increased. The remaining 20% of net K+ secretion proceeded at zero net Na+ transport and in the absence of significant chemical and electrical potential differences between lumen and interstitium of the duct. This active component of net K+ secretion was accompanied by an equal rate of active HCO −3 secretion.
These findings confirm the independence of this active secretion of K+ and HCO −3 from Na+ transport. They indicate an electrically neutral secretion of K+ and HCO −3 , probably by the postulated luminal K+−H+-exchange mechanism. The 80% of net K+ secretion, which were abolished by amiloride together with Na+ reabsorption, seem to be functionally coupled with Na+ transport. The linkage of K+-to-Na+ is probably mediated by a luminal carrier exchanging Na+ for K+ and H+.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba, W. I., Lant, A. F., Smith, A. J., Townshend, M. M., Wilson, G. M.: Pharmacological effects in animals and normal human subjects of the diuretic amiloride hydrochloride (MK-870). Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.9, 318–327 (1968)
Baer, J. E., Jones, C. B., Spitzer, S. A., Russo, H. F.: The potassium-sparing and natriuretic activity of N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinecarboxamide hydrochloride dihydrate (amiloride hydrochloride). J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.157, 472–485 (1967)
Bentley, P. J.: Amiloride-a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J. Physiol. (Lond.)195, 317–330 (1968)
Biber, T. U. L., Curran, P. F.: Direct measurement of uptake of sodium at the outer surface of the frog skin. Physiologist12, 176 (1969)
Biber, T. U. L., Aceves, J., Mandel, L. J.: Potassium uptake across serosal surface of isolated frog skin epithelium. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 1366–1373 (1972)
Crabbé, J.: A hypothesis concerning the mode of action of amiloride and of triamterene. Arch. int. Pharmacol.173, 474–477 (1968)
Dörge, A., Nagel, W.: Effect of amiloride on sodium transport in frog skin. II. Sodium transport pool and unidirectional fluxes. Pflügers Arch.321, 91–101 (1970)
Duarte, C. G., Chomety, F., Giebisch, G.: Effect of amiloride, ouabain and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat. Amer. J. Physiol.221, 632–639 (1971)
Ehrlich, E. N., Crabbé, J.: The mechanism of action of amipramizide. Pflügers Arch.302, 79–96 (1968)
Eigler, J., Kelter, J., Renner, E.: Wirkungscharakteristika eines neuen Acylguanidins, Amiloride-HCl (MK-870), an der isolierten Haut von Amphibien. Klin. Wschr.45, 737–738 (1967)
Gatzy, J. T.: Sites of amiloride action on toad bladder. Pharmacologist10, 198 (1968)
Giebisch, G., Malnic, G., Klose, R. M., Windhager, E. E.: Effect of ionic substitutions on distal potential differences in rat kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.211, 560–568 (1966)
Gruber, W. D., Knauf, H., Frömter, E.: The action of aldosterone on Na+ and K+ transport in the rat submaxillary main duct. Pflügers Arch.344, 33–49 (1973)
Handler, J. S., Preston, A. S., Orloff, J.: Effect of ADN, aldosterone, ouabain and amiloride on toad bladder epithelial cells. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 1071–1074 (1972)
Hierholzer, K., Lange, S.: The effects of adrenal steroids on renal function. In: Kidney and urinary tract physiology Ed. K. Thurau, p. 303. London: Butterworth Baltimore: University Park Press 1974
Higgins, J. T., Frömter, E.: Potential profile in necturus urinary bladder. Pflügers Arch.347, R32 (1974)
Kirschner, L. B., Greenwald, L., Kerstetter, T. H.: Effect of amiloride on sodium transport across body surfaces of freshwater animals. Amer. J. Physiol.224, 832–837 (1973)
Knauf, H.: The isolated salivary duct as a model for electrolyte transport studies. Pflügers Arch.333, 82–94 (1972)
Knauf, H., Frömter, E.: Elektrische Untersuchungen am Hauptausführungsgang der Speicheldrüsen des Menschen. I. Potentialmessung. Pflügers Arch.316, 238–258 (1970a)
Knauf, H., Frömter, E.: Studies on the origin of the transepithelial electrical potential difference in salivary duct epithelium. In: Electrophysiology of epithelial cells. Ed. G. Giebisch. Stuttgart-New York: F. K. Schattauer 1970b
Knauf, H., Wais, U., Lübcke, R., Albiez, G.: On the mechanism of action of triamterene. Effects on transport of Na+, K+ and H+/HCO −3 -ions. Europ. J. clin. Invest. (in press, 1976)
Koefoed-Johnsen, V., Ussing, H. H.: The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta physiol. scand.42, 298–308 (1958)
Lübcke, R.: Weschselwirkungen zwischen Na+-und K+-Transport, dargestellt am Epithel des Speicheldrüsenganges der Ratte. Thesis, University Freiburg, 1975
Malnic, G., Klose, R. M., Giebisch, G.: Microperfusion study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Amer. J. Physiol.211, 529–547 (1966a)
Malnic, G., Klose, R. M., Giebisch, G.: Microperfusion study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transfer in rat kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.211, 548–559 (1966b)
Mello-Aires, M., Giebisch, G., Malnic, G., Curran, P. F.: Kinetics of potassium transport across single distal tubules of rat kidney. J. Physiol. (Lond.)232, 47–70 (1973)
Nagel, W., Dörge, A.: Effect of amiloride on intracellular sodium content. Pflügers Arch.317, 84–92 (1970)
Schneyer, L. H.: Secretion of potassium by perfused excretory duct of rat submaxillary gland. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 1324–1329 (1969)
Schneyer, L. S.: Amiloride inhibition of ion transport in perfused excretory duct of rat submaxillary gland. Amer. J. Physiol.219, 1050–1055 (1970)
Wais, U., Knauf, H.: H+-transport and microsomal HCO −3 -ATPase in salivary duct epithelium. Pflügers Arch.355, R 76 (1975)
Wright, F. S.: Potassium transport by the renal tubule. In: Kidney and urinary tract physiology. Ed. K. Thurau, p. 82. London: Butterworth Baltimore: University Press 1974
Young, J. A., Frömter, E., Schlögel, E., Hamann, K. T.: A microperfusion investigation of sodium resorption and potassium secretion by the main excretory duct of the rat submaxillary gland. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.295, 157–172 (1967)
Young, J. A., Martin, C. J., Asz, M., Weber, F. D.: A microperfusion investigation of bicarbonate secretion by the rat submaxillary gland. The action of a parasympathomimetic drug on electrolyte transport. Pflügers Arch.319, 185–199 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grant Kn 138/1,3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knauf, H., Lübcke, R. Evidence for Na+ independent active secretion of K+ and HCO −3 by rat salivary duct epithelium. Pflugers Arch. 361, 55–59 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587339
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587339