Summary
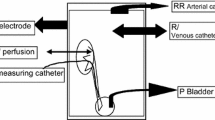
The escape-phenomenon was simultaneously investigated in the vascular beds of intestine and kidney of the cat under conditions of constant flow perfusion. Constrictions were induced either by nerval stimulation (4–6 Hz, 0.5–1.5 msec, 2.5–8 V) or by infusion of noradrenaline (local concentration 0.347 and 0.320 μg/ml, respectively).
During electrical stimulation the escape in the intestinal circulation amounted to 77.8±1.7 [%], meaning that nearly 3/4 of the initial constriction vanished under the stimulation, which lasted 3.3 min in the mean. In the renal circulation the escape amounted to 81.1±1.7[%], the two values were not significantly different (n=2×82,P>0.1).
During humoral induction of the constrictions, the intestinal vascular bed showed an escape of 53.0±2.5[%], the renal circulation one of only 23.8±1.7[%] considering all results with escape (n=2×82,P<0,001). The phenomenon appeared in the intestinal vascular bed in 90.0% (n=90), in the renal vascular bed only in 67.8% (n=118) of all examinations. Including all values with and without perceptible escape the difference in the strength of escape in both circulations would be still more obvious.
The results demonstrate on the one hand a significant difference between nerval and humoral induction of the constriction in both investigated vascular beds. On the other hand under humoral treatment they show a distinct degree of organ specifity. Both statements are in accordance with the concept that the escape depends widely on a high and equal velocity in arrival of transmitter causing an initial synchronisation or matching in the activity of smooth muscle cells. Finally, after the in situ seen reactions (Fig. 3) there can be no doubt in the existence of an humoral induced escape in the renal circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Basar, E., Weiss, Ch.: Analyse des Frequenzganges druckinduzierter Änderungen des Strömungswiderstandes isolierter Rattennieren. Pflügers Arch.304, 121–135 (1968).
Bevan, J. A., Chesher, G. B., Su, C.: Release of adrenergic transmitter from terminal nerve plexus in the artery. Agents and Actions,1, 20–26 (1969).
Brown, G. L., Gillespie, J. S.: The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)138, 81–102 (1957).
Dresel, P., Wallentin, I.: Effects of sympathetic vasoconstrictor fibres, noradrenaline and vasopressin on the intestinal vascular resistance during constant blood flow or blood pressure. Acta physiol. scand.60, 427–436 (1966).
Folkow, B., Häggendal, J., Lisander, B.: Extend of release and elimination of noradrenaline at peripheral adrenergic nerve terminals. Acta physiol. scand.72, Suppl. 307, 1–38 (1968).
Folkow, B., Lewis, D. H., Lundgren, O., Mellander, S., Wallentin, I.: The effect of graded vasoconstrictor fibre stimulation on the intestinal resistance and capacitance vessels. Acta physiol. scand.61, 445–457 (1964a).
Folkow, B., Lewis, D. H., Lundgren, O., Mellander, S., Wallentin, I.: The effect of the sympathetic vasoconstrictor fibres on the distribution of capillary blood flow in the intestine. Acta physiol. scand.61, 458–466 (1964b).
Gero, J., Gerova, M.: Response of vascular smooth muscle to differentiated equiquantal stimulation. Satellite Symposium “Vascular smooth muscle”, Tübingen 1971(a), p. 5.
Gero, J., Gerova, M.: Dynamics of transmitter-receptor interaction in vascular smooth muscle. Proc. 25th Int. Congr. Physiol. Sciences, Munich 1971(b), p. 200.
Gerova, M., Gero, J.: The effect of prolonged sympathetic stimulation on conduit vessel diameter. Experientia (Basel)24, 1134–1135 (1968).
Greenway, C. V., Lawson, A. E., Mellander, S.: The effects of stimulation of the hepatic nerves, infusions of noradrenaline and occlusion of the carotid arteries on liver blood flow in the anaesthetized cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)192, 21–41 (1967).
Greenway, C. V., Lawson, A. E., Stark, R. D.: Vascular responses of the spleen to nerve stimulation during normal and reduced blood flow. J. Physiol. (Lond.)194, 421–433 (1968).
Grupp, G., Heimpel, H.: Zum Problem der „reaktiven Hyperämie” der Niere. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.267, 426–433 (1958).
Haefely, W., Hürlimann, A., Thoenen, H.: Relation between the rate of stimulation and the quantity of noradrenaline liberated from sympathetic nerve endings in the isolated perfused spleen of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)181, 48–52 (1965).
Häggendal, J., Johansson, B., Jonason, J., Ljung, B.: Correlation between noradrenaline release and effector response to nerve stimulation in the rat portal vein in vitro. Acta physiol. scand.80, Suppl. 349, 17–32 (1970).
Hanson, K. M.: Response of the gastrointestinal vasculature to the administration of vasopressin (pitressin). Physiologist12, 247 (1969).
Hanson, K. M.: Vascular response of intestine and liver to intravenous infusion of vasopressin. Amer. J. Physiol.219, 779–784 (1970).
Henrich, H., Biester, J., Lutz, J.: The effect of beta-receptors on the vascular escape phenomenon. In: Vascular Smooth Muscle, Ed. E. Betz, pp. 49–50. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972.
Henrich, H., Lutz, J.: Untersuchungen über das vasculäre Escape-Phänomen am Intestinalkreislauf der Ratte. Pflügers Arch.319, R 40 (1970).
Henrich, H., Lutz, J.: Das vasculäre Escape-Phänomen am Intestinalkreislauf und seine Auslösung durch unterschiedliche vasoconstrictorische Substanzen. Pflügers Arch.329, 82–94 (1971).
Honda, N., Aizawa, C., Yoshitoshi, Y.: Prostocclusive reactive hyperemia in the rabbit kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.215, 190–196 (1968).
Honda, N., Morikawa, A., Nihei, H., Aizawa, C., Yoshitoshi, Y.: Postocclusive vascular responses in isolated perfused kidney of rabbits. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 1581–1587 (1972).
Johansson, B., Sparks, H. V., Bieber, B.: The escape of the renal blood flow response during sympathetic nerve stimulation. Angiologica7, 333–343 (1970).
Kramer, K., Winton, F. R.: The influence of urea and of change in arterial pressure on the oxygen consumption of the isolated kidney of the dog. J. Physiol. (Lond.)96, 87–103 (1939).
Lutz, J., Henrich, H.: Gefäßkontraktion in situ bei druck- und stromkonstanter Perfusion der intestinalen Strombahn und ihre Abhängigkeit vom Ausgangsdruck. Pflügers Arch.319, 68–81 (1970).
Lutz, J., Henrich, H.: Vascular escape phenomenon during infusion of noradrenaline in the simultaneously perfused vascular beds of intestine and kidney. Pflügers Arch.332, R 61 (1972).
Richardson, D. R., Johnson, P. C.: Comparison of autoregulatory escape and autoregulation in the intestinal vascular bed. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 586–590 (1969).
Ross, G.: Effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine on the mesenteric circulation of the cat. Amer. J. Physiol.212, 1037–1042 (1967).
Ross, G.: Escape of mesenteric vessels from adrenergic and nonadrenergic vasoconstriction. Amer. J. Physiol.221, 1217–1222 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutz, J., Henrich, H. Vergleich des vasculären Escape-Phänomens an der intestinalen und renalen Strombahn bei nervaler sowie humoraler Auslösung. Pflugers Arch. 339, 37–48 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586980
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586980