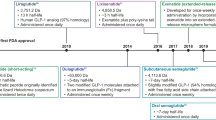
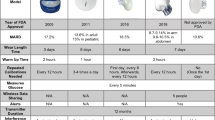
Summary
Glucose concentration was determined enzymatically in tubular fluid samples taken during free-flow micropuncture along the length of the proximal convolution in anaesthetized rats. The glucose concentration decreased exponentially in the first half of the proximal convolution to a mean value of 0.9 mM/l, and did not change in the remaining length accessible to micropuncture. An identical mean value was found in the final urine. When the rates of salt and water reabsorption were varied experimentally, calculated glucose reabsorption showed no relationship to tubular length measured from glomerulum to puncture site. It appears, therefore, that in addition to the mass of reabsorptive tissue and the glucose concentration of tubular fluid, the reabsorption of water and electrolytes plays an important part in determining the rate of glucose reabsorption by the kidney.
Zusammenfassung
In Mikropunktionsuntersuchungen an Nieren narkotisierter Ratten wurde die tubuläre Glucosekonzentration bei freiem Harnfluß und bei normaler Plasmakonzentration an verschiedenen Stellen des proximalen Tubulus gemessen. Die Glucosebestimmung erfolgte enzymatisch. Die Glucosekonzentration nahm über die erste Hälfte des proximalen Konvolutes etwa exponentiell bis zu einem Wert von 0,9 mM/l ab und änderte sich in der zweiten Hälfte nicht mehr. Die Glucosekonzentration im Endharn lag ungefähr im gleichen Bereich wie am Ende des proximalen Konvolutes. Ungeachtet des stetigen Abfalles der tubulären Glucosekonzentration zeigte der berechnete Glucosetransport keine Korrelation zur Länge des punktierten Tubulus vom Glomerulum bis zur Punktionsstelle, wenn unterschiedliche Resorptionsraten von Wasser und NaCl provoziert wurden, so daß der Glucosetransport nicht allein von der Masse des resorbierenden Epithels abhängig sein kann. Es wird besprochen, daß neben der Masse des resorbierenden Epithels und der Glucosekonzentration in der tubulären Flüssigkeit die Elektrolytund Wasserresorption bzw. indirekt das Glomerulumfiltrat die Höhe der renalen Glucosereabsorption wesentlich beeinflussen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Barthelmai, W., u.R. Czok: Enzymatische Bestimmung der Glukose in Blut, Liquor und Harn. Klin. Wschr.40, 585 (1962).
Brunner, F. P., F. C. Rector Jr., andD. W. Seldin: Mechanism of glomerulotubular balance. II. Regulation of proximal tubular reabsorption by tubular volume, as studied by stopped-flow microperfusion. J. clin. Invest.45, 603 (1966).
Deetjen, P., u.J. W. Boylan: Mikroperfusionsuntersuchungen zum tubulären Glucosetransport. — Aktuelle Probleme der Nephrologie, IV. Symposion der Gesellschaft für Nephrologie, S. 545. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1966,
——: Glucose reabsorption in the rat kidney. Microperfusion studies. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.299, 18 (1968).
Gertz, K. H., G. Braun, andJ. W. Boylan: The effect of saline infusion and hemorrhage on effective glomerular filtration pressure and single nephron filtration rate. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. (in Vorbereitung).
—,J. A. Mangos, G. Braun, andH. D. Pagel: On the glomerular tubular balance in the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.285, 360 (1965).
Horster, M., andK. Thurau: Micropuncture studies on the filtration rate of single superficial and juxtamedullary glomerula in the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.301, 162 (1968)
Liew, J. B. van, P. Deetjen, andJ. W. Boylan: Glucose reabsorption in the rat kidney. — Dependence on glomerular filtration. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.295, 232 (1967).
Loeschke, K., K. Baumann, H. Renschler u.K. J. Ullrich: Differenzierung zwischen aktiver und passiver Komponente des Glucosetransportes am proximalen Konvolut der Rattenniere. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.294, R21 (1967).
Möllendorf, W. von: Anatomie der Nierensysteme. In: Handbuch der normalen und pathologischen Physiologie, S. 192. Berlin: Springer 1929.
Ni, T. G., andP. B. Rehberg: On the mechanism of sugar excretion, I. Glucose. Biochem. J.24, 1039 (1930).
Renschler, H. E.: Die Anwendung enzymatischer Methoden zur Bestimmung von Inulin. Klin. Wschr.41, 615 (1963).
Schmidt, F. H.: Die enzymatische Bestimmung von Glucose und Fructose nebeneinander. Klin. Wschr.39, 1244 (1961).
Shannon, J. A., S. Farber, andL. Troast: The measurement of GlucoseT m in the normal dog. Amer. J. Physiol.133, 752 (1941).
— andS. Fisher: The renal tubular reabsorption of glucose in the normal dog. Amer. J. Physiol.122, 765 (1938).
Smith, H. W., W. Goldring, H. Chasis, H. A. Ranges, andS. E. Bradley: The application of saturation methods to the study of glomerular and tubular function in the human kidney. J. Mt. Sinai Hosp.10, 59 (1943).
Ullrich, K. J., u.A. Hampel: Eine einfache Mikroküvette für Monochromator Zeiss und Beckman Modell DU. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.268, 177 (1958).
Vogel, G., F. Lauterbach u.W. Kröger: Die Bedeutung des Natriums für die renalen Transporte von Glucose und Para-Aminohippursäure. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.283, 151 (1965).
Walker, A. M., P. A. Bott, J. Oliver, andM. C. Mac Dowell: The collection and analysis of fluid from single nephrons of the mammalian kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.134, 580 (1941).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung einer Sachbeihilfe der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohde, R., Deetjen, P. & Hardt, K. Die Glucoseresorption in der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch. 302, 219–232 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586727
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586727