Summary
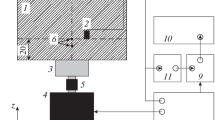
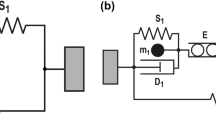
This report deals with a simplified and improved method for measuring the force-velocity relationship of the cat papillary muscle by means of a coil-type galvanometer and a horizontally oriented lever system. The pre- and afterload generator consists of a rotor coil and a D. C. electromagnet. Because of its variable magnetic field it can easily be adapted to the tolerances of different coils and mounting systems. The ultrasound reflection method is used to measure displacements. This gives a linear and stable measurement of changes of muscle length without physical contact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodem, R., Sonnenblick, E. H.: Deactivation of contraction by quick release in the isolated papillary muscle of the cat. Circulat. Res.34, 214–225 (1974)
Gülch, R. W. Jacob, R.: Length-tension diagram and forcevelocity relations of mammalian cardiac muscle under steadystate conditions. Pflügers Arch.355, 331–346 (1975)
Iwatsuki, N., Shimosato, S.: Diethyl ether and contractility of isolated cat heart muscle. Brit. J. Anesth.43, 420–426 (1971)
Kämmereit, A., Medugorac, I., Steil, E., Jacob, R.: Mechanics of the isolated ventricular myocardium of rats conditioned by physical training. Basic Res. Cardiol.70, 495–507 (1975)
Kaufmann, R., Lab, M. J., Hennekes, R., Krause, H.: Feedback interaction of mechanical and electrical events in the isolated mammalian ventricular myocardium (cat papillary muscle) Pflügers Arch.324, 100–123 (1971)
Kemmotsu, O.: Effects of inhalation anesthetics on myocardial contractility. Jap. J. Anesthesiol.23, 402–413 (1974)
Shimosato, S., Sugai, N., Etsten, B. E.: The effect of methoxyflurane on the inotropic state of myocardial muscle. Anesthesiology30, 506–512 (1969)
Shimosato, S., Sugai, N., Iwatsuki, N., Etsten, B. E.: The effect of ethrane on cardiac mechanics. Anesthesiology30, 513–518 (1969)
Strauer, B. E.: Contractile response to morphine, piritramide, meperidine and fentanyl: A comparative study of effects on the isolated ventricular myocardium. Anesthesiology37 304–310 (1972)
Sugai, N., Shimosato, S., Etsten, B. E.: Effect of halothane on force-velocity relations and dynamic stiffness of isolated heart muscle. Anesthesiology29, 267–274 (1968)
Zirpke, K., Kummer, K.: Technische Mechanik. Darmstadt: Technischer-Tabellen-Verlag, Fikentscher u. Co., 1966
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siepmann, H.P., Krossa, M. & Arndt, J.O. A new device to derive the force-velocity relationship of the isolated papillary muscle using a sonomicrometer and an electromagnet. Pflugers Arch. 364, 195–197 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585190
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585190