Abstract
-
1.
The function of supraorbital organ II/2 of the head lateral line system of the surface feeding fishAplocheilus lineatus is characterized here by the lateral line nerve response evoked by biologically relevant surface wave trains.
-
2.
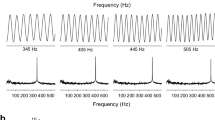
A single organ is particularly sensitive to the high frequency, low amplitude cycles at the beginning of a click evoked wave train. by using gated sinusoidal signals it was shown that the following mechanisms are responsible: a. a strong phasic component superimposed on the tonic response component, b. high sensitivity of the organ in the frequency range between 70 and 120 Hz (corresponding to the frequency range of the first cycles of a prey evoked wave), c. the organ is responsive to the acceleration component of wave stimulation (b∼f2).
-
4.
As the time structure of a surface wave is encoded in a corresponding discharge pattern in the lateral line nerve it is probable that the time structure (‘stimulus pattern’) of a signal is used byA. lineatus to estimate the distance to its source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleckmann H (1980) Reaction time and stimulus frequency in prey localization in the surface-feeding fishAplocheilus lineatus. J Comp Physiol 140:163–172
Bleckmann H, Schwartz E (1982) The functional significance of frequency modulation within the wave train for prey localization in the surface feeding fishAplocheilus lineatus (Cyprinodontidae). J Comp Physiol 145:331–339
Bleckmann H, Topp G (1981) Surface wave sensitivity of the lateral line organs of the topminnowAplocheilus lineatus (Pisces, Cyprinodontidae). Naturwissenschaften 67:624
Görner P (1963) Untersuchungen zur Morphologie und Elektrophysiologie des Seitenlinienorgans vom Krallenfrosch (Xenopus laevis Daudin). Z Vergl Physiol 47:316–338
Grodd W (1977) Oberflächenwellen zur Reizung von Seitenlinien-organen bei Fischen und Amphibien. Diplomarbeit, Gießen
Harris GG, Milne DC (1966) Input-output characteristics of the lateral-line sense organs ofXenopus laevis. J Acoust Soc Am 40/1:32–42
Kroese ABA, Zalm JM van der, Bercken J van der (1980) Extracellular receptor potentials from the lateral line organ ofXenopus laevis. J Exp Biol 86:63–77
Kuiper JW (1956) The microphonic effect of the lateral line organ. Thesis, University of Groningen, The Netherlands
Lang HH (1980) Surface wave discrimination between prey and nonprey by the back swimmerNotonecta glauca L. (Hemiptera, Heteroptera). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 6:233–246
Müller U (1976) Die Seitenlinienzentren vonAplocheilus lineatus (Cyprinodontidae, Teleostei). Diplomarbeit, Gießen
Müller U, Schwartz E (1982) Influence of single neuromasts on prey localizing behavior of the surface feeding fishAplocheilus lineatus. J Comp Physiol 149:399–408
Rudolf P (1967) Zum Ortungsverfahren vonGyrinus substriatus Steph. Z Vergl Physiol. 56:341–375
Schwartz E (1965) Bau und Funktion der Seitenlinien des Strenhenhechtlings (Aplocheilus lineatus Cuv u. Val.) Z Vergl Physiol 50: 55–67
Schwartz E (1970) Ferntastsinnesorgane von Oberflächenfischen. Z Morphol Tiere 67:40–57
Schwartz E (1971) Die Ortung von Wasserwellen durch Oberflächenfische. Z Vergl Physiol 74:64–80
Sommerfeld A (1970) Vorlesungen über theoretische Physik. Bd. 2: Mechanik der deformierbaren Medien. 6. Aufl. Leipzig: Akad Verl Ges
Unbehauen H (1980) Morphologische und elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen zur Wirkung von Wasserwellen auf das Seitenorgan des Streifenhechtlings (Aplocheilus lineatus). Dissertation, Tübingen
Waldner I (1981) Habintuation vonAplocheilus lineatus auf Oberflächenwellen des Wassers. Dissertation, Gießen
Weber DD, Schiewe MH (1976) Morphology and function of the lateral line of juvenile steelhead trout in relation to gas-bubble disease. J Fish Biol 9:217–233
Wolf K (1963) Physiological salines for fresh-water teleosts. Progressive Fish-Culturist (Washington) 25:135–140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topp, G. Primary lateral line response to water surface waves in the topminnowAplocheilus lineatus (Pisces, Cyprinodontidae). Pflugers Arch. 397, 62–67 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585170
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585170