Abstract
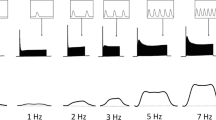
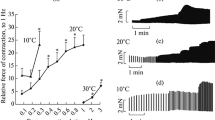
The effect of a short 4 second ultrasound application (1.0 W/cm2 SATA at 963 KHz) on the post-tetanic-potentiation of isolated isometrically contracting rat papillary muscle has been evaluated. Post tetanic-potentiation was produced in hypoxic isolated papillary muscle by interrupting the control stimulation rate of 6/minute with 10 stimulating pulses at 0.2 sec intervals for one cycle. Ultrasound application varied from one second prior to the stimulating train to a period covering the entire train. Ultrasound application just preceding and impinging upon the pulse train, enhanced post-tetanic-potentiation contractions. However, delay in ultrasound application and covering the stimulating pulse train, reduced post-tetanic-potentiation contractions. These data suggest that a window exists for the effects of ultrasound on contracting myocardium which may be used to probe critical events in the cardiac cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arentzen CE, Rankin JS, Anderson PAW, Freezor MD, and Anderson RW. (1978). Force — Frequency Characteristics of the Left Ventricle in the Conscious Dog. Circ. Res.42:64–71.
Berkowitz RS. and Ullrick WC. (1972). Influence of Hyperthermia on Myocardial Contractility. Experientia.28:644–665.
Chapman RA (1979). Excitation-Contraction-Coupling in Cardiac Muscle. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol.35:1–52.
Forester GV, Mainwood GW (1974). Interval Dependent Inotropic Effects in the Rat Myocardium and the Effect of Calcium. Pflugers Arch.352:189–196.
Forester GV, Roy OZ, and Mortimer AJ (1982). Enhancement of Contractility in Rat Isolated Papillary Muscle with Therapeutic Ultrasound. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.14:475–477.
Furukawa Y, Kobayashi M. and Chiba S. (1980). Effects of Temperature on Inotropic Responses of Isolated Canine Atria under Spontaneous or Electrically Paced Rhythm. Jap. Heart. J.21:391–398.
Mortimer AJ, Roy OZ, Trollope BJ, McEwen JI, Taichman GC, Forester GV, and Keon WJ, (1980). A Relationship between Ultrasonic Intensity and Changes in Myocardial Mechanics. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.58:67–73.
Wells PNT (1977). Ultrasonics, Academic Press, London, pp. 421–443.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forester, G.V., Mortimer, A.J., Roy, O.Z. et al. Effect of brief ultrasound exposure on post-tetanic potentiation in cardiac muscle. Pflügers Arch. 400, 208–210 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585044
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585044