Abstract
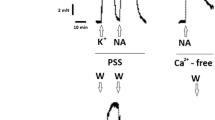
We have investigated the effect of isoprenaline on the amplitude of the transient contraction of isolated arteries induced by releasing the intracellular Ca with an agonist during incubation in a Ca-free solution. Under some conditions this force development is an indication of the amount of Ca in the intracellular store. Loading the store in high K+ solution in the presence of isoprenaline increases the amplitude of the subsequent contraction in Ca-free solution by 6 to 16% as compared to the control. The presence of isoprenaline during the loading procedure in the control solution with 5.9 mM K+ does not affect the amplitude of the subsequent contraction of the rabbit ear artery. In the rabbit coronary artery such pretreatment with isoprenaline inhibits the contraction to 40% of the control. These results indicate that β-agonists may stimulate the Ca uptake in the intracellular store and, depending on the tissue, inhibit the influx of Ca.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelstein RS, Conti MA, Hathaway DR, Klee CB (1978) Phosphorylation of Smooth Muscle Myosin Light Chain Kinase by the Catalytic Subunit of Adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 253:8347–8350
Bülbring E, den Hertog A (1980) The action of isoprenaline on the smooth muscle of the guineapig taenia coli. J Physiol 304:277–296
Bülbring E, Ohashi H, Tomita T (1981) In: Smooth muscle: an assessment of current knowledge. Bulbring E, Brading AF, Jones AW, Tomita T (ed) Edward Arnold, London, pp 219–248
Casteels R, Raeymaekers L (1979) The action of acetylcholine and catecholamines on an intracellular calcium store in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol 294:51–68
Ito Y, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1979) Effects of acetylcholine and catecholamines on the smooth muscle cells of the porcine coronary artery. J Physiol 294:595–611
Kerrick WGL, Hoar PE (1981) Inhibition of smooth muscle tension by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature 292:253–255
Mrwa U, Troschka M, Rüegg JC (1979) Cyclic AMP-dependent inhibition of smooth muscle actomyosin. FEBS Lett 107:371–374
Rüegg JC et al (1981) Cyclic-AMP Mediated Relaxation of Chemically Skinned Fibers of Smooth Muscle. Pflügers Arch 390:198–201
Scheid CR, Honeyman TW, Fay FS (1979) Mechanism of β-adrenergic relaxation of smooth muscle. Nature 277:32–36
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV, Smiesko V (1972) Cyclic AMP and vascular smooth muscle. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 1:175–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Eldere, J., Raeymaekers, L. & Casteels, R. Effect of isoprenaline on intracellular Ca uptake and on Ca influx in arterial smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 395, 81–83 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584974
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584974