Abstract
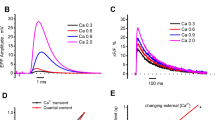
Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) were recorded extracellularly from synaptic spots on crayfish opener muscles. Release of transmitter was determined by counting the average number of quanta which appear after a stimulus. When [Mg]0 was increased from 2.5 to 12.5 mM, release was inhibited. Quantitatively the effect of [Mg]0 could be described by a competitive inhibition of the entry (not of the release) of Ca2+ after an impulse, with apparent dissociation constants KMg between 1.4 and 18 mM [Mg]0, assuming saturation kinetics for entry of Ca2+ and release. At constant [Ca]0, twin pulse facilitation (F s ) for short intervals (about 10 ms) increased when [Mg]0 was raised from low values, reached a maximum at a certain {ie237-1} and unexpectedly decreased again at higher [Mg]0. At higher [Ca]0, {ie237-2} shifted to higher values. This maximum of facilitation is predicted qualitatively by our theoretical model. However, the amplitude of facilitation was larger than predicted theoretically, and the {ie237-3} were smaller than predicted. The theoretical possibilities to correct these discrepancies within the framework of ‘residual calcium’ based facilitation and saturation kinetics of entry and release were analyzed, but all were in conflict with experimental findings. It is concluded that an essential element is missing in the present theory of facilitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoit P, Mambrini J (1970) Modification of transmitter release by ions which prolong the presynaptic action potential. J Physiol (Lond) 210:681–695
Del Castillo J, Katz B (1954) Quantal components of the endplate potential. J Physiol (Lond) 124:560–573
Dodge FA Jr, Rahamimoff R (1967) Cooperative action of calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol (Lond) 193:419–432
Dudel J (1977) Dose-response curve of glutamate applied by superfusion to crayfish muscle synapses. Pflügers Arch 368:49–54
Dudel J (1981) The effect of reduced calcium on quantal unit current and release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Pflügers Arch 391:35–40
Dudel J, Kuffler SW (1961) The quantal nature of transmission and spontaneous miniature potentials at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol (Lond) 155:514–529
Dudel J, Parnas H, Parnas I (1981) The effect of Magnesium on the time course of facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett 22:165–168
Jenkinson DH (1957) The nature of antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol (Lond) 138:434–444
Katz B, Miledi R (1967) A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol (Lond) 192:407–436
Katz B, Miledi R (1968) The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol (Lond) 195:481–492
Misler S, Hurlbut WP (1979) Action of black widow spider venom on quantized release of acetylcholine of the frog neuromuscular junction: Dependence upon external Mg. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:991–995
Parnas H, Dudel J, Parnas I (1982) Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish: I. Saturation kinetics of release and of entry and removal of calcium. Pflügers Arch 393:1–14
Parnas H, Segel LA (1980) A theoretical explanation for some effects of calcium on the facilitation of neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol 84:3–29
Parnas H, Segel LA (1981) A theoretical study of calcium entry in nerve terminals, with application to neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol 91:125–169
Parnas I, Parnas H, Dudel J (1982) Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish: II. Duration of facilitation and removal process of calcium from the terminal. Pflügers Arch 393:232–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and by the USA-Israel Binational Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudel, J., Parnas, I. & Parnas, H. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish. Pflugers Arch. 393, 237–242 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584076
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584076