Abstract
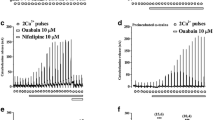
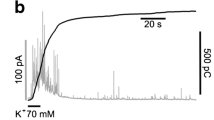
Single cells from rat lacrimal glands were studied with the tighit-seal whole-cell recording method. Ca-dependent K and Cl currents were measured in response to dialysis with inositoltrisphosphate or GTPγS, two compounds known for elevating internal Ca2+ concentration. The activation of the Ca-dependent currents elicited by either compound was partially inhibited by sustained depolarization or by removal of external Ca2+. Conversely, hyperpolarization or removal of external Mg2+ led to augmentations of the Ca-dependent currents. These effects became apparent about 1 min after initiation of cell dialysis with inositoltrisphosphate-or GTPγS-containing solutions, and they further developped during the ensuing 10 min. Holding potential and external divalent cations did not affect the Ca-dependent currents elicited by dialysing the cells with strongly buffered solutions containing 0.5 μM free Ca2+. In ca2+-free external saline, cell currents were independent of the holding potential. It is suggested that InsP3 augments intracellular Ca2+ levels not only by releasing Ca2+ from internal stores but also by slowly increasing the Ca permeability of the plasma membrane. The results indicate that Ca2+ entry through the plasma membrane increases with Ca2+ entry through the plasma membrane increases with hyperpolarization. The similarity of the effects seen in InsP3- and GTPγS-dialysed cells gives support to the hypothesis that production of the former depends on a GTP-binding protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker PF, Blaustein MP, Hodgkin AL (1969) The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol 200:431–458
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF (1984) Inositoltrisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature 312:315–320
Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD (1985) Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature 314:534–536
DiPolo R, Bezanilla F, Caputo C, Rojas H (1985) Voltage dependence of the Na/Ca exchange in voltage-clamped, dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol 86:457–478
Evans MG, Marty A (1986a) Ca-dependent Cl currents in isolated cells from rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol 378:437–460
Evans MG, Marty A (1986b) Potentiation of muscarinic and alphaadrenergic responses by an analogue of guanosine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4099–4103
Findlay I (1984) A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol 350:179–195
Findlay I, Petersen OH (1985) Acetylcholine stimulates a Ca2+-dependent Cl− conductance in mouse lacrimal acinar cells. Pflügers Arch 403:328–330
Ginsborg BL, House CR, Mitchell MR (1980) A calcium-readmission response recorded fromNauphoeta salivary gland acinar cells. J Physiol 304:437–447
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Irvine RF, Moor RM (1986) Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 240:917–920
Kanagasuntheram P, Randle PJ (1976) Calcium metabolism and amylase in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem J 160:547–564
Keryer G, Rossignol B (1976) Effect of carbachol on45Ca uptake and protein secretion in rat lacrimal gland. Am J Physiol 230:99–104
Krishtal OA, Pidoplichko VI (1980) A receptor for protons in the nerve cell membrane. Neuroscience 5:2325–2327
Latorre R (1986) The large calcium-activated potassium channel. In: Miller C (ed) Ion channel reconstitution. Plenum Press, New York, p 431
Litosch I, Wallis C, Fain JN (1985) 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositode breakdown. J Biol Chem 260:5464–5471
Marty A, Tan YP, Trautmann A (1984) Three types of calciumdependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol 357:293–325
Marty A, Evans MG, Tan YP, Trautmann A (1986) Muscarinic response in rat lacrimal glands. J Exp Biol 124:15–32
Maruyama Y, Gallacher DV, Petersen OH (1983) Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in baso-lateral membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature 302:827–829
O'Doherty J, Stark RJ, Crane SJ, Brugge KL (1983) Changes in cytosolic calcium during cholinergic and adrenergic stimulation of the parotid salivary gland. Pflügers Arch 298:241–246
Pallotta BS (1985) Calcium-activated potassium channels in rat muscle inactivate from a short-duration open state. J Physiol 363:501–516
Parod RJ, Leslie BA, Putney JW Jr (1980) Muscarinic and alphaadrenergic stimulation of Na and Ca uptake by dispersed lacrimal cells. Am J Physiol 239:G99-G105
Petersen OH (1980) The electrophysiology of gland cells. Academic Press, London
Petersen OH, Maruyama Y (1984) Calcium activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature 307:693–696
Prentki M, Biden TJ, Janjic D, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Wolheim CB (1984) Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Nature 309:562–564
Putney JW Jr (1976) Role of calcium in the fade of the potassium release response in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol 281:283–394
Putney JW Jr (1979) Stimulus-permeability coupling: role of calcium in the receptor regulation of membrane permeability. Pharmacol Rev 30:209–245
Selinger Z, Batzri S, Eimerl S, Schramm M (1973) Calcium and energy requirements for K+ release mediated by the epinephrine alpha-receptor in rat parotid slices. J Biol Chem 248:369–372
Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I (1983) Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature 306:67–69
Takemura H (1985) Changes in cytosolic free calcium concentration in isolated rat parotid cells by cholinergic and α-adrenergic agonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 131:1048–1055
Trautmann A, Marty A (1984) Activation of Ca-dependent K channels by carbamylcholine in rat lacrimal glands. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 81:611–615
von Tscharner V, Prod'hom B, Baggiolini M, Reuter H (1986) Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in cytosolic calcium concentration. Nature 324:369–372
Vergara C, Latorre R (1983) Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers: Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade. J Gen Physiol 82: 543–568
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llano, I., Marty, A. & Tanguy, J. Dependence of intracellular effects of GTPγS and inositoltrisphosphate on cell membrane potential and on external Ca ions. Pflugers Arch. 409, 499–506 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583807
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583807