Abstract
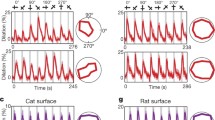
The role of perivascular H+ and K+ in the adjustment of pial arterial diameter during changes in arterial blood pressure was investigated in chloralose anesthetized cats. Blood pressure was reduced by i.v. mecamylamine or pentolinium and was increased by i.v. hypertensin. Pial arterioles and arteries with a control diameter ranging from 37–218 μ at a spontaneous mean arterial blood pressure of 128±16 (SD) mm Hg were studied. Vascular diameter as measured by TV image splitting showed the typical reactions, i.e. constriction during increase (up to 200 mm Hg) and dilation during decrease in blood pressure (down to 60 mm Hg). Perivascular H+ and K+ activities were measured using pH microelectrodes (Hinke type) and K+ ion exchanger microelectrodes, respectively. Under control conditions perivascular pH was 7.25±0.11 (SD) and K+ activity was 2.46±0.65 (SD) mM, respectively. During changes in blood pressure the vascular reactions of pial arteries were not accompanied by significant alterations in perivascular H+ or K+ activity. From these data it can be concluded that mechanisms other than those which are mediated by H+ or K+ are involved in the adjustment of pial arterial diameter during changes in arterial blood pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bill, A., Linder, J.: Sympathetic control of cerebral blood flow in acute arterial hypertension. Acta Physiol. Scand.96, 114–121 (1976)
Boisvert, D. P. J., Jones, J. V., Harper, A. M.: Cerebral blood flow autoregulation to acutely increasing blood pressure during sympathetic stimulation. In: Cerebral function, metabolism and circulation, D. H. Ingvar, N. A. Lassen (eds.), pp. 46–47. Copenhagen: Munksgaard 1977
Edvinsson, L., Owman, Ch., Siesjö, B. K.: Physiological role of cerebrovascular sympathetic nerves in the autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. Brain Res.117, 519–523 (1976)
Eklöf, B., MacMillan, V., Siesjö, B. K.: Cerebral energy state and cerebral venouspO2 in experimental hypotension caused by bleeding. Acta Physiol. Scand.86, 515–527 (1972)
Fitch, W., MacKenzie, E. T., Harper, A. M.: Effects of decreasing arterial blood pressure on cerebral blood flow in the baboon. Influence of the sympathetic nervous system. Circ. Res.37, 550–557 (1975)
Halsey, J. H., Robinson, C.: The non role of CSF ph in cerebral autoregulation. Circulation, Suppl. III,49, III-89 (1974)
Heistad, D. D., Marcus, M. L., Abboud, F. M.: Effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation on cerebral blood flow. In: Cerebral function, metabolism and circulation (D. H. Ingvar, N. A. Lassen, eds.), pp. 306–307. Copenhagen: Munksgaard 1977
Herbert, D. A., Mitchell, R. A.: Blood gas tension and acid-base balance in awake cats. J. Appl. Physiol.30, 434–436 (1971)
Hernandez-Perez, M. J., Anderson, D. K.: Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow and its relation to cerebrospinal fluid pH. Am. J. Physiol.231, 929–935 (1976)
Heuser, D.: The significance of cortical extracellular H+, K+ and Ca2+ activities for regulation of local cerebral blood flow under conditions of enhanced neuronal activity. In: Cerebral vascular smooth muscle and its control (M. J. Purves, ed.), pp. 339–349. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1978
Heuser, D., Betz, E.: Änderungen der lokalen perivaskulären H+ und K+-Aktivitäten an Piagefäßen der Katze bei experimenteller Hypertonie. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Kreislaufforsch.40, 180–183 (1974)
Hoyer, S., Hamer, J., Alberti, E., Stoeckel, H., Weinhardt, F.: The effect of stepwise arterial hypotension on blood flow and oxidative metabolism of the brain. Pflügers Arch.351, 161–172 (1974)
Kontos, H. A., Wei, E. P., Navari, R. M., Levasseur, J. E., Rosenblum, W. I., Patterson, J. L.: Responses of cerebral arteries and arterioles to acute hypotension and hypertension. Am. J. Physiol.234, H371–H383 (1978)
Kovach, A. G. B., Hamar, J., Nyary, I., Sandor, P., Reivich, M., Dora, E., Gunlai, L., Eke, A.: Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in hemorrhagic shock in the baboon. In: Blood flow and metabolism in the brain (A. M. Harper, W. B. Jennett, J. D. Miller, J. O. Rowan, eds.), pp. 2.17–2.19. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone 1975
Kuschinsky, W., Wahl, M.: Perivascular pH and pial arterial diameter during bicuculline induced seizures in cats. Pflügers Arch. (in press, 1979)
Kuschinsky, W., Wahl, M., Bosse, O., Thurau, K.: Perivascular potassium and pH as determinants of local pial arterial diameter in cats. A microapplication study. Circ. Res.31, 240–247 (1972)
Lux, H. D., Neher, E.: The equilibration time course of [K+]0 in cat cortex. Exp. Brain Res.17, 190–205 (1973)
MacKenzie, E. T., Strandgaard, S., Graham, D. I., Jones, J. V., Harper, A. M., Farrar, J. K.: Effects of acutely induced hypertension in cats on pial arteriolar caliber, local cerebral blood flow, and the blood-brain barrier. Circ. Res.39, 33–41 (1976)
MacKenzie, E. T., McGeorge, A. P., Graham, D. I., Fitsch, W.: Edvinsson, L., Harper, A. M.: Effects of increasing arterial pressure on cerebral blood flow in the baboon: influence of the sympathetic nervous system. Pflügers Arch.378, 189–195 (1979)
Mchedlishvili, G. I., Nikolaishvili, L. S., Antia, R. V.: Are the pial arterial responses dependent on the direct effect of intravascular pressure and extravascular and intravascularpO2,pCO2, and pH? Microvasc. Res.10, 298–311 (1976)
Morris, M. E.: Hypoxia and extracellular potassium activity in the guinea-pig cortex. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.52, 872–882 (1974)
Morris, M. E.: Brain extracellular potassium and general anaesthetics. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.54, 863–872 (1978)
Olesen, J.: The effect of intracarotid epinephrine, norepinephrine, and angiotensin on the regional cerebral blood flow in man. Neurology22, 978–987 (1972)
Olesen, J.: Quantitative evaluation of normal and pathologic cerebral blood flow regulation to perfusion pressure changes in man. Arch. Neurol.28, 143–149 (1973)
Rubio, R., Berne, R. M., Bockmann, E. L., Curnish, R. R.: Relationship between adenosine concentration and oxygen supply in rat brain. Am. J. Physiol.228, 1896–1902 (1975)
Siesjö, B. K., Zwetnow, N. N.: The effect of hypovolemic hypotension on extra- and intracellular acid-base parameters and energy metabolites in the rat brain. Acta Physiol. Scand.79, 114–124 (1970)
Schneider, W., Wahl, M., Kuschinsky, W., Thurau, K.: The use of microelectrodes for measurement of local H+ activity in the cortical subarachnoidal space of cats. Pflügers Arch.372, 103–107 (1977)
Skinhøj, E.: The upper limit of autoregulation and the sympathetic system. In: Cerebral circulation and metabolism (T. W. Langfitt, L. C. McHenry, M. Reivich, H. Wollman, eds.), pp. 487–488. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1975
Urbanics, R., Leniger-Follert, E., Lübbers, D. W.: Time course of changes of extracellular H+ and K+ activities during and after direct electrical stimulation of the brain cortex. Plügers Arch.378, 47–53 (1978)
Wahl, M., Deetjen, P., Thurau, K., Ingvar, D. H., Lassen, N. A.: Micropuncture evaluation of the importance of perivascular pH for the arteriolar diameter on the brain surface. Pflügers Arch.316, 152–163 (1970)
Wahl, M., Kuschinsky, W., Bosse, O., Thurau, K.: Dependency of pial arterial and arteriolar diameter on perivascular osmolarity in the cat. A microapplication study. Circ. Res.32, 162–169 (1973)
Wei, E. P., Kontos, H. A., Patterson, J. L.: Vasoconstrictor effect of angiotensin on pial arteries. Stroke9, 487–489 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahl, M., Kuschinsky, W. Unimportance of perivascular H+ and K+ activities for the adjustment of pial arterial diameter during changes of arterial blood pressure in cats. Pflugers Arch. 382, 203–208 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583703
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583703