Summary
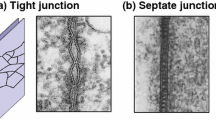
Cells ofChironomus salivary glands communicate through intercellular connections of high permeability. Electron micrographs of salivary glands show two kinds of junctions between the membranes of adjacent cells, which may be responsible for cell coupling: septate junctions and close membrane junctions.
A large fraction of lateral cell surfaces is occupied by septate junctions, while the area of close membrane junctions appears to be very small. Consequently septate junctions have been considered as likely sites for intercellular coupling. There are however some indications that intercellular communication is provided by structures which seem to be unstable. As osmotic effects are among the factors which can disrupt cellular communications, we have tried to eliminate possible effects of the fixing solutions on the ultrastructure of intercellular connections by using isoosmotic fixatives. Under these conditions large regions of close membrane junctions of the nexus kind have been observed to occur between gland cells. They are of similar size as septate junctions. It seems to be possible that as in other communicating cell systems nexus could be the sites for intercellular coupling of salivary gland cells.
Zusammenfassung
Speicheldrüsen von Mückenlarven (Chironomus Thummi) haben eine ausgedehnte interzelluläre Kommunikation. In elektronenmikroskopischen Bildern der Speicheldrüsen wurden zwei Arten von interzellulären Verbindungen gefunden, die für die Zellkopplung verantwortlich sein könnten: septate junctions und close membrane junctions. Da die räumliche Ausdehnung der septate junctions viel größer zu sein scheint als die der close junctions, wurden erstere als wahrscheinliche Kopplungsstrukturen angesehen. Es gibt jedoch Hinweise, daß die Strukturen, welche die Zellkopplung bewirken, sehr labil sind. Unter den Faktoren, die zu einer Unterbrechung der zellulären Kommunikationen führen können, sind auch osmotische Effekte. Um mögliche Einflüsse dieser Art auf die Ultrastruktur zu verhindern, wurden die Drüsen für die mikroskopische Inspektion in isoosmotischen Lösungen fixiert. Unter diesen Bedingungen lassen sich ausgedehnte Membrankontakte vom nexus-Typ zwischen den Drüsenzellen erkennen. Ihre Ausdehnung scheint ebenso groß zu sein wie die der septate junctions. Es besteht nach diesen Befunden die Möglichkeit, daß wie in anderen kommunizierenden Zellsystemen, so auch in Speicheldrüsen die interzelluläre Kommunikation durch nexus bewirkt wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargmann, W., Harnack, M. von, Jakob, K.: Über den Feinbau des Nervensystems des Seesternes (Asterias rubens L.). Z. Zellforsch.56, 573–594 (1962).
Barr, L.: Propagation in vertebrate visceral smooth muscle. J. theoret. Biol.4, 73–76 (1963).
—— Berger, W., Dewey, M. M.: Electrical transmission at the nexus between smooth muscle cells. J. gen. Physiol.51, 347–368 (1968).
—— Dewey, M. M., Berger, W.: Propagation of action potentials and the structure of the nexus in cardiac muscle. J. gen. Physiol.48, 797–823 (1965).
Bullivant, St., Loewenstein, W. R.: Structure of coupled and uncoupled cell junctions. J. Cell Biol.37, 621–632 (1968).
Dewey, M. M., Barr, L.: Intercellular connection between smooth muscle cells: the nexus. Science137, 670–671 (1962).
—— —— A study of the structure and distribution of the nexus. J. Cell Biol.23, 553–585 (1964).
Forssmann, W. G., in: Seminar 2493 „Elektronenmikroskopie“ der Technischen Akademie, Esslingen, e. V., 23.–25. April 1969.
Gobel, St.: Axo-Axonic septate junctions in the basket formations of the cat cerebellar cortex. J. Cell Biol.51, 328–333 (1971).
Kloetzel, J. A., Laufer, H.: A fine-structural analysis of larval salivary gland function inChironomus Thummi (Diptera). J. Ultrastruct. Res.29, 15–36 (1969).
Leik, J., Kelly, D. E.: Septate junctions in the gastrodermal epithelium ofPhialidium: A fine structural study utilizing ruthenium red. Tissue and Cell2 (3), 435–441 (1970).
Loewenstein, W. R., Kanno, Y.: Studies on an epithelial (gland) cell junction. I. Modifications of surface membrane permeability. J. Cell Biol.22, 565–586 (1964).
—— Nakas, M., Socolar, S. J.: Junctional membrane uncoupling: permeability transformations at a cell membrane junction. J. gen. Physiol.50, 1865–1891 (1967).
Maunsbach, A. B.: Comparison of renal tubule ultrastructure after perfusion fixation with different fixatives. J. Cell Biol.23, 108a-109a (1964).
—— The influence of different fixatives and fixation methods on the ultrastructure of rat kidney proximal tubule cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res.15, 242–282 (1966).
McNutt, N. S.: Ultrastructure of intercellular junctions in adult and developing cardiac muscle. Amer. J. Cardiol.25, 169–183 (1970).
Millonig, G.: Advantages of a phosphate buffer for osmium tetroxide solutions in fixation. J. appl. Physics.13, 1637 (1961).
Politoff, A. L., Socolar, S. J., Loewenstein, W. R.: Permeability of a cell membrane junction. J. gen. Physiol.53, 498–515 (1969).
Revel, J. P., Karnovsky, M. J.: Hexagonal array of subunits in intercellular junctions of the mouse heart and liver. J. Cell Biol.33, C7-C12 (1967).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–212 (1963).
Rose, B.: Intercellular communication and some structural aspects of membrane junctions in a simple cell system. J. Membrane Biol.5, 1–19 (1971).
—— Loewenstein, W. R.: Junctional membrane permeability. J. Membrane Biol.5, 20–50 (1971).
Satir, P., Gilula, N. B.: The cell junction in a lamellibranch gill ciliated epithelium. J. Cell Biol.47, 468–487 (1970).
Wiener, J., Spiro, D., Loewenstein, W. R.: Studies on an epithelial (gland) cell junction. II. Surface structure. J. Cell Biol.22, 587–598 (1964).
Wood, R. L.: Intercellular attachment in the epithelium of Hydra as revealed by electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.6, 343–351 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by financial grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SFB38.
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. H. Leonhardt, Institut für Anatomie I, Homburg, for the use of his electron microscope (Zeiss EM 9-DFG grant LE 69−8) during part of this work and Prof. Dr. H. Kroeger, Institut für Genetik, Saarbrücken for the supply withChironomus larvae.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, W.K., Uhrík, B. Membrane junctions between salivary gland cells ofChironomus thummi. Z.Zellforsch 127, 116–126 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582761
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582761