Abstract
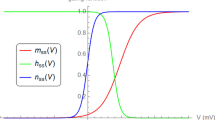
Myoballs were cultured from biopsies of adult human skeletal muscle without the use of antimitotic drugs. The sodium currents flowing during stepwise depolarization of the myoball membrane were investigated with the whole-cell recording technique. The temperature range covered 10–37°C. Two types of sodium channel were distinguished by their different sensitivity to tetrodotoxin (TTX). The channel with normal TTX sensitivity seemed identical with the sodium channel in adult muscle, the channel with less TTX sensitivity seemed identical with the juvenile channel found in developing and in denervated muscle. The activation and inactivation parameters of both channel types were quantitatively determined. The activation parameters of the two channel types were identical, but in comparison to theh ∞-curve of the adult sodium channels theh ∞-curve of the juvenile channels was positioned at more negative potentials, had a less steep slope, and when the temperature was decreased, its point of inflection shifted more in negative direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almers W, Roberts WM, Ruff RL (1984) Voltage clamp of rat and human skeletal muscle: measurements with an improved loosepatch technique. J Physiol 347:751–768
Boldin S, Jäger U, Ruppersberg JP, Pentz S, Rüdel R (1987) Cultivation, morphology, and electrophysiology of contractile rat myoballs. Pflügers Arch 409:462–467
DeCoursey TE, Bryant SH, Lipicky RJ (1982) Sodium currents in human skeletal muscle fibres. Muscle Nerve 5:614–618
Edmonds DT (1987) A physical model of sodium channel gating. Eur Biophys J 14:195–201
Frelin C, Vijverberg HPM, Romey G, Vigne P, Lazdunski M (1984) Different functional states of tetrodotoxin sensitive and tetrodotoxin resistant Na+ channels occur during the in vitro development of rat skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch 402:121–128
Gonoi T, Sherman SJ, Catterall WA (1985) Voltage clamp analysis of tetrodotoxin-sensitive and-insensitive sodium channels in rat muscle cells developing in vitro. J Neurosci 5:2550–2564
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 117:500–544
Kirsch GE, Anderson MF (1986) Sodium channel kinetics in normal and denervated rabbit muscle membrane. Muscle Nerve 9:738–747
Kirsch GE, Sydes JS (1987) Temperature dependence of Na currents in rabbit and frog muscle membranes. J Gen Physiol 89:239–251
Marquardt DW (1963) An algorithm for least squares estimates of non-linear parameters. J Indian Soc Appl Math 11:431–441
Pappone PA (1980) Voltage-clamp experiments in normal and denervated mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol 306:377–410
Pröbstle T, Rüdel R, Ruppersberg JP (1987) Hodgkin-Huxley parameters of TTX-sensitive and TTX-insensitive sodium channels in human myoballs. J Physiol 390:78P
Rüdel R, Lehmann-Horn F (1985) Membrane changes in cells from myotonia patients. Physiol Rev 65:310–365
Ruppersberg JP, Schure A, Rüdel R (1987) Inactivation of TTX-sensitive and TTX-insensitive sodium channels of rat myoballs. Neurosci Lett 78:166–170
Trautmann A, Delaporte C, Marty A (1986) Voltage-dependent channels of human muscle cultures. Pflügers Arch 406:163–172
Weiss RE, Horn R (1986) Functional differences between two classes of sodium channels in developing rat skeletal muscle. Science 233:361–364
Yasin R, van Beer G, Nurse K, Al Ani S, Landon DN, Thompson EJ (1977) A quantitative technique of growing human skeletal muscle in culture starting from mononucleated cells. J Neurol Sci 32:347–360
Zite-Ferenczy F, Matthias K, Taylor SR, Rüdel R (1986) The dynamic sodium current of human skeletal muscle. Fortschr Zool 33:52–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pröbstel, T., Rüdel, R. & Ruppersberg, J.P. Hodgkin-Huxley parameters of the sodium channels in human myoballs. Pflugers Arch. 412, 264–269 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582507
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582507