Abstract
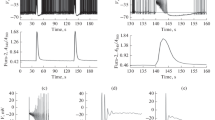
The depolarizing drive that maintains bursting inHelix neurons is carried by a long-lasting calcium-activated inward current. This current was studied using cell-attached and inside-out patches from the right parietal fast burster neuron ofHelix pomatia.
One population of unitary currents was inward at −50 mV and showed an increased probability of opening when Ca2+ was injected or when excised patches were bathed in solutions with 10−7 to 10−5 M free Ca2+ levels. Cell-attached patches (patch electrodes filled with 10−7 M Ca2+ Ringer) had single channel conductances near 30 pS with reversal potentials near −20 mV; excised patches had similar conductances in symmetrical Na+ solutions and reversal potentials within a few millivolts of zero. Calculations, assuming a simple spherical cell, yield a channel density of only about 1/6 μm2. The increased channel opening probability characteristically persisted well beyond the duration of transient whole-cell inward current. We conclude from this that the later phase of Ca-activated inward currents is normally masked by outward currents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WB, Levitan IB (1985) Voltage and ion dependencies of the slow currents which mediate bursting inAplysia neurone R15. J Physiol 360:69–93
Bevan S, Gray PTA, Ritchie JM (1984) A calcium activated cationselective channel in rat cultured Schwann cells. Proc R Soc Lond B 222:349–355
Colquhoun D, Neher E, Reuter H, Stevens CF (1981) Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature 294:752–754
Colquhoun D, Sakmann B (1981) Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature 294:464–466
Frazier WT, Kandel ER, Kupfermann I, Waziri R, Coggeshall RE (1967) Morphological and functional properties of identified neurons in the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia californica. J Neurophysiol 30:1288–1351
Gainer H (1972) Electrophysiological behavior of an endogenously active neurosecretory cell. Brain Res 39:403–418
Hofmeier G, Lux HD (1981) The time courses of intracellular free calcium and related electrical effects after injection of CaCl2 into neurons of the snailHelix pomatia. Pflügers Arch 391:242–251
Kerkut GA, Lambert JDC, Gayton RJ, Loker JE, Walker RJ (1975) Mapping of nerve cells in the suboesophageal ganglia ofHelix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol 50A:1–25
Kramer RH, Zucker R (1985) Calcium-dependent inward current inAplysia bursting pace-maker neurones. J Physiol 362:107–130
Lewis DV (1984) Spike afterpotentials in R15 ofAplysia: Their relationship to slow inward current and calcium influx. J Neurophysiol 51:387–403
Marty A, Tan YP, Trautmann A (1984) The types of calcium-dependent channels in rat lacrinal glands. J Physiol 357:293–325
Maruyama Y, Peterson OH (1982) Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature 299:159–161
Swandulla D, Lux HD (1985) Activation of the nonspecific cation conductance by intracellular Ca2+ elevation in bursting pacemaker neurons ofHelix pomatia. J Neurophysiol 54:1430–1443
Vincent J, Poulain DA, Arnaud E (1978) Bursting activity in relation to neurosecretory cells. In: Chalazonitis, Boisson (eds) Abnormal neuronal discharges. Raven Press, New York, pp 103–110
Yellen G (1982) Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature 296:357–359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Partridge, L.D., Swandulla, D. Single Ca-activated cation channels in bursting neurons ofHelix . Pflugers Arch. 410, 627–631 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581323
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581323