Abstract
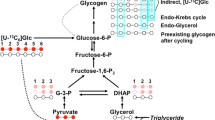
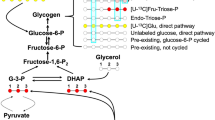
The effect of a phenacyl imidazolium compound (LY177507 or Proglycosyn, Eli Lilly) on the direct (glucose→glucose-6-phosphate→glycogen) and indirect (three-carbon compounds→glucose-6-phosphate→glycogen) pathways of liver glycogen synthesis was studied in conscious rats. [1-13C]Glucose (99% enriched) was infused intraduodenally into chronically catheterized Proglycosyn-treated (n=7) and saline-treated (n=7) rats for 120 min. Net hepatic glycogen synthetic rates were increased twofold in drug-treated rats compared with saline-treated controls. The percentage of liver glycogen synthesized by the direct pathway was calculated by comparing the13C isotopic enrichment in the C1 and C6 positions of hepatic glycogen and plasma glucose using13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy techniques and was found to be 59±5% and 39±2% (P<0.05) in the saline treated and Proglycosyn-treated groups, respectively. Net flux rates for the direct and indirect pathways were calculated to be 0.24±0.04 and 0.17±0.03 μmol/g liver per min, respectively, in the saline-treated group and 0.30±0.04 (P=NS) and 0.46±0.06 (P<0.05) μmol/g liver per min, respectively, in the Proglycosyn-treated group. Thus, Proglycosyn increases net hepatic glycogen synthesis in vivo exclusively through augmentation of the indirect pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris RA, Yamanouchi K, Roach PH, Yen TT, Dominianni SJ, Stephens TW. Stabilization of glycogen stores and stimulation of glycogen synthesis in hepatocytes by phenacyl imidazolium compounds. J Biol Chem 264: 14674–14680, 1989
Yamanouchi K, Stephens TW, Chikada K, Depaoli-Roach A, Harris RA, Metabolic effects of Proglycosyn (abstract). Diabetes 40 [Suppl 1]: 102, 1991
Newgard CB, Hirsch LJ, Foster DW, McGarry JD, Studies on the mechanism by which exogenous glucose is converted into liver glycogen in the rat: a direct or an indirect pathway? J Biol Chem 258:8046–8052, 1983
Newgard CB, Moore SV, Foster DW, McGarry JD, Efficient hepatic glycogen synthesis in refeeding rats requires continued carbon flow through the gluconeogenic pathway. J Biol Chem 259:6958–6963, 1984
Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Smith D, Johnson CM, Blair JB, Shulman RG, DeFronzo RA, Mechanism of liver glycogen repletion in vivo by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Clin Invest 76: 1229–1236, 1985
Shulman GI, Rossetti L, Rothman DL, Blair JB, Smith D, Quantitative analysis of glycogen repletion by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the conscious rat. J Clin Invest 80:387–393, 1987
Cline GW, Shulman GI, Quantitative analysis of the pathways of glycogen repletion in periportal and perivenous hepatocytes in vivo. J Biol Chem 226:4094–4098, 1991
Shulman GI, Rossetti L, Influence of the route of glucose administration on hepatic glycogen repletion. Am J Physiol 257:E681-E685, 1989
Shulman GI, DeFronzo RA, Rossetti L, Differential effect of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia on pathways of hepatic glycogen repletion. Am J Physiol 260:E371-E735, 1991
Rossetti L, Giaccari A, Insulin does not affect the pathways by which hepatic glycogen is repleted (abstract). Diabetes 40 [Suppl 1]:25A, 1991
Guo Z, Wals PA, Katz J, Stimulation of glycogen synthesis by Proglycosyn (LY177507) by isolated hepatocytes of normal and streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Biol Chem 266:22323–22327, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cline, G.W., Greenawalt, K. & Shulman, G.I. Enhancement of the gluconeogenic flux of hepatic glycogen repletion by a phenacyl imidazolium compound in vivo. Acta Diabetol 30, 70–72 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00578216
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00578216