Abstract
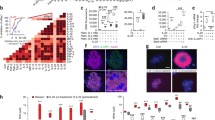
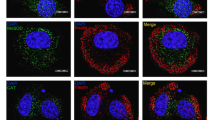
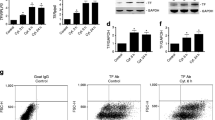
The influence of beta cell activity on cytokineinduced functional and structural impairments as well as the ability of those damaged cells to recover were investigated. Rat islets cultured for 4 days in the presence of 5, 10, and 30 mmol/l glucose were exposed to interferon-γ (IFN, 500 U/ml) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF, 250 U/ml) for the last 24 h. After cytokine removal islets were allowed to recover spontaneously in culture medium containing 10 mmol/l glucose for a further 7 days. Cytokines significantly inhibited insulin release into culture medium, insulin storage, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, protein, and DNA synthesis. In the presence of cytokines there was a six- to eightfold increase in nitrite production by the islets. The functional impairments were more pronounced in metabolically stimulated beta cells. In addition, cytokines caused membrane alterations as indicated by increased spontaneous chromium-51 release. The cytokines specifically induced the synthesis of two proteins (72 and 88 kDa, respectively). By immunoblotting, the 72-kDa protein was identified as heat shock protein. After a 1-week recovery period, insulin storage and stimulated insulin secretion of cytokine-treated islets were still significantly diminished. However, protein and DNA synthesis of cytokine-exposed islets returned to pre-exposure levels. In conclusion, high beta cell activity increases islet susceptibility to TNF+IFN. Cytokine-induced, longlasting, inhibitory effects are primarily directed to betacell-specific functions, while general vital cell functions clearly recover after cytokine removal. The induction of certain proteins and the increased protein synthesis and replication rate after cytokine removal might reflect activated repair processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nerup J, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Mølvig J, Helquist S, Wogensen L, Egeberg J, Mechanisms of pancreatic β-cell destruction in type I diabetes. Diabetes Care 11 (Suppl 1):16–23, 1988
Mandrup-Poulsen T, Helquist S, Mølvig J, Wogensen LD, Nerup J, Cytokines as effector molecules in autoimmune endocrine diseases with special reference to insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Autoimmunity 4:191–218, 1989
Mandrup-Poulsen T, Bendtzen K, Nerup J, Egeberg J, Nielsen JH, Mechanisms of pancreatic islet-cell destruction: dose-dependent cytotoxic effect of soluble blood mononuclear cell mediators on isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy 41:250–259, 1986
Sandler S, Bendtzen K, Borg LAH, Eizirik DL, Strandell E, Welsh N, Studies on the mechanisms causing inhibition in rat pancreatic islets exposed to human interleukin-1β indicate a perturbation in the mitochondrial function. Endocrinology 124:1492–1501, 1989
Delaney CA, Green MHL, Lowe JE, Green IC, Endogenous nitric oxide induced by interleukin-1β in rat islets of Langerhans and HIT-T15 cells causes significant DNA damage as measured by the ‘comet’ assay. FEBS Lett 333:291–295, 1993
Mandrup-Poulsen T, Bendtzen K, Dinarello CA, Nerup J, Human tumor necrosis factor potentiates human interleukin 1-mediated rat pancreatic beta-cell toxicity. J Immunol 139:4077–4082, 1987
Eizirik DL, Interleukin 1-induced impairment of pancreatic islet oxidative metabolism of glucose is potentiated by tumor necrosis factor. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 119:321–325, 1988
Pukel C, Baquerizo H, Rabinovitch A, Destruction of rat islet cell monolayers by cytokines. Synergistic interactions of gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor, lymphotoxin and interleukin 1. Diabetes 37:133–136, 1988
Kuttler B, Wanka H, Dunger A, Hahn HJ, Expression of MHC antigens on pancreatic islet cells. In: Flatt P R, Lenzen S (eds) Frontiers of insulin secretion and pancreatic B-cell research. Smith-Gordon, London, 1995 (in press)
Soldevila G, Buscema M, Doshi M, James RF, Bottazzo GF, Pujol-Borrel R, Cytotoxic effect of IFN-γ plus TNF-α on human islet cells. J Autoimmun 4:291–306, 1991
Sumoski W, Baquerizo H, Rabinovitch A, Oxygen free radical scavengers protect rat islet cells from damage by cytokines. Diabetologia 32:792–796, 1989
Southern C, Schulster D, Green IC, Inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α via an L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide generating mechanism. FEBS Lett 276:42–44, 1990
Welsh N, Eizirik DL, Bendtzen K, Sandler S, Interleukin-1β-induced nitric oxide production in isolated rat pancreatic islets requires gene transcription and may lead to inhibition of the Krebs cycle enzyme aconitase. Endocrinology 129:3167–3173, 1991
Corbett JA, Wang JL, Sweetland MA, Lancester JR, McDaniel ML, IL-1β induces the formation of nitric oxide by β-cells purified from rodent islets of Langerhans:evidence for the β-cell as a source and a site of action of nitric oxide. J Clin Invest 90:2384–2391, 1992
Schmidt HHHW, Warner TD, Ishii K, sheng H, Murad F, Insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells caused byL-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science 255:721–723, 1992
Corbett JA, Lancester JR, Sweetland MA, McDaniel ML, Interleukin-1β induced formation of EPR-detectable iron-nitrosyl complexes in islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem 266: 21351–21354, 1991
Malaisse WJ, Alloxan toxicity to the pancreatic B-cell. A new hypothesis. Biochem Pharmacol 31:3527–3534, 1982
Mandrup-Poulsen T, Spinas GA, Prowse SJ, Hansen BS, Jørgensen DW, Bendtzen K, Nielsen JH, Nerup J, Islet cytotoxicity of interleukin 1: influence of culture conditions and islet donor characteristics. Diabetes 36:641–647, 1987
Klöting I, Vogt L, BB/O(ttawa)K(arlsburg) rats: features of a subline of diabetes-prone BB rats. Diabetes Res 18:79–87, 1991
Hehmke B, Kohnert KD, Odselius R, The use of a new dextran gradient medium for rapid isolation of functionally intact neonatal rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes Res 3:13–16, 1986
Swanson SM, Ijaz A, Fahning ML, The use of acridine orange and ethidium bromide to determine the viability of pre-implantation mouse embryos cultured in vitro. Br Vet J 143:306–311, 1987
Green L, Wagner D, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR, Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138, 1982
Dunger A, Lucke S, Besch W, Hahn HJ, The rat pancreatic B-cell during pregnancy and after delivery. Int J Feto-Maternal Med 2:55–61, 1990
Besch W, Woltanski KP, Keilacker H, Diaz-Alonso JM, Schulz B, Amendt P, Kohnert KD, Ziegler M, Measurement of insulin in human sera using a new RIA kit. 1. Insulin determination in the absence of insulin antibodies-conventional assay and micromodification. Exp Clin Endocrinol 90:264–270, 1987
Kissane JM, Robins E, The fluorometric measurement of DNA synthesis in animal tissue with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem 233:184–188, 1958
Witt S, Dietz H, Ziegler B, Keilacker H, Ziegler M, Anwendung monoklonaler Glukagon-und insulinantikörper-Reduzierung des Pankreainsulins bei Ratten durch Behandlung mit komplettem Freundschen Adjuvans. Acta Histochem 35:217–223, 1988
Cordell UL, Falini B, Erber WN, Immunoenzymatic labelling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline-phosphatase (APAAP complex). J Histochem Cytochem 32:219–229, 1984
Esen A, A simple method for quantitative, semiquantitative, and qualitative assay of protein. Anal Biochem 89:264–273, 1978
Laemmli UK, Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685, 1970
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J, Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354, 1979
Spinas GA, Palmer JP, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Andersen H, Nielsen JH, Nerup J, The bimodal effect of interleukin 1 on rat pancreatic beta-cells-stimulation followed by inhibition-depends upon dose, duration of exposure, and ambient glucose concentration. Acta Endocrinol 119:307–311, 1988
Palmer JP, Helquist S, Spinas GA, Mølvig J, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Andersen H, Nerup J, Interaction of β-cell activity and IL-1 concentration and exposure time in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 38:1211–1216, 1989
Helquist S, Bouchelouche P, Andersen H, Nerup J, Modulation of calcium flux influences interleukin 1β effects on insulin release from isolated islets of Langerhans. Acta Endocrinol 121:447–455, 1989
Gotfredsen CF, Buschard K, Frandsen EK, Reduction of diabetes incidence of BB Wistar rats by early prophylactic insulin treatment of diabetes-prone animals. Diabetologia 28:933–935, 1985
Atkinson MA, MacLaren NK, Luchetta R, Insulitis and diabetes in NOD mice reduced by prophylactic insulin therapy. Diabetes 39:933–937, 1990
Portha B, Pican L, Insulin treatment improves the spontaneous remission of neonatal streptozotocin diabetes in the rat. Diabetes 31:165–169, 1982
Keller RJ, Jackson RA, Eisenbarth GS, Preservation of beta cell function in islet cell antibody (ICA) positive first degree relatives tested with insulin. Diabetes 41 (S1):13A, 1992
Shah SC, Malone JI, Simpson NE, A randomized trial of intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 320:550–554, 1989
Eizirik DL, Strandell E, Sandler S, Culture of mouse pancreatic islets in different glucose concentrations modified B cell sensitivity to streptozotocin. Diabetologia 31:168–174, 1988
Mehta V, Hao W, Brooks-Worrell BM, Palmer JP, The functional state of the β-cell modulates IL-1 and TNF-induced cytotoxicity. Lymphokine Cytokine Res 12:255–259, 1993
Tomita T, Lacy PE, Matschinsky FM, McDaniel ML, Effect of alloxan on insulin secretion in isolated rat islets perifused in vitro. Diabetes 23:517–524, 1974
Sandler S, Bendtzen K, Eizirik DL, Strandell E, Welsh M, Welsh N, Metabolism and β-cell function of rat pancreatic islets exposed to human interleukin-β in the presence of a high glucose concentration. Immunol Lett 26:245–252, 1990
Ignarro LJ, Signal transduction mechanisms involving nitric oxide. Biochem Pharmacol 41:485–490, 1991
Helquist S, Polla BS, Johannesen J, Nerup J, Heat shock protein induction in rat pancreatic islets by recombinant human interleukin 1β. Diabetologia 34:150–156, 1991
Welsh N, Welsh M, Lindquist S, Eizirik DL, Bendtzen K, Sandler S, Interleukin-1β increases the biosynthesis of the heat shock protein hsp 70 and selectively decreases the biosynthesis of five proteins in rat pancreatic islets. Autoimmunity 9:33–40, 1991
Eizirik DL, Cagliero E, Björklund A, Welsh N, Interleukin-1β induces the expression of an isoform of nitric oxide synthase in insulin-producing cells, which is similar to that observed in activated macrophages. FEBS Lett 308:249–252, 1992
Borg LAH, Cagliero E, Sandler S, Welsh N, Eizirik DL, Interleukin-1β increases the activity of superoxide dismutase in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 130:2851–2857, 1992
Kaufmann SHE, Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today 11:129–135, 1990
Beckmann RP, Mizzen LA, Welch WJ, Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science 248:850–854, 1990
Chiang HL, Terlecky SR, Plant CP, Dice JF, A role for a 70-kilo dalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Science 246:382–385, 1989
Margulis BA, Sandler S, Eizirik DL, Welsh N, Welsh M, Liposomal delivery of purified heat shock protein HSP 70 into rat pancreatic islets as protection against interleukin-1β-induced impaired β-cell function. Diabetes 40:1418–1422, 1991
Welsh N, Sandler S, Protective action by hemin against interleukin-1β induced inhibition of rat pancreatic islet function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 103:109–114, 1994
Pedersen CR, Josefsen K, Bock T, Hansen SV, Buschard K, Beta-cell expression of 65-kDa heat shock protein mRNA is function-and age-dependent. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand 100:765–771, 1992
Yamada K, Inada C, Otabe S, Takane N, Hayashi H, Nonaka K, Effects of free radical scavengers on cytokine actions on islet cells. Acta Endocrinol 128:379–384, 1993
Kam PCA, Govender G, Nitric oxide: basic science and clinical application. Anaesthesia 49:515–521, 1994
Bolaffi JL, Rodd GG, Wang J, Grodsky GM, Interrelationship of changes in islet nicotine adeninedinucleotide, insulin secretion, and cell viability induced by interleukin-1β. Endocrinology 134:537–542, 1994
Corbett JA, McDaniel ML, Reversibility of interleukin-1β-induced islet destruction and dysfunction by the inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. Biochem J 299:719–724, 1994
Andersen HU, Jørgensen KH, Egeberg J, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Nerup J, Nicotinamide prevents interleukin-1 effects on accumulated insulin release and nitric oxide production in rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 43:770–777, 1994
Ziegler B, Wilke B, Woltanski KP, Knospe S, Hahn HJ, Protection of insulin secretion by magnesium during islet culture: independence of cAMP or insulin accumulation. Exp Clin Endocrinol 82:199–207, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunger, A., Schröder, D., Augstein, P. et al. Impact of metabolic activity of beta cells on cytokine-induced damage and recovery of rat pancreatic islets. Acta Diabetol 32, 217–224 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00576253
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00576253