Abstract
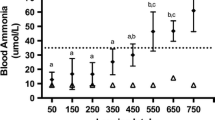
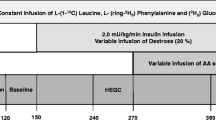
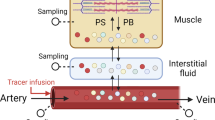
In a series of studies in normal and type 1 diabetic subjects, we analysed the relationship between isotope-calculated leucine clearance and plasma leucine concentration. All studies were performed under euglycaemic conditions. Plasma leucine concentrations were either experimentally decreased by means of insulin infusion, or increased by means of exogenous amino acid infusion in the presence of hyperinsulinaemia. Leucine clearance rates were compared in normal and diabetic subjects at similar plasma insulin levels. The effect of hyperinsulinaemia was examined by measuring clearance rates in normal subjects at comparable leucine levels but different insulin concentrations. Our data show that leucine clearance is inversely related to leucine concentration, and that it is not independently stimulated by hyperinsulinaemia. Type 1 diabetes is not associated with decreased leucine clearance. A general equation relating leucine concentration and clearance is proposed. These data support the view that peripheral leucine utilization is not decreased in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherwin RS, Amino acid and protein metabolism in normal and diabetic humans. In: Brownlee M (ed) Handbook of diabetes mellitus, vol 3. Garland STPM Press, New York/London, pp 1–47, 1981
Umpleby AM, Boroujerdi MA, Brown PM, Carson ER, Sönksen PH, The effect of metabolic control on leucine metabolism in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 29:131–161, 1986
Nair KS, Garrow JS, Ford C, Mahler RF, Halliday D, Effect of poor diabetic control and obesity on whole body protein metabolism in man. Diabetologia 25:400–403, 1983
Tessari P, Pehling G, Nissen SL, Gerich JE, Service FJ, Rizza RA, Haymond MW, Regulation of whole-body leucine metabolism with insulin during mixed-meal absorption in normal and diabetic humans. Diabetes 37:512–519, 1988
Luzi L, Castellino P, Simonson DC, Petrides AS, De Fronzo RA, Leucine metabolism in IDDM. Role of insulin and substrate availability. Diabetes 39:38–48, 1990
Tessari P, Nosadini R, Trevisan R, Vigili de Kreutzenberg S, Inchiostro S, Duner E, Biolo G, Marescotti MC, Tiengo A, Crepaldi G, Defective suppression by insulin of leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproate metabolism in insulin-dependent, type 1 diabetes. J Clin Invest 77:1797–1804, 1986
Tessari P, Inchiostro S, Biolo G, Trevisan R, Fantin G, Marescotti MC, Iori E, Tiengo A, Crepaldi G, Differential effects of hyperinsulinemia and hyperaminoacidemia on leucine-carbon metabolism in vivo. Evidence for distinct mechanisms in regulation of net amino acid deposition. J Clin Invest 79:1062–1069, 1987
Nissen SL, Van Huysen C, Haymond MW, Measurement of branched-chain amino acids and branched-chain alpha-keto-acids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 232:170–175, 1982
Inchiostro S, Biolo G, Bruttomesso D, Fongher C, Sabadin L, Carlini M, Duner E, Tiengo A, Tessari P, Effects of insulin and amino acid infusion on leucine and phenylalanine kinetics in type 1 diabetes. Am J Physiol 262:E203-E210, 1992
Schwenk WF, Beaufrere B, Haymond MW, Use of reciprocal pool specific activities to model leucine metabolism in man. Am J Physiol 249:E646, 1985
Dixon WJ, Brown MB, Engelman L, Jennrich RI (eds), BMDP statistical software manual. UCLA, Berkeley, 1990: 1:489–527
Castellino P, Luzi L, Simonson DC, Haymond MW, De Fronzo RA, Effect of insulin and plasma amino acid concentration on leucine metabolism in man. J Clin Invest 80:1784–1793, 1987
Pacy PJ, Nair KS, Ford C, Halliday D, Failure of insulin infusion to stimulate fractional muscle protein synthesis in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes 38:618–624, 1989
Flakoll PG, Kulaylat M, Frexes-Steed M, Hourani H, Brown LL, Hill JO, Abumrad NN, Amino acids augment insulin's suppression of whole-body proteolysis. Am J Physiol 258: E839, 1989
Guidotti GC, Borghetti AF, Gazzola GC, The regulation of amino acid transport in animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 515:329–366, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tessari, P., Biolo, G., Inchiostro, S. et al. Relationship between plasma leucine concentration and clearance in normal and type 1 diabetic subjects. Acta Diabetol 29, 6–10 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572821
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572821