Abstract
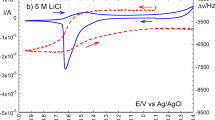
The following conclusions can be drawn: the hydration number of the lithium ion is determined by the concentration of the LiCl solution and is not a function of the temperature within the limits of 20–60°C. For a concentration of the solution above 25 wt. %, ion pairs with a common hydration shell appear; in LiCl solution with a concentration of approximately 5 M, all of the water is in the hydration shells of the lithium (h + =5.4) and chlorine (h =4.6) ions; this solution is the most structured and has an electrical conductivity maximum in measurement with a 1 kHz variable current.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. A. Rabinovich, Thermodynamic Activity of Ions in Solutions of Electrolytes [in Russian], Khimiya, Leningrad (1985).
A. V. Skolunov, Khim. Volokna, No. 6, 26 (1993).
A. V. Skolunov, Khim. Volokna, No. 2, 25 (1994).
A. V. Skolunov and A. P. Tomilov, Elektrokhimiya,28, No. 6, 887 (1992).
I. V. Kreitus, Phys. Chem.,89, No. 10, 1987 (1985).
Additional information
All-Russian Scientific-Research Institute of Polymer Fibres, Mytishchi. Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 4, pp. 16–20, July–August, 1995.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skolunov, A.V., Serkov, A.T. Study of hydration of lithium ion in lithium chloride solution in active membrane transfer. Fibre Chem 27, 234–239 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572797
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572797