Abstract
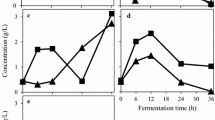
The ever increasing deficit of protein on the globe has made it necessary to search for its new sources. Due to this reason attention was focussed on the fungusB. theobromae Pat. cultivated on the carbohydrates medium. Its protein content converted into dry matter claims on the average 12.5 %, whereof the digestible protein constitutes a half of that value. The analysis of aminoacid composition has revealed that the protein is not of full value in the sense of nourishment, since it does not contain methionine. Nevertheless, it may be looked upon as a certain kind of protein supplement to the food of reared animals, because it is deprived of any dangerous aflatoxins and antibiotic substances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasoadure, S., 1970, Culture studies on Botryodiplodia theobromae Pat. Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 42: 153–160.
Chaturvedi, C., 1966, Utilization of oligosaccharides by theree imperfecti fungi. Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 29: 323–329.
Ekundayo, J.A., & R.H. Haskins. 1969a. Pycnidium production by Botryodiplodia theobromae. II. The relation of light to the induction of pycnidia. Canad. J. Botany 47: 1153–1156.
Hegsted, D.M., 1964. Proteins. In: Nutrition, G.H. Beaton & Mc Henry, eds. Acad. Press, London — New York.
Junkiewicz, T. & B. Stefaniakowa. 1969. Identyfikacja i ilościowe oznaczanie aflatoksyn w orzeszkach ziemnych, śrucie arachidowej i mieszankach paszowych. Med. Wet. XXV: 110–114.
Karkocha I. & H. Mlodecki. 1962. Badania nad wartościa. odżywczca niektórych grzybów krajowych. Roczniki PZH. XII: 473–482.
Kedzia, W., & H. Koniar. 1964. Diagnostyka Mikrobiologiczna. p. 223. PZWL, Warszawa.
Machoy, Z. & Z. Myśliwiec. 1978. Initial qualitative evaluation of lipids of Botryodiplodia theobromae. Societas Scientiarum Stetinensis. p. 55–60. PWN Warszawa — Poznań.
Moore, S. & H. Speckman, D.H. Gsackman, W.H. Stein. Chromatography of aminoacids on sulfonated polystyrene reins an amproved system. Anal. Chem. VII, 30: 1185–1190.
PN-58-A-79005. 1967. Oznaczanie bialka strawnego. In: Metody badania żywności wg norm WPLiS, Warszawa.
Put, A., Z. Machoy, J. Wójcicki & Z. Cymerski. 1978. Investigation of toxity of the fungus Botryodiplodia theobromae Pat. p. 27–31. Societas Scientiarum Stetinensis. PWN Warszawa — Poznań.
Van Etten, J. & R. Brambl. 1968. Protein synthesis during fungal spore germination. J. Bacterial 98: 1042–1048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machoy, Z., Niewiarowska-Pawlus, A., Stelmaska-Dworak, E. et al. Estimation of biological value of mycelial protein in Botryodiplodia theobromae (Pat.) and the possibility of its utilization. Mycopathologia 72, 167–169 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572659
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572659