Abstract
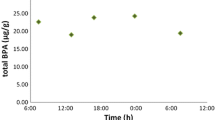
Seven workers at a work site where methylenedianiline (MDA) was used as a curing agent for an epoxy resin were studied during 4 workdays and one weekend. Internal exposure was monitored by analysis of 4,4′-MDA in hydrolysed urine and blood. After acidic hydrolysis, MDA was extracted, derivatised by use of pentafluoropropionic anhydride, and determined by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry, with negative ion chemical ionization. There was wide variation of MDA concentrations in hydrolysed blood between the workers (range 10–60 nmol/l). Also, the urinary excretion rate varied considerably both between and within the individual workers (0–90 μmol/h). The urinary excretion displayed some variation in relation to exposed periods. The urinary levels were linearly related to the concentrations in blood (r s= 0.93,P = 0.02). The present results show the value of excretion of MDA in hydrolysed urine and concentrations in blood as means for the biological monitoring of MDA exposure. In this case, the exposure was probably mainly dermal, in spite of extensive protection measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkesson B, Vinge E, Skerfving S (1989) Pharmacokinetics of triethylamine and triethylamine-N-oxide in man. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 100:529–538
Avery MJ (1989) Determination of aromatic amines in urine and serum. J Chromatogr 488:470–475
Bailey E, Brooks AG, Bird I, Farmer PB, Street B (1990) Monitoring exposure to 4,4′-methylenedianiline by gas chromatographymass spectrometry determination of adducts to hemoglobin. Anal Biochem 190:175–181
Brorson T, Skarping G, Nielsen J (1990) Biological monitoring of isocyanates and related amines. II Test chamber exposure of humans to 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI). Int Arch Occup Environ Health 63:385–389
Brunmark P, Bruze M, Skarping G (1995a) Biomonitoring of 4,4′-methylenedianiline by measurement in hydrolysed urine and plasma after epicutaneous exposure in humans.
Brunmark P, Dalene M, Skarping G (1995) Biomonitoring of occupational exposure by determination of 4,4′-methylene dianiline in hydrolysed human urine and blood plasma using gas chromatography and negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 120:41
Cocker J, Gristwood W, Wilson HK (1986) Assessment of occupational exposure to 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane (methylene dianiline) by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of urine. Br J Ind Med 43:620–625
Cocker J, Boobis AR, Davies DS (1988) Determination of theN-Acetyl metabolites of 4,4′-methylene dianiline and 4,4′-methyl-ene-bis(2-chloroaniline) in urine. Biomed Environ Mass Spectrom 17:161–167
El Hawari HM, Stoltz M, Czarnecki D, Alm P (1986) Dermal absorption of carbon-14-labeled 4,4′-methylenedianiline (4,4′-MDA) in rats, guinea pigs, and monkeys. Report no 560/5-86011, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington D.C., USA
Falke P, Tenner R, Knopp H (1986) Quantitative determination of condensation products of aniline and formaldehyde by different chromatographic methods. J Pract Chem 328:142–148
Fregert S (1981) Manual of contact dermatitis. Munkgaard, Copenhagen
IARC (1986) Monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, 39:347
Kopelman H, Robertson MH, Sanders PG, Ash I (1966) The Epping jaundice. Br Med J 1:514–516
McGill DB, Motto JD (1974) An industrial outbreak of toxic hepatitits due to methylenedianiline. N Engl J Med 291:278–282
Miller JC, Miller JN (1988) Statistics for analytical chemistry, 2nd edn. Ellis Horwood, Chichester, UK
OSHA (1992) Occupational safety and health administration. United States Federal Register, 29 CFR Parts 1910 and 1926
Selden A, Berg P, Jakobsson R, De Laval J (1992) Methylene dianiline: assessment of exposure and cancer morbibity in power generator workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 63:403–408
Skarping G, Dalene M, Brunmark P (1995) Liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry determination of aromatic amines in hydrolysed urine from workers exposed to thermal degradation products of polyurethane. Chromatogr 39. No 9/10:619–623
Tiljander A, Skarping G, Dalene M (1989) Chromatographic determinations of amines in biological fluids with special reference to the biological monitoring of isocyanates and amines. III. Determination of 4,4′-methylenedianiline in hydrolysed human urine using derivatization and capillary gas chromatography with selected ion monitoring. J Chromatogr 479:145–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalene, M., Skarping, G. & Brunmark, P. Assessment of occupational exposure to 4,4′-methylenedianiline by the analysis of urine and blood samples. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 67, 67–72 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572228
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572228