Summary
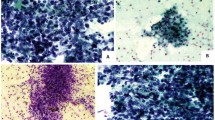
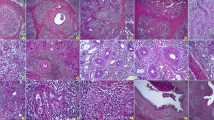
In a 41 year old woman with Sjögren's syndrome immuno-suppressive therapy was successfully administered by means of Azothioprine/Fluocortolon. Biopsies were taken before and after from the enlarged left superficial lobe of the parotid. Tissues were examined by light- and electron-microscopy. The parenchyma of the gland was found almost totally replaced by lymphoid tissue and by islands of so called myo-epithelial cells. Their architecture may be described as follows: The normal contact between the intercalated duct epithelia with their surrounding myo-epithelial cells is interrupted by infiltrating lymphoid tissue and proliferating myo-epithelial cells. Intercalated duct cells are destroyed in this process, and hyalin substances, produced by the myo-epithelial cells, are deposited in the interstitium, probably representing a form of antigen-antibody reaction. Thus, the normal intercalated duct is replaced by enlarged islands of myo-epithelial cells that are surrounded by a basal membrane.
Following immuno-suppressive therapy, the following alterations could be demonstrated: The basal membrane around the islands and the hyalin deposits have disappeared. The peripheral ring and the inner net of myo-epithelial cells have been dissolved, and extra-insular lymphoid tissue cells have invaded the remnants of the islands. The significance of myo-epithelial islands for the pathogenicity of Sjögren's syndrome and the effects of immuno-suppressive drugs are being discussed.
Zusammenffassung
Bei einer 41 jährigen Frau wurde durch Biopsie aus der linken vergrößerten Parotis ein Sjögren-Syndrom diagnostiziert. Unter immunsupressiver Therapie mit Azathioprin/Fluocortolon bildete sich die Parotisschwellung vollständig zurück. Das vor und nach der Behandlung gewonnene Parotisgewebe wurde light- und elektronenmikroskopisch untersucht. Dabei fanden sich neben der lymphocytären Infiltration des Drüsengewebes zahlreiche sog. myoepitheliale Zellinseln mit folgendem Aufbau: Die Myoepithelzellen bilden in der Inselperipherie eine Hülle mit einer äußeren Basalmembran und stehen in der Insel netzartig miteinander in Verbindung. Einzelne Myoepithelien dringen zwischen die Epithelien der Schaltstückreste, andere enthalten basalmembranartige Substanzen in ihrem Cytoplasma. Zwischen den Myoepithelzellen liegen mononucleäre Zellformen und kollagenhaltige Areale. Nach der immunsuppressiven Therapie beobachtet man eine Auflösung der inselumhüllenden Basalmembran und des peri- und intrainsulären Hyalins. Die Hülle der Myoepithelien und ihr intrainsuläres Netz werden zerstört. Es kommt zu einer verstärkten lymphocytären Invasion. Die Bedeutung der Myoepithelzellen für die Pathogenese des Sjögren-Syndroms und die Wirkung der Immunsuppressiva werden diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Asamer, H., Dittrich, P.: Die immunsuppressive Therapie der Glomerulonephritis. Med. Min.65, 1076–1081 (1970).
Bertram, U.: Xerostomia. Acta odont. stand.25, Suppl. 49, 1–126 (1967).
Boquist, L., Kumlien, A., Östberg, Y.: Ultrastructural findings in a case of benign lymphoepithelial lesion (Sjögren's syndrome) Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.)70, 216–226 (1970).
Donath, K., Seifert, G.: Ultrastructur und Pathogenese der myoepithelialen Sialadenitis. Virchows Arch., Abt. A, Path. Anat. (im Druck) (1972).
Feltkamp, T. E. W., van Rossum, A. L.: zit. bei J. Hurlimann. Current topics in Pathology, Vol. 55, pp. 69–108. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1971.
Kitamura, T., Kanda, T., Ishikawa, T., Shimizu, T.: Parotid gland of Sjögren's syndrome. Arch. Otolaryng.91, 64–70 (1970).
Rother, K.: GefäB- und Nierenläsionen durch Antigen-Antikörper-Komplexe. Med. Welt22, 988–995 (1971).
Seifert, G.: Mundhöhle, Mundspeicheldrüsen, Tonsillen und Rachen. Spezielle pathologische Anatomic, Bd. 1, S. 1–415. Hrsg. von W. Doerr u. E. Uehlinger. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1966.
—: Die Pathologie der Speicheldrüsen im Rahmen der Kollagenkrankheiten. HNO (Berl.)19, 193–200 (1971).
Wilmanns, W.: Immunbiologische Grundlagen der medikamentösen Immunsuppression. Medikamentöse Immunsuppression, S. 3–17. Hrsg. von D. Rieken u. K. Schumacher. Stuttgart: Thieme 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirsig, W., Donath, K. Zur ultrastruktur der parotis beim sjögren-syndrom vor und nach immunsuppressiver therapie. Arch. Klin. Exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- U. Kehlk. Heilk. 201, 309–323 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571668
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571668