Abstract
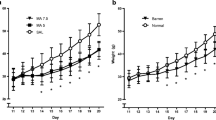
Adult behavioral and endocrine effects of neonatal administration of morphine (M) were studied in female rats injected s.c. with M on either days 3–12 (M1) or days 12–21 (M2). The dose given twice daily was increased to 8 mg/kg in group M1 and to 16 mg/kg in group M2. Compared to saline-treated controls, growth rates were temporarily suppressed (P<0.05) and body weights were reduced (P<0.05) util day 20 in M1 and until day 64 in M2 rats. The open-field test performed on days 29–31 failed to differentiate between neonatal treatment groups. On days 90–95 M1 but not M2 animals showed impaired learning of a conditioned emotional responses (CER). On day 40 all groups showed similar increased levels of plasma corticosterone 30 min following injection of naloxone (5 mg/kg). Compared to controls on day 156, both M1 and M2 rats showed diminished (P<0.05) analgesic responses (hot-plate test) to M (10 mg/kg). In response to M challenge (40 mg/kg) on day 170, all groups showed comparable acute increases in plasma corticosterone levels. These findings provide further evidence that early exposure to M results in growth retardation and protracted tolerance and that, depending on dose and time of exposure, neonatal M may result in impaired learning of CER in adulthood. These effects suggest that early morphine can produce long-lasting alterations of learned behavior without lasting impairment of pituitary-adrenal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ary, M. L., Lomax, P.: Reinstatement of precipitated narcotic withdrawal hypothetmia in the rat. Life Sci.18, 1199–1202 (1976)
Bakke, J. L., Lawrence, N., Bennett, J.: Late effects of perinatal morphine on pituitary-thyroidal and gonadal function. Biol. Neonate23, 59–77 (1973)
Bass, N. H., Lundborg, P.: Respiratory depressant effects of morphine on the central nervous system of the infant rat. Biol. Neonate23, 456–468 (1973)
Banerjee, U.: Programmed self-administration of potentially addictive drugs in young rats and its effects on learning. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.)38, 111–124 (1974)
Banerjee, U.: Conditioned learning in young rats born of drugaddicted parents and raised on addictive drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.)41, 113–116 (1975)
Berger, B. D., Stein, L.: An analysis of the learning deficits produced by scopolamine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.)14, 271–283 (1969)
Cohen, M., Keats, A. S., Krivoy, W., Ungar, G.: Effect of actinomycin D on morphine tolerance. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.119, 381–384 (1965)
Davis, W. M., Lin, C. H.: Prenatal morphine effects on survival and behavior of rat offspring. Res. Commun. Chem. Pharmacol.3, 205–214 (1972)
Denenberg, V.: The effects of early experience. In: The behavior of domestic animals (E. S. E. Hafez, ed.), pp. 94–130. London: Bailliere, Tindall and Cox 1969
Denenberg, V. H., Zarrow, M. X.: Effects of handling in infancy upon adult behavior and adrenocortical activity: suggestions for a neuroendocrine mechanism. In: Early childhood (D. N. Walcher and D. N. Peter, eds.), pp. 39–71. New York: Academic Press 1971
Eddy, N. D., Leimbach, D.: Synthetic analgesics. II. Diethienybutenyl and diethienylbutylamines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.107, 385–393 (1953)
Fishbein, J. O., Ford, D. H.: The effect of maternal morphine administration on the offspring. ISPNE Abstracts (1973)
Friedler, G.: Growth retardation in offspring of female rats treated with morphine prior to conception. Science175, 645–655 (1972)
Glick, S. D., von Redlich, D., Levine, S.: Fluorometric determination of corticosterone and cortisol in 0.02–0.05 milliliters of plasma or submilligram samples of adrenal tissue. Endocrinology74, 652–655 (1964)
Huidobro, J. P., Huidobro, F.: Acute morphine tolerance in newborn and young rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.)28, 27–34 (1973)
Johannesson, T., Steele, W. J., Becker, B. A.: Infusion of morphine in maternal rats at near-term: maternal and foetal distribution and effects on analgesia, brain DNA, RNA and protein. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.31, 353–368 (1972)
Kokka, N., George, R.: Effects of narcotic analgesics, anesthetics, and hypothalamic lesions on growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion in rats. In: Narcotics and the hypothalamus (E. Zimmermann and R. George, eds.). New York: Raven Press 1974
Kupferberg, J. H., Way, E.: Pharmacologic basis for the increased sensitivity of the newborn rat to morphine. J. Pharmacol.141, 105–112 (1963)
Levine, S., Haltmeyer, G. C., Karas, G. C., Denenberg, V. H.: Physiological and behavioral effects of infantile stimulation. Physiol. Behav.2, 55–59 (1967)
Lorenz, R. J., Branch, B. J., Taylor, A. N.: Ontogenesis of circadian pituitary-adrenal periodicity in rats affected by neonatal treatment with ACTH. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.145, 528–532 (1974)
Nicak, A., Masnyk, S.: Modification of the analgetic effect in relation to the developmental stage in rats. Med. Pharmacol. Exp.14, 273–275 (1966)
Quadagno, D. M., Shryne J., Andersen, C., Gorski, R. A.: Influence of gonadal hormones on social, sexual, emergence and openfield behavior in the rat: rattus norvegicus. Anim. Behav.20, 732–740 (1972)
Schapiro, S.: Some physiological, biochemical and behavioral consequences of neonatal hormone administration: cortisol and thyroxin. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol.10, 214–228 (1968)
Sonderegger, T., Bromley, B., Zimmermann, E.: Neonatal morphine exposure of female rats by pellet implantation. Proc. Exp. Biol. Med.20, 639–646 (1977)
Steele, W. J., Johannesson, T.: Effects of prenatally-administered morphine on brain development and resultant tolerance to the analgesic effects of morphine in offspring of morphine treated rats. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.36, 243–256 (1975)
Werboff, J., Gottlieb, J. S.: Drugs in pregnancy: behavioral teratology. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv.18, 420–423 (1963)
Zimmermann, E., Critchlow, V.: Inhibition of morphine-induced pituitary adrenal activation by dexamethasone in the female rat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.143, 1224–1226 (1973)
Zimmermann, E., Branch, B., Taylor, A. N., Young, J., Pang, C. N.: Long-lasting effects of prepuberal administration of morphine in adult rats. In: Narcotics and the hypothalamus (E. Zimmermann and R. George, eds.). New York: Raven Press 1974
Zimmermann, E., Pang, C. N., Branch, B., Taylor, A. N.: ACTH secretion in rats bearing subcutaneous morphine pellets. Fed. Proc.34, 201 (1975)
Zimmermann, E., Sonderegger, T., Bromley, B.: Development and adult pituitary-adrenal function in female rats injected with morphine during different postnatal periods. Life Sci.20, 639–646 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonderegger, T., Zimmermann, E. Adult behavior and adrenocortical function following neonatal morphine treatment in rats. Psychopharmacology 56, 103–109 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571416
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571416