Abstract
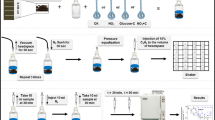
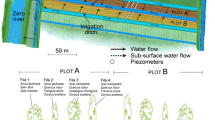
In a field experiment, the effect of animal slurry, (with and without the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide on total denitrification losses estimated by the C2H2 inhibition technique was measured over 2 years (1989–1990). During this period, four different plots (each with four replicates) were fertilized six times with 150 kg N ha-1 in the form of cattle-pig slurry or NH4NO3. Soil samples (0–20 cm) were analysed at regular intervals for NH sup+inf4 and NO sup−inf3 concentrations. The soil water content was determined gravimetrically. During the first year (1989) total denitrification losses from unfertilized, mineral-fertilized, and animal slurry-amended plots (with or without dicyandiamide) were estimated as 0.2, 3.1, 0.7, and 0.6 kg N ha-1, respectively. During the second year (1990) the denitrification losses were 0.4, 1.3, 0.7, and 0.7 kg N ha-1, respectively. There was a clear relationship between the NO sup−inf3 concentration or soil water content and the denitrification rate. The results are siteund experiment-specific and cannot be generalized so far.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Seada MNI, Ottow JCG (1985) Effect of increasing oxygen concentration on total denitrification and nitrous oxide release from soil by different bacteria. Biol Fertil Soils 1:31–38
Amberger A, Vilsmeier K, Gutser R (1982) Stickstoffreaktionen verschiedener Güllen und deren Wirkung im Pflanzenversuch. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 145:325–336
Benckiser G, Haider K, Sauerbeck D (1986) Field measurements of gaseous nitrogen losses from an Alfisol planted with sugar-beets. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 149:249–261
Benckiser G, Gaus G, Syring KM, Haider K, Sauerbeck D (1987) Denitrification losses from an Inceptisol field treated with mineral fertilizer or sewage sludge. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 150:241–248
Crawford DM, Chalk PM (1992) Mineralization and immobilization of soil and fertilizer nitrogen with nitrification inhibitors and solvents. Soil Biol Biochem 24:559–568
Groffman PM, Tiedje JM (1989) Denitrification in north temperate forest soils: Relationship between denitrification and environmental factors at the landscape scale. Soil Biol Biochem 21:621–626
Guirauld G, Marol V, Fardeau JC (1992) Balance and immobilization of (15NH4)2SO4 in a soil after the addition of DIDIN as a nitrification inhibitor. Biol Fertil Soils 14:23–29
Haider K, Heinemeyer O, Mosier AR (1990) Direct and indirect effects of plants on denitrification. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkd Ges 60:101–108
Hoffmann G, Teicher K (1961) Ein kolorimetrisches Verfahren zur Bestimmung der Ureaseaktivität in Böden. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 95:55–63
Kapp M, Schwarz J, Benckiser G, Ottow JCG, Daniel P, Opitz von Boberfeld W (1990) Der Einsatz der Acetylen-Inhibierungstechnik zur Quantifizierung von Denitrifikationsverlusten in unterschiedlich gedüngten Weidelgrasbeständen. Forum Städte-Hyg 41:168–172
Lehn-Reiser M, Munch JC, Chapot JY, Ottow JCG (1990) In-situ Messungen von Denitrifikationsverlusten einer kalkhaltigen Braunerde nach Einarbeitung verschiedener Gründüngungspflanzen (Vicia sativa, Brassica napus). Forum Städte-Hyg 41:164–167
McCarty GW, Bremner JM (1989) Inhibition of nitrification in soil by heterocyclic nitrogen compounds. Biol Fertil Soils 8:204–211
Moraghan JG, Buresh RJ (1977) Correction for dissolved nitrous oxide in nitrogen studies. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41:1201–1203
Mosier AR, Parton W (1985) Denitrification in a shortgrass prairie: A modeling approach. In: Caldwell DE, Brierly JA, Brierly CL (eds) Planetary ecology. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 441–452
Mosier AR, Guenzi WD, Schweitzer EE (1986) Field denitrification estimation by nitrogen-15 and acetylene inhibition techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:831–833
Navone R (1964) Proposed method for nitrate in potable waters. J Am Water Works Assoc 56:781–783
Ottow JCG (1992) Denitrifikation eine kalkulierbare Größe in der Stickstoffbilanz von Böden? Wasser und Boden 9:578–581
Ottow JCG, Fabig W (1985) Influence of oxygen on denitrifcation and redox level in different bacterial cultures. In: Caldwell DE, Brierly JA, Brierly CL (eds) Planetary ecology. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 427–440
Parkin TB (1990) Characterizing the variability of soil denitrification. In: Revsbech NP, Soerensen J (eds) Denitrification in soil and sediment. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 213–228
Prade K, Trolldenier G (1988) Effect of wheat roots on denitrification at varying soil air-filled porosity and organic-carbon content. Biol Fertil Soils 7:1–6
Rajbanshi SS, Benckiser G, Ottow JCG (1992a) Mineralization kinetics and utilization as an N source of dicyandiamide (DCD) in soil. Naturwissenschaften 79:26–27
Rajbanshi SS, Benckiser G, Ottow JCG (1992b) Effects of concentration, incubation temperature and repeated application on degradation kinetics of dicyandiamide (DCD) in model experiments with a silt loam soil. Biol Fertil Soils 13:61–64
von Rheinbaben W (1990) Nitrogen losses from agricultural denitrification — a critical evaluation. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 153:157–166
Ritzl I, Reiml D (1988) aufige und wichtige Folgen vermehrten Gülleanfalls. Z Wasser Abwasser Forsch 21:40–44
Ryden JC, Dawson KP (1982) Evolution of the acetylene inhibition technique for measurement of denitrification in grassland soils. J Sci Food Agric 33:1197–1206
Sahrawat KL, Keeney DR, Adams SS (1987) Ability of nitrapyrin, dicyandiamide and acetylene to retard nitrification in a mineral and an organic soil. Plant and Soil 101:179–182
Scharpf HC, Wehrman J (1976) Die Bedeutung des Mineralstickstoffvorrates des Bodens zu Vegetationsbeginn für die Bemessung der N-Düngung zu Winterweizen. Landwirtsch Forsch 32:100–114
Simarmata T, Benckiser G, Ottow JCG (1993) Effect of an increasing carbon-nitrate-N ratio on the reliability of acetylene in blocking the N2O-reductase activity of denitrifying bacteria in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 15:107–112
Thompson RB (1989) Denitrification in slurry-treated soil: Occurence at low temperatures, relationship with soil nitrate and reduction by nitrification inhibitor. Soil Biol Biochem 21:875–882
Vinther FP (1992) Measured and simulated denitrification activity in a cropped sandy and loamy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 14:43–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, L., Kapp, M., Benckiser, G. et al. Evaluation of denitrification losses by the acetylene inhibition technique in a permanent ryegrass field (Lolium perenne L.) fertilized with animal slurry or ammonium nitrate. Biol Fert Soils 18, 327–333 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00570636
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00570636